Abstract
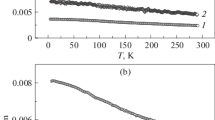
The paper presents the results of experimental research on the annihilation of positrons in hydrogen storage materials based on magnesium and single-wall carbon nanotubes during thermal annealing. It is shown that the characteristics of positron annihilation in such materials are related to their microstructural changes. In a composite based on magnesium hydride and carbon nanotubes, the rate of hydrogen release during dehydrogenation reveals three peaks due to the specific morphology of carbon nanotubes included in the magnesium matrix. During dehydrogenation, the composite undergoes irreversible changes in its electronic and/or defect structure.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Zhang, X., Liu, Y., Ren, Z., Zhang, X., Hu, J., Huang, Z., Lu, Y., Gao, M., and Pan, H., Realizing 6.7 wt % Reversible Storage of Hydrogen at Ambient Temperature with Non-Confined Ultrafine Magnesium Hydrides, Energy Environ. Sci., 2020, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 2302–2313. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EE03160G
Wen, J., de Rango, P., Allain, N., Laversenne, L., and Grosdidier, T., Improving Hydrogen Storage Performance of Mg-Based Alloy through Microstructure Optimization, J. Power Sources, 2020, vol. 480, article 228823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228823
Sun, Y., Shen, C., Lai, Q., Liu, W., Wang, D. W., and Aguey-Zinsou, K.F., Tailoring Magnesium Based Materials for Hydrogen Storage through Synthesis: Current State of the Art, Energy Storage Mater., 2018, vol. 10, pp. 168–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2017.01.010
Liu, Y., Zou, J., Zeng, X., and Ding, W., Study on Hydrogen Storage Properties of Mg–X (X = Fe, Co, V) Nano-Composites Co-Precipitated from Solution, RSC Adv., 2015, vol. 5, no. 10, pp. 7687–7696. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA12977F
Shao, H., Wang, Y., Xu, H., and Li, X., Preparation and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Nanostructured Mg2Cu Alloy, J. Solid State Chem., 2005, vol. 178, no. 7, pp. 2211–2217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2005.04.036
Hanada, N., Ichikawa, T., and Fujii, H., Catalytic Effect of Nanoparticle 3d-Transition Metals on Hydrogen Storage Properties in Magnesium Hydride MgH2 Prepared by Mechanical Milling, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, vol. 109, no. 15, pp. 7188–7194. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp044576c
Cho, E.S., Ruminski, A.M., Liu, Y.S., Shea, P.T., Kang, S., Zaia, E.W., Park, J.Y., Chuang, Y.D., Yuk, J.M., Zhou, X., Heo, T.W., Guo, J., Wood, B.C., and Urban, J.J., Hierarchically Controlled Inside-Out Doping of Mg Nanocomposites for Moderate Temperature Hydrogen Storage, Adv. Function. Mater., 2017, vol. 27, no. 47, article 1704316. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201704316
Shao, H., Asano, K., Enoki, H., and Akiba, E., Preparation and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Nanostructured Mg–Ni BCC Alloys, J. Alloy. Compd, 2009, vol. 477, no. 1–2, pp. 301–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.11.004
Wang, Y., Lan, Z., Huang, X., Liu, H., and Guo, J., Study on Catalytic Effect and Mechanism of MOF (MOF = ZIF-8, ZIF-67, MOF-74) on Hydrogen Storage Properties of Magnesium, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2019, vol. 44, no. 54, pp. 28863–28873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.09.110
Kadri, A. and Yao, X., Enhanced Sorption Performance of MgH2 Doped with Reduced Metal-Organic Framework of Ni-Co-MOF-74, Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng., 2019, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 3149–3155.
Lototskyy, M., Sibanyoni, J.M., Denys, R.V., Williams, M., Pollet, B.G., and Yartys, V.A., Magnesium–Carbon Hydrogen Storage Hybrid Materials Produced by Reactive Ball Milling in Hydrogen, Carbon, 2013, vol. 57, pp. 146–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.01.058
Wu, C.Z., Wang, P., Yao, X., Liu, C., Chen, D.M., Lu, G.Q., and Cheng, H.M., Effect of Carbon/Noncarbon Addition on Hydrogen Storage Behaviors of Magnesium Hydride, J. Alloy. Compd, 2006, vol. 414, no. 1–2, pp. 259–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2005.07.021
Chen, D., Chen, L., Liu, S., Ma, C.X., Chen, D.M., and Wang, L.B., Microstructure and Hydrogen Storage Property of Mg/MWNTs Composites, J. Alloy. Compd, 2004, vol. 372, no. 1–2, pp. 231–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2003.08.104
Huang, Z.G., Guo, Z.P., Calka, A., Wexler, D., and Liu, H.K., Effects of Carbon Black, Graphite and Carbon Nanotube Additives on Hydrogen Storage Properties of Magnesium, J. Alloy. Compd, 2007, vol. 427, no. 1–2, pp. 94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.03.069
Lueking, A.D., Burgess Clifford, C.E., and Narayanan, D.L., Induced Defects in Carbonaceous Materials for Hydrogen Storage, ACS Div. Fuel Chem. Preprints, 2004, vol. 49, article 843.
Peles, A. and Van de Walle, C.G., Role of Charged Defects and Impurities in Kinetics of Hydrogen Storage Materials: A First-Principles Study, Phys. Rev. B, 2007, vol. 76, no. 21, article 214101. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.76.214101
Sarahan, M.C., Ramasse, Q.M., Morgan, D.G., and Browning, N.D., Statistical Analysis of Point Defects in Hydrogen Storage Materials, Micros. Microanal., 2009, vol. 15, no. S2, pp. 462–463. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1431927609095890
Wert, C.A., Trapping of Hydrogen in Metals, in Hydrogen in Metals II, Berlin: Springer, 1978, pp. 305–330.
Geld, P.V., Ryabov, R.A., and Kodes, E.S., Hydrogen and Imperfections of Metal Structure, Moscow: Metallurgy, 1979.
Čížek, J., Procházka, I., Bečvář, F., Kužel, R., Cieslar, M., Brauer, G., Anwand, W., Kirchleim, R., and Pundt, A., Hydrogen-Induced Defects in Bulk Niobium, Phys. Rev. B, 2004, vol. 69, no. 22, article 224106. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.69.224106
Sakaki, K., Yamada, T., Mizuno, M., Araki, H., and Shirai, Y., Hydrogen-Induced Vacancy Generation Phenomenon in Pure Pd, Mater. Trans., 2002, vol. 43, no. 11, pp. 2652–2655. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.43.2652
Laptev, R.S., Kudiiarov, V.N., Bordulev, Y.S., Mikhaylov, A.A., and Lider, A.M., Gas-Phase Hydrogenation Influence on Defect Behavior in Titanium-Based Hydrogen-Storage Material, Progr. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int., 2017, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 105–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2017.01.001
Kudiyarov, V.N., Elman, R.R., and Kurdyumov, N., The Effect of High-Energy Ball Milling Conditions on Microstructure and Hydrogen Desorption Properties of Magnesium Hydride and Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with Iron Nanoparticles, Metals, 2021, vol. 11, no. 9, article 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11091409
Wu, C. and Cheng, H.M., Effects of Carbon on Hydrogen Storage Performances of Hydrides, J. Mater. Chem., 2010, vol. 20, no. 26, pp. 5390–5400. https://doi.org/10.1039/B926880D
Yao, X., Wu, C., Du, A., Lu, G.Q., Cheng, H., Smith, S.C., Zou, J., and He, Y., Mg-Based Nanocomposites with High Capacity and Fast Kinetics for Hydrogen Storage, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, vol. 110, no. 24, pp. 11697–11703. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp057526w
Shim, J.H., Park, M., Lee, Y.H., Kim, S., Im, Y.H., Suh, J.Y., and Cho, Y.W., Effective Thermal Conductivity of MgH2 Compacts Containing Expanded Natural Graphite under a Hydrogen Atmosphere, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2014, vol. 39, no. 1, pp. 349–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.09.092
Amirkhiz, B.S., Danaie, M., and Mitlin, D., The Influence of SWCNT–Metallic Nanoparticle Mixtures on the Desorption Properties of Milled MgH2 Powders, Nanotechnology, 2009, vol. 20, no. 20, article 204016. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/20/20/204016
Wu, C., Wang, P., Yao, X., Liu, C., Chen, D., Lu, G.Q., and Cheng, H., Effects of SWNT and Metallic Catalyst on Hydrogen Absorption/Desorption Performance of MgH2, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, vol. 109, no. 47, pp. 22217–22221. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0545041
Pandey, S.K., Singh, R.K., and Srivastava, O.N., Investigations on Hydrogenation Behaviour of CNT Admixed Mg2Ni, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2009, vol. 34, no. 23, pp. 9379–9384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.09.077
Du, A.J., Smith, S.C., Yao, X.D., He, Y., and Lu, G.Q., Atomic Hydrogen Diffusion in Novel Magnesium Nanostructures: The Impact of Incorporated Subsurface Carbon Atoms, J. Phys. Conf. Ser. IOP Publ., 2006, vol. 29, no. 1, article 032. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/29/1/032
Ullah Rather, S. and Hwang, S.W., Comparative Hydrogen Uptake Study on Ttanium–MWCNTs Composite Prepared by Two Different Methods, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2016, vol. 41, no. 40, pp. 18114–18120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.07.194
Wu, C.Z., Wang, P., Yao, X., Liu, C., Chen, D.M., Lu, G.Q., and Cheng, H.M., Hydrogen Storage Properties of MgH2/SWNT Composite Prepared by Ball Milling, J. Alloy. Compd, 2006, vol. 420, no. 1–2, pp. 278–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2005.10.028
Campos, R.B.V., Camargo, S.A.D.S., Brum, M.C., and Santos, D.S.D., Hydrogen Uptake Enhancement by the Use of a Magnesium Hydride and Carbon Nanotubes Mixture, Mater. Res., 2017, vol. 20, pp. 85–88. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2017-0445
Shen, C. and Aguey-Zinsou, K.F., Nanosized Magnesium Electrochemically Deposited on a Carbon Nanotubes Suspension: Synthesis and Hydrogen Storage, Frontiers Energy Res., 2017, vol. 5, article 27. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2017.00027
Bordulev, I., Laptev, R., Kabanov, D., Ushakov, I., Kudiiarov, V., and Lider, A., Source for In Situ Positron Annihilation Spectroscopy of Thermal and Hydrogen-Induced Defects Based on the Cu-64 Isotope, Materials, 2021, vol. 14, no. 21, article 6693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216693
Anastasopol, A., Eijt, S.W.H., Schut, H., Mulder, F.M., Plazaola, F., and Dam, B., Thermal Stability of MgyTi1–y Thin Films Investigated by Positron Annihilation Spectroscopy, Phys. Proc., 2012, vol. 35, pp. 16–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2012.06.004
Lillo-Ródenas, M.A., Guo, Z.X., Aguey-Zinsou, K.F., Cazorla-Amorós, D., and Linares-Solano, A., Effects of Different Carbon Materials on MgH2 Decomposition, Carbon, 2008, vol. 46, no. 1, pp. 126–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2007.10.033
Rahmaninasab, M.A., Raygan, S., Abdizadeh, H., Pourabdoli, M., and Mirghaderi, S.H., Properties of Activated MgH2 + Mischmetal Nanostructured Composite Produced by Ball-Milling, Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy, 2018, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40243-018-0122-z
Xiao, X., Liu, Z., Saremi-Yarahmadi, S., and Gregory, D.H., Facile Preparation of β-/γ-MgH2 Nanocomposites under Mild Conditions and Pathways to Rapid Dehydrogenation, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, vol. 18, no. 15, pp. 10492–10498. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP07762A
Liu, Y, Wang, S., Li, Z., Gao, M., Liu, Y., Sun, W., and Pan, H., Enhanced Hydrogen Storage Performance of MgH2 by the Catalysis of a Novel Intersected Y2O3/NiO Hybrid, Processes, 2021, vol. 9, no. 5, article 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050892
Nachev, S., de Rango, P., Skryabina, N., Skachkov, A., Aptukov, V., Fruchart, D., and Marty, P., Mechanical Behavior of Highly Reactive Nanostructured MgH2, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2015, vol. 40, no. 47, pp. 17065–17074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.05.022
Nachev, S., de Rango, P., Fruchart, D., Skryabina, N., and Marty, P., Correlation between Microstructural and Mechanical Behavior of Nanostructured MgH2 upon Hydrogen Cycling, J. Alloy. Compd, 2015, vol. 645, pp. S434–S437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.12.088
Lu, X., Zhang, L., Yu, H., Lu, Z., He, J., Zheng, J., Wu, F., and Chen, L., Achieving Superior Hydrogen Storage Properties of MgH2 by the Effect of TiFe and Carbon Nanotubes, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, vol. 422, article 130101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130101
Ismail, M., Juahir, N., and Mustafa, N.S., Improved Hydrogen Storage Properties of MgH2 Co-Doped with FeCl3 and Carbon Nanotubes, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, vol. 118, no. 33, pp. 18878–18883. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp5046436
Kajiwara, K., Sugime, H., Noda, S., and Hanada, N., Fast and Stable Hydrogen Storage in the Porous Composite of MgH2 with Nb2O5 Catalyst and Carbon Nanotube, J. Alloy. Compd, 2022, vol. 893, article 162206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162206
Funding
The work was performed under the Development Program of TPU and supported by the State Assignment “Nauka” (project No. FSWW-2020-0017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Fizicheskaya Mezomekhanika, 2022, Vol. 25, No. 3, pp. 75–83.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kudiyarov, V.N., Laptev, R.S., Bordulev, Y.S. et al. Positron Annihilation in a Composite Based on Magnesium Hydride and Carbon Nanotubes during Dehydrogenation. Phys Mesomech 25, 445–452 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1029959922050071
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1029959922050071