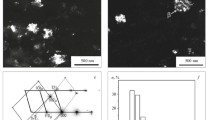
Abstract
The formation of ultrafine-grained structures is a well-known method of decreasing the temperature and/or increasing the strain rate to provide superplasticity in titanium alloys. Under certain conditions, dissolved hydrogen can produce a plasticizing effect on titanium alloys, showing up as a decrease in their stress and/or an increase in their ultimate strain. Here we study the effect of 0.3 wt % of dissolved hydrogen on the structure, phase state, and superplastic properties of an ultrafine-grained (α + β) Ti-Al-V-Mo system (VT16 alloy) at a temperature of 823–923 K. The ultrafine-grained structure of Ti-Al-V-Mo (VT16 alloy) and Ti-Al-V-Mo-0.3 wt % H (VT16-H alloy) results from severe plastic deformation via uniaxial compression with a change in the strain axis and in the temperature from 1023 to 823 K. In the temperature range used, the presence of hydrogen in the solid solution of VT16 alloy decreases its superplastic properties. During deformation, hydrogen is redistributed in the bulk of the material by elastic stress fields and is accumulated in the most stressed regions, leading to plastic strain localization and to a decrease in the strain to fracture. The release of hydrogen from VT16-H alloy during deformation activates its β → α transformation and associated diffusion redistribution of its alloying elements, contributing to the accommodation of grain boundary sliding and to the increase in the strain to fracture.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ashida, M., Chen, P., Doi, H., Tsutsumi, Y., Hanawa, T., and Horita, Z., Superplasticity in the Ti-6Al-Nb Alloy Processed by High-Pressure Torsion, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, vol. 640, pp. 449–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.06.020
Zherebtsov, S.V., Kudryavtsev, E.A., Salishchev, G.A., Straumal, B.B., and Semiatin, S.L., Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Behavior of Ultrafine Ti-6Al-4V during Low Temperature Superplastic Deformation, Acta Mater., 2016, vol. 121, pp. 152–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.09.003
Grabovetskaya, G.P., Mishin, I.P., Stepanova, E.N., Zabudchenko, O.V., and Ratochka, I.V., Effect of the Structural and Phase State on the Deformation Behavior and Mechanical Properties of the Ultrafine-Grained Titanium Alloy (Ti–Al–V–Мо) at Temperatures in the Range of 293–973 K, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, vol. 800, p. 140334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.140334
Matsumoto, H., Yoshida, K., Lee, S.-H., Ono, Y., and Chiba, A., Ti–6Al–4V Alloy with an Ultrafine-Grained Microstructure Exhibiting Low-Temperature–High-Strain-Rate Superplasticity, Mater. Lett., 2013, vol. 98, pp. 209–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2013.02.033
Kolachev, B.А. and Nosov, V.K., Hydrogen Plasticizing and Superplasticity of Titanium Alloys, Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 1984, vol. 57, no. 2, pp. 288–297.
Nosov, V.K., Ovchinnikov, A.V., and Shchugorev, Yu.Yu., Applications of Hydrogen Plasticizing of Titanium Alloys, Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 2008, vol. 50, pp. 378–382.
Niu, Y. and Li, M., Effect of 0.16 wt % Hydrogen Addition on High Temperature Deformation Behavior of the Ti600 Titanium Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol. 513–514, pp. 228–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2009.01.064
Zhao, J., Ding, H., Zhao, W., and Jiang, Z., Effects of Hydrogen on the Hot Deformation Behaviour of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy: Experimental and Constitutive Model Studies, J. Alloy. Compd, 2013, vol. 574, pp. 407–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.05.159
Li, X.F., Jiang, J., Wang, S., Chen, J., and Wang, Y.Q., Effect of Hydrogen on the Microstructure and Superplasticity of Ti-55 Alloy, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2017, vol. 42, pp. 6338–6349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.01.018
Zhang, X., Zhao, Y., and Zeng, W., Effect of Hydrogen on the Superplasticity of Ti600 Alloy, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2010, vol. 35, pp. 4354–4360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.01.110
Il’in A.A., Mechanisms and Kinetics of Phase and Structural Transformations in Titanium Alloys, Moscow: Nauka, 1994.
