Abstract
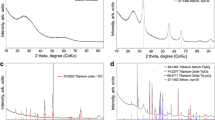
Electrochemical reduction of indium tin oxide (ITO) in SiO2 solution was investigated by analyzing the properties of ITO and the reactant diffusion in ITO films. In the electrochemical system, an ITO anode and cathode were immersed in 1 wt % SiO2 solution (pH 6.8). The electrodes were set to 15 V at room temperature under different durations of electrochemical treatment. The properties of the cathodic ITO film were analyzed after treatment. The ITO films varied from transparent to black and gray during the treatment. In2O3 underwent reduction and transformed to In, as indicated by X-ray diffractometry. The surface morphologies of the ITO samples revealed that the ITO crystals were damaged. The damage resulted in numerous aggregated particles forming on the film surface after electrochemical treatment. The major elements of the particles were confirmed to be oxygen and In. The electrical resistance of the treated ITO considerably increased because of the damage to the In2O3 crystals. The simulation of the diffusion model and experimental results indicated that the electrochemical reaction rate of ITO was controlled by the reactant diffusion in the ITO film.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Fortunato, E., Barquinha, P., and Martins, R., Oxide semiconductor thin-film transistors: a review of recent advances, Adv. Mater., 2012, vol. 22, p. 2945.
Park, J.S., Maeng, W.J., Kim, H.S., and Park, J.S., Review of recent developments in amorphous oxide semiconductor thin-film transistor devices, Thin Solid Films, 2012, vol. 520, p. 1679.
Liau, L.C.-K. and Lin, Y.-G., Fabrication of assembled ZnO/TiO2 heterojunction thin film transistorsusing solution processing technique, Solid-State Electron., 2015, vol. 103, p. 54.
Ruhle, S., Anderson, A.Y., Barad, H.-N., Kupfer, B., Bouhadana, Y., Rosh-Hodesh, E., and Zaban, A., All-oxide photovoltaics, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2012, vol. 3, p. 3755.
Wick, R. and Tilley, S.D., Photovoltaic and photoelectrochemical solar energy conversion with Cu2O, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2015, vol. 119, p. 26243.
Tetreault, N. and Gratzel, M., Novel nanostructures for next generation dye-sