Abstract
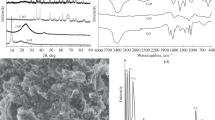
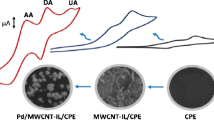
In this research work, a straightforward strategy for the development of carbon-based electrodes is presented using nanoclay as a modifier, and a room temperature ionic liquid was employed as a binder for the simultaneous determination of dopamine (DP) and uric acid (UA) in the presence of ascorbic acid (AA) in real samples in the form of serum and urine. The synergistic effect between nanoclay and the ionic liquid results in an increase in the activity of the prepared carbon ionic liquid/nanoclay (NC-CILE) nanocomposites, promoting the electron transfer and electrocatalytic activity. Considerable stability, electrocatalytic properties, and large surface area make it possible to exploit low detection limit sensors for long term applications in real samples and wide linear dynamic ranges. The electrochemical behavior of the prepared NC‑CILE electrode was diagnostically studied by cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry analyses. The response currents were linear in the DP and UA concentration ranges of 1.0–100.0 and 0.1–10.0 μM, respectively. In addition, at 50.0 µM of AA, the detection limits for DP and UA were estimated to be around 0.45 and 0.025 μM (S/N = 3), respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Wightman, R.M., Amatorh, C., Engstrom, R.C., Hale, P.D., Kristensen, E.W., Kuhr, W.G., and May, L.J., Real-time characterization of dopamine overflow and uptake in the rat striatum, Neuroscience, 1988, vol. 25, no. 2, p. 513.
Balamurugan, A. and Chen, S.M., Poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene-co-(5-amino-2-naphthalenesulfonic acid)) (PEDOT–PANS) film modified glassy carbon electrode for selective detection of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid and uric acid, Anal. Chim Acta, 2007, vol. 596, no. 1, p. 92.
Huang, Q., Zhang, H., Hu, S., Li, F., Weng, W., Chen, J., Wang, Q., He, Y., Zhang, W., and Bao, X., A sensitive and reliable dopamine biosensor was developed based on the Au@carbon dots–chitosan composite film, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2014, vol. 52, p. 277.
Lakshmi, D., Whitcombe, M.J., Davis, F., Sharma, P.S., and Prasad, B.B., Electrochemical detection of uric acid in mixed and clinical samples: a review, Electroanalysis, 2011, vol. 23, no. 2, p. 305.
Farzin, L., Shamsipur, M., Samandari, L., and Sheibani, S., Advances in the design of nanomaterial-based electrochemical affinity and enzymatic biosensors for metabolic biomarkers: a review, Microchim. Acta, 2018, vol. 185, no. 5, p. 276.
Mazloum-Ardakani, M., Beitollahi, H., Ganjipour, B., Naeimi, H., and Nejati, M., Electrochemical and catalytic investigations of dopamine and uric acid by modified carbon nanotube paste electrode, Bioelectrochemistry, 2009, vol. 75, no. 1, p. 1.
Han, D., Han, T., Shan, C., Ivaska, A., and Niu, L., Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid with chitosan-graphene modified electrode, Electroanalysis, 2010, vol. 22, no. 17, p. 2001.
Huang, Q., Hu, S., Zhang, H., Chen, J., He, Y., Li, F., Weng, W., Ni, J., Bao, X., and Lin, Y., Carbon dots and chitosan composite film based biosensor for the sensitive and selective determination of dopamine, Analyst, 2013, vol. 138, no. 18, p. 5417.
Zhang, H., Huang, Q., Huang, Y., Li, F., Zhang, W., Wei, C., Chen, J., Dai, P., Huang, L., Huang, Z., and Kang, L., Graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets doped graphene oxide for electrochemical simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid, Electrochim. Acta, 2014, vol. 142, p. 125.
Habibi, B. and Pournaghi-Azar, M.H., Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid by use of a MWCNT modified carbon-ceramic electrode and differential pulse voltammetry, Electrochim. Acta, 2010, vol. 55, no. 19, p. 5492.
Zhang, Y., Pan, Y., Su, S., Zhang, L., Li, S., and Shao, M., A novel functionalized single-wall carbon nanotube modified electrode and its application in determination of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of high concentrations of ascorbic acid, Electroanalysis, 2007, vol. 19, no. 16, p. 1695.
Zhao, Y., Gao, Y., Zhan, D., Liu, H., Zhao, Q., Kou, Y., Shao, Y., Li, M., Zhuang, Q., and Zhu, Z., Selective detection of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid and uric acid by a carbon nanotubes-ionic liquid gel modified electrode, Talanta, 2005, vol. 66, no. 1, p. 51.
Yan, Q., Zhao, F., Li, G., and Zeng, B., Voltammetric determination of uric acid with a glassy carbon electrode coated by paste of multiwalled carbon nanotubes and ionic liquid, Electroanalysis, 2006, vo1. 8, no. 11, p. 1075.
Rafati, A.A., Afraz, A., Hajian, A., and Assari, P., Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid using a carbon paste electrode modified with multiwalled carbon nanotubes, ionic liquid, and palladium nanoparticles, Microchim. Acta, 2014, vol. 181, nos. 15–16, p. 1999.
Safavi, A., Maleki, N., Moradlou, O., and Tajabadi, F., Simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid, and uric acid using carbon ionic liquid electrode, Anal. Biochem., 2006, vol. 359, no. 2, p. 224.
Opallo, M. and Lesniewski, A., A review on electrodes modified with ionic liquids, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2011, vol. 656, nos. 1–2, p. 2.
Chernyshov, D.V., Shvedene, N.V., Antipova, E.R., and Pletnev, I.V., Ionic liquid-based miniature electrochemical sensors for the voltammetric determination of catecholamines, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2008, vol. 621, no. 2, p. 178.
Kim, N.H., Malhotra, S.V., and Xanthos, M., Modification of cationic nanoclays with ionic liquids, Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2006, vol. 96, nos. 1–3, p. 29.
Eslami, E., Farjami, F., Aberoomand Azar, P., and Saber Tehrani, M., Adsorptive stripping voltammetric determination of imipramine and amitriptiline at a nanoclay composite carbonionic liquid electrode, Electroanalysis, 2014, vol. 26, no. 2, p. 424.
Zare, M.A., Saber Tehrani, M., Waqif Husain, S., and Aberoomand Azar, P., Multiwall carbon nanotube-ionic liquid modified paste electrode as an efficient sensor for the determination of diazepam and oxazepam in real samples, Electroanalysis, 2014, vol. 26, no. 12, p. 2599.
Farias, J.S., Zanin, H., Caldas, A.S., Dos Santos, C.C., Damos, F.S., and Luz, R.D.C.S., Functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotube electrochemical sensor for determination of anticancer drug flutamide, J. Electron. Mater., 2017, vol. 46, no. 10, p. 5619.
Maleki, N., Safavi, A., and Tajabadi, F., High-performance carbon composite electrode based on an ionic liquid as a binder, Anal. Chem., 2006, vol. 78, no. 11, p. 3820.
Marcin, O. and Lesniewski, A., A review on electrodes modified with ionic liquids, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2011, vol. 656, nos. 1–2, p. 2.
Chernyshov, D.V., Shvedene, N.V., Antipova, E.R., and Pletnev, I.V., Ionic liquid-based miniature electrochemical sensors for the voltammetric determination of catecholamines, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2008, vol. 621, no. 2, p. 178.
Bard, A.J. and Faulkner, L.R., Fundamentals and applications, Electrochem. Methods, 2001, vol. 2, p. 482.
Xu, T.Q., Zhang, Q.L., Zheng, J.N., Lv, Z.Y., Wei, J., Wang, A.J., and Feng, J.J., Simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid using Pt nanoparticles supported on reduced graphene oxide, Electrochim. Acta, 2014, vol. 115, p. 109.
Lin, K.C., Tsai, T.H., and Chen, S.M., Performing enzyme-free H2O2 biosensor and simultaneous determination for AA, DA, and UA by MWCNT–PEDOT film, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2010, vol. 26, no. 2, p. 608.
Rafati, A.A., Afraz, A., Hajian, A., and Assari, P., Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid using a carbon paste electrode modified with multiwalled carbon nanotubes, ionic liquid, and palladium nanoparticles, Microchim. Acta, 2014, vol. 181, nos. 15–16, p. 1999.
Xu, T.Q., Zhang, Q.L., Zheng, J.N., Lv, Z.Y., Wei, J., Wang, A.J., and Feng, J.J., Simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid using Pt nanoparticles supported on reduced graphene oxide, Electrochim. Acta, 2014, vol. 115, p. 109.
Huang, J., Liu, Y., Hou, H., and You, T., Simultaneous electrochemical determination of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid using palladium nanoparticle-loaded carbon nanofibers modified electrode, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2008, vol. 24, no. 4, p. 632.
Pourghobadi, Z. and Pourghobadi, R., Electrocatalytic alfuzosin oxidation on electrochemically oxidized glassy carbon modified with multiwalled carbon nanotubes and nickel oxide nanoparticles, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2019, vol. 166, no. 2, p. B76.
Madrakian, T., Afkhami, A., Rahimi, M., Ahmadi, M., and Soleimani, M., Preconcentration and spectrophotometric determination of oxymetholone in the presence of its main metabolite (mestanolone) using modified maghemite nanoparticles in urine sample, Talanta, 2013, vol. 115, p. 468.
Rahimi Fard, M. and Pourghobadi, Z., The spectrophotometric determination of nystatin in real samples using solid phase extraction based on sodium dodecyl sulphate-coated magnetite nanoparticles, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. Res., 2018, vol. 5, no. 2, p. 249.
Zapp, E., Brondani, D., Vieira, I.C., Scheeren, C.W., Dupont, J., Barbosa, A.M., and Ferreira, V.S., Biomonitoring of methomyl pesticide by laccase inhibition on sensor containing platinum nanoparticles in ionic liquid phase supported in montmorillonite, Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 2011, vol. 155, no. 1, p. 331.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of this work by the Khorramabad Branch, Islamic Azad University, for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eslami, E., Pourghobadi, Z. An Evaluation on Determining Dopamine and Uric Acid in the Presence Ascorbic Acid Aded Using Carbon Paste Electrodes Modified by Nanoclay-Ionic Liquids. Russ J Electrochem 57, 757–764 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S102319352012006X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S102319352012006X