Abstract
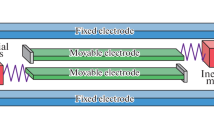
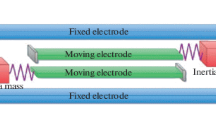
In this work, a model of a microelectromechanical accelerometer with two movable beam elements located between two stationary electrodes is proposed. The action of inertia forces in the longitudinal direction leads to a change in the spectral properties of the system, which can be used as an output signal of the sensor. The dynamics of the system in the presence of weak electrostatic coupling between the sensitive elements is characterized by the phenomenon of modal localization, which is a significant change in the amplitude relationships for the forms of in-phase and antiphase oscillations with small changes in the measured component of the object’s acceleration vector. It has been shown that the sensitivity of the proposed sensor based on modal localization can be orders of magnitude higher than the sensitivity of systems based on measuring the shift of natural frequencies.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
V. Ya. Raspopov, Micromechanical Devices (Mashinostroenie, Moscow, 2007) [in Russian].
Y. Hasani, Microsyst. Technol. 25, 1369 (2019).
F. Chen, Y. Zhao, J. Wang, H. Zou, M. Kraft, and X. Li, IEEE Sens. J. 18 (5), 1859 (2018).
Ya.V. Belyaev, A. A. Belogurov, A. N. Bocharov, D. V. Kostygov, I. V. Lemko, A. A. Mikhteeva, A. V. Yakimova, N. N. Nevirkovets, and N. M. Chernetskaya, in Proc. 25th St. Petersburg Int. Conf. on Integrated Navigation Systems (ICINS), St. Petersburg, May 28–30,2018 (St. Petersburg, 2018), pp. 1–7.
S. A. Zotov, B. R. Simon, A. A. Trusov, and A. M. Shkel, IEEE Sens. J. 15 (9), 5045 (2015).
Sh. Wang, X. Wei, Yu. Zhao, Zh. Jiang, and Ya. Shen, Sens. Actuators, A 283, 151 (2018).
F.-T. Shi, S.-C. Fan, C. Li, and X.-B. Peng, Sensors 18, 2266 (2018).
C. Pierre and E. H. Dowell, J. Sound Vib. 144 (3), 549 (1987).
Ch. Zhao, M. H. Montaseri, G. S. Wood, S. H. Pu, A. A. Seshia, and M. Kraft, Sens. Actuators, A 249, 93 (2016).
S. Ilyas and M. I. Younis, Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 125, 103516 (2020).
L. I. Mandel’shtam, Lectures on Optics, Relativity Theory and Quantum Mechanics, Ed. by S. M. Rytov (Nauka, Moscow, 1972) [in Russian].
L. Ya. Banakh, Decomposition Methods in the Study of Vibrations of Mechanical Systems (R&C Dynamics, Moscow, 2016) [in Russian]
P. W. Anderson, Phys. Rev. 109, 1492 (1958).
M. Pandit, C. Zhao, G. Sobreviela, X. Zou, and A. Seshia, J. Microelectromech. Syst. 28 (5), 782 (2019).
B. Peng, K.-M. Hu, L. Shao, H. Yan. L. Li, X. Wei, W.-M. Zhang, J. Microelectromech. Syst. 29 (1), 3 (2020).
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project no. 20-01-00537.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morozov, N.F., Indeitsev, D.A., Igumnova, V.S. et al. A Novel Model of a Mode-Localized MEMS Accelerometer. Dokl. Phys. 65, 371–375 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1028335820100031
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1028335820100031