Abstract
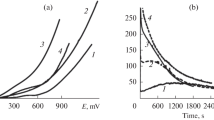
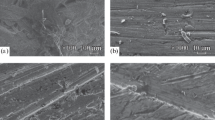
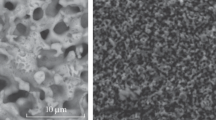
The peculiarities of electrochemical dealloying of two homogeneous Ag–Zn alloys in the (LiCl)0.57(CsCl)0.26(KCl)0.17 melt are studied. The zinc content in the alloys is 67 and 46 mol % which corresponds to the ε and β phases in the phase diagram at 300°С. Polarization curves are measured and the corrosion potential is determined to be –0.78 and –0.55 V, respectively, vs. Ag/AgCl reference electrode. The complete removal of zinc from the alloy surface is achieved by dealloying in the galvanostatic mode at the current density of about 20 mA/cm2 for the ε phase and 7 mA/cm2 for the β phase. On the surface of the Zn0.67Ag0.33 alloy, the characteristic homogeneous porous structures are formed in which the pores and the ligaments are approximately of the same size in the interval of 0.5–5 µm. For the Zn0.46Ag0.54 alloy, the dendrite structures with the silver particle size of about 0.5–4 and 5–20 µm are obtained.










Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Zhang, J. and Li, Ch.M., Nanoporous metals: fabrication strategies and advanced electrochemical applications in catalysis, sensing and energy systems, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, vol. 41, p. 7016.
Weissmüller, J. and Sieradzki, K., Dealloyed nanoporous materials with interface-controlled behavior, MRS Bull., 2018, vol. 43, p. 14.
Delgado, J., Benkirane, A., Claver, C., Curulla-Ferre, D., and Godard, C., Advances in the preparation of highly selective nanocatalysts for the semi-hydrogenation of alkynes using colloidal approaches, Dalton Trans., 2017, vol. 46, p. 12381.
Yang, W., Ma, W., Zhang, Zh., and Zhao, Ch., Ligaments size-dependent electrocatalytic activity of nanoporous Ag network for CO2 reduction, Faraday Discuss., 2018, vol. 210, p. 289.
Li, Zh., Lu, X., Li, B., Lu B., and Wang, Q., Research on electrochemical oxidation of formaldehyde on the nanoporous silver electrode in alkaline solution, ECS Electrochem. Lett., 2015, vol. 4, p. H24.
Barsuk, D., Zadick, A., Chatenet, M., Georgarakis, K., Panagiotopoulos, N., Champion, Y., and Alberto Moreira, J., Nanoporous silver for electrocatalysis application in alkaline fuel cells, Mater. Des., 2016, vol. 111, p. 528.
Zhang, Y., Luc, W., Hutchings, G.S., and Jiao, F., Photoelectrochemical carbon dioxide reduction using a nanoporous Ag cathode, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, vol. 8, p. 24652.
Su, L. and Gan, Y.X., Nanoporous Ag–Sn anodes for energy conversion in photochemical fuel cells, Mater. Des., 2016, vol. 111, p. 528.
Ma, Ch., Trujillo, M.J., and Camden, J.P., Nanoporous silver film fabricated by oxygen plasma: A facile approach for SERS substrates, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, vol. 8, p. 23978.
Detsi, E., Sànchez Sellès, M., Onck Jeff, Th, p., and Hosson, M.De., Nanoporous silver as electrochemical actuator, Scr. Mater., 2013, vol. 69, p. 195.
Lizhi, Y., Luhua, J., Tianran, Zh., Guoxiong, W., Suli, W., Xinhe, B., and Gongquan, S., Electrochemically synthesized freestanding 3D nanoporous silver electrode with high electrocatalytic activity, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2016, vol. 6, p. 7163.
Marshakov, I.K., Vvedenskii, A.V., Kondrashin, V.Yu., and Bokov, G.A. Anodnoe rastvorenie i selektivnaya korroziya splavov (Anodic Dissolution and Selective Corrosion of Alloys), Voronezh: Voronezh. Univ., 1988.
Pertsov, N.V., Zozulya, V.V., and Prokopenko, V.A., Formation of a porous material upon electrochemical leaching of a homogeneous gold-containing alloy, Colloid J., 2000, vol. 62, no. 1, p. 119.