Dutta, A. and Birla, N.C., Stress Induced Hydrogen Diffusion in α + β Titanium Alloy during Superplastic Deformation, Scripta Mater., 1987, vol. 21, pp. 1051–1054. https://doi.org/10.1016/0036-9748(87)90248-1
Teter, D.F., Robertson, I.M., and Birnbaum, H.K., The Effects of Hydrogen on the Deformation and Fracture of β-Titanium, Acta Mater., 2001, vol. 49, pp. 4313–4323. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(01)00301-9
Bokshtein, S.Z., Ginzburg, S.S., Nazarova, E.N., and Nefudov, V.G., Study of Hydrogen Distribution in Metal Materials by Autoradiographic Methods, Zh. Fiz. Khim., 1981, no. 5, pp. 1269–1273.
Oriani, R.A. and Josephic, P.H., Equilibrium Aspects of Hydrogen-Induced Cracking of Steels, Acta Metall., 1974, vol. 22, pp. 1065–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(74)90061-3
Imai, H., Yamane, G., Matsumoto, H., Vidal, V., and Velay, V., Superplasticity of Metastable Ultrafine-Grained Ti 6242S Alloy: Mechanical Flow Behavior and Microstructural Evolution, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019, vol. 754, pp. 569–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.03.085
Murzinova, М.А., Salishchev, G.A., and Afonichev, D.D., Superplasticity of Hydrogen-Containing VT6 Titanium Alloy with a Submicrocrystalline Structure, Phys. Met., Metallogr., 2007, vol. 104, no. 2, pp. 195–202.
Portnoy, V.K., Novikov, I.I., Il’in, A.A., Fedotov, I.L., Sirina, Yu.V., and Mamonov, A.M., Effect of Hydrogen on the Superplasticity of VT6 Alloy Sheets, Metally, 1995, no. 6, pp. 89–94.
Yoshimura, H., Kimura, K., Hayashi, M., Ishii, M., Hanamura, T., and Takamura, J., Ultra-Fine Equiaxed Grain Refinement and Improvement of Mechanical Properties of α + β Type Titanium Alloys by Hydrogenation, Hot Working, Heat Treatment and Dehydrogenation, Mater. Trans. JIM, 1994, vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 266–272. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans1989.35.266
Grabovetskaya, G.P., Zabudchenko, O.V., Mishin, I.P., Stepanova, E.N., Ratochka, I.V., and Lykova, O.N., Evolution of the Structural-Phase State of a Titanium Alloy of the System Ti–Al–V–Mo during Formation of an Ultrafine-Grained Structure Using Reversible Hydrogenatetion, Russ. Phys. J., 2019, vol. 62, no. 8, pp. 1330–1337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-019-01851-4
Vinokurov, V.A., Ratochka, I.V., Naidenkin, E.V., Mishin, I.P., and Rozhentseva, N.V., Method of Severe Plastic Deformation for Forming a Submicrocrystalline Structure in Titanium Alloys, RF Patent no. 2388566, Bull. no. 13, 2010.
Malykhin, D.G. and Korneyeva, V.V., Determination of Dislocation Density by X-Ray Analysis of Microdistortions in Polycrystalline Materials, Kharkov Univ. Herald, Ser. Phys.: Nucl. Part. Fields, 2010, vol. 887, no. 1, pp. 115–117.
Naydenkin, E.V., Soldatenkov, A.P., Mishin, I.P., Oborin, V.A., and Shanyavskiy, A.A., Very High Cycle Fatigue Failure of Near Titanium Alloy, Phys. Mesomech., 2021, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 326–334. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1029959921030115
Maltsev, M.V. and Kashnikov, N.I., Martensite Decomposition in Continuously Heated VT16 Titanium Alloy, Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 1978, vol. 45, no. 2, pp. 426–428.