Li, Zh., Wang, D., Li, B., and Lua, The dealloying kinetics of Ag25Zn75 in 0.1 M H2SO4, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2010, vol. 157, p. K223.
Li, Z.Q., Li, B.Q., Qin, Z. X., and Lu, X., Fabrication of porous Ag by dealloying of Ag–Zn alloys in H2SO4 solution, J. Mater. Sci., 2010, vol. 45, p. 6494.
Li, Zh., Lu, X., and Qin, Z., Formation of nanoporous silver by dealloying Ag22Zn78 alloy at low temperature in H2SO4, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2013, vol. 8, p. 3564.
Li, Zh., Bai, L., and Lu, X., Inhomogeneity of bulk nanoporous silver fabricated via dealloying Ag–Zn alloy in sulphuric acid, Micro Nano Lett., 2013, vol. 8, p. 805.
Zhang, Ch., Sun, J., Xu, J., Wang, X., Ji, H., Zhao, Ch., and Zhang, Zh., Formation and microstructure of nanoporous silver by dealloying rapidly solidified Zn–Ag alloys, Electrochim. Acta, 2012, vol. 63, p. 302.
Li, Zh., Wang X., and Lu X., Refinement of nanoporous silver by adding surfactant to the electrolyte, ECS Electrochem. Lett., 2014, vol. 3, p. C13.
Zhao, X., Wang, F., Li, R.W., Zhang, J.C., and Huang, M.Wu., Effect of Ag content on phase evolution during the de-alloying of Ag–Al alloy: Combining the electrochemical noise with the wavelet and analysis, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2017, vol. 12, p. 11150.
Song, T., Gao Y., Zhang, Zh., and Zhai, Q., Dealloying behavior of rapidly solidified Al–Ag alloys to prepare nanoporous Ag in inorganic and organic acidic media, Cryst. Eng. Comm., 2011, vol. 13, p. 7058.
Li, G., Song, X., Lu, F., and Sun, Zh., Formation and control of nanoporous Ag through electrochemical dealloying of the melt-spun Cu–Ag–Ce alloys, J. Mater. Res., 2012, vol. 27, p. 1612.
Xu, H. and Zhang, T., Formation of ultrafine spongy nanoporous metals (Ni, Cu, Pd, Ag and Au) by dealloying metallic glasses in acids with capping effect, Corr. Sci., 2019, vol. 153, p. 1.
Yeh, F.-H., Tai, Ch.-Ch., Huang, J.-F., and Sun, I.-W., Formation of porous silver by electrochemical alloying/dealloying in a water-insensitive zinc chloride-1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium chloride ionic liquid, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, vol. 110, p. 5215.
Sitnikov, L.V., Kulik, N.P., Tkachev, N.K., Pankratov, A.A., Malkov, V.B., Ivenko, V.M., Molchanova, N.G., Moskalenko, N.I., and Antonov, B. D., Selective anodic dissolution of gold alloys in a molten eutectic mixture of cesium, potassium, sodium chlorides, Rasplavy, 2018, no. 4, p. 463.
Nikitina, E.V., Kazakovtseva, N.A., Tkachev, N.K., Karfidov, E.A., Maikov, M.A., and Malkov, V.B., Selective dissolution of brass in molten eutectic mixture of carbonates of lithium, sodium, potassium, Rasplavy, 2017, no. 6, p. 565.
HSC 6.12. Outotec Reseach Oy, 1974-2007.
Lyakishev, N.P., Diagrammy sostoyaniya dvoinykh metallicheskikh sistem (Phase Diagrams of Binary Metal Systems), Moscow: Mashinostroenie, 1996, vol. 1, p. 109.
Xu, J., Wang, Y., and Zhang, Zh., Potential and concentration dependent electrochemical dealloying of Al2Au in sodium chloride solutions, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, vol. 116, p. 5689.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The study was carried out with the use of equipment of the Center of Collective Use “Substance Composition” at the Institute of High Temperature Electrochemistry, Ural Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences. We are grateful to A.A. Pankratova, V.B. Malkova, B.D. Antonova, and N.I. Moskalenko for carrying out the analyses.
Funding
The study was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 20-03-00267a).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Translated by T. Safonova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulik, N.P., Shurov, N.I. & Tkachev, N.K. Selective Anodic Dissolution of Ag–Zn Alloys in the Eutectic Melt of Alkali Metal Chlorides at 300°С. Russ J Electrochem 57, 598–606 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193521050086
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193521050086