Novikov, I.I. and Portnoy, V.K., Superplasticity of Ultrafine-Grained Alloys, Moscow: Metallurgia, 1981.
Semiatin, S.L., Corbett, M.W., Fagin, P.N., Salishchev, G.A., and Lee, C.S., Dynamic-Coarsening Behavior of an α/β Titanium Alloy, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37, pp. 1125–1136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-006-1091-x
Frost, H.J. and Eshby, M.F., Deformation Mechanism Maps, Chelyabinsk: Metallurgia, 1989.
Koppers, M., Herzig, C.H.R., Friesel, M., and Mishin, Y., Intrinsic Self-Diffusion and Substitutional Al Diffusion in α-Ti, Acta Mater., 1997, vol. 45, pp. 4181–4191. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(97)00078-5
Larikov L.N. and Isaichev, V.I., Diffusion in Metals and Alloys, Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 1986.
Popov, A.A., Illarionov, A.G., Stepanov, S.I., Elkina, O.A., and Ivasishin, O.M., Effect of Quenching Temperature on Structure and Properties of Titanium Alloy: Structure and Phase Composition, Phys. Met. Metallogr., 2014, vol. 115. no. 5, pp. 507–516. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X14050068
Mikhaylovskaya, A.V., Mosleh, A.O., Mestre-Rinn, P., Kotov, A.D., Sitkina, M.N., Bazlov, A.I., and Louzguine-Luzgin, D.V., High-Strength Titanium-Based Alloy for Low-Temperature Superplastic Forming, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2021, vol. 52(1), pp. 293–302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-020-06058-8
Motyk, M., Sieniawski, J., and Ziaja, W., Microstructural Aspects of Superplasticity in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, vol. 599, pp. 57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.01.067
Meier, M.L., Lesuer, D.R., and Mukherjee, A.K., Grain Size and β Volume Fraction Aspects of the Superplasticity of Ti-6Al-4V, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1991, vol. 136, pp. 71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(91)90442-P
Kim, J.S., Kim, J.H., Lee, Y.T., Park, C.G., and Lee, C.S., Microstructural Analysis on Boundary Sliding and Its Accommodation Mode during Superplastic Deformation of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1999, vol. 263, pp. 272–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(98)01157-5
Kaibyshev, O.A., Superplasticity of Commercial Alloys, Moscow: Metallurgia, 1984.
Birnbaum, H.K. and Sofronis, P., Hydrogen-Enhanced Localized Plasticity—A Mechanism for Hydrogen-Related Fracture, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1994, vol. 176, pp. 191–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(94)90975-X
Astafurova, E.G., Melnikov, E.V., Astafurov, S.V., Ratochka, I.V., Mishin, I.P., Maier, G.G., Moskvina, V.A., Zakharov, G.N., Smirnov, A.I., and Bataev, V.A., Hydrogen Embrittlement Effects on Austenitic Stainless Steels with Ultrafine-Grained Structure of Different Morphology, Phys. Mesomech., 2019, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 313–326. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1029959919040076
Beachem, C.D., A New Model for Hydrogen Assisted Cracking (Hydrogen “Embrittlement”), Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1972, vol. 3, pp. 437–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02642048
Zhilyaev, A.P. and Pshenichnyuk, A.I., Superplasticity and Grain Boundaries in Ultrafine-Grained Materials, Moscow: Fizmatlit, 2008.
Funding
The work was performed under the government statement of work for ISPMS SB RAS, research line FWRW-2021-0004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Fizicheskaya Mezomekhanika, 2022, Vol. 25, No. 3, pp. 38–50.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grabovetskaya, G.P., Mishin, I.P., Stepanova, E.N. et al. Hydrogen Effect on the Evolution of the Structural-Phase State and Superplastic Properties of Ultrafine-Grained Ti-Al-V-Mo Alloy. Phys Mesomech 25, 413–423 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1029959922050046
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1029959922050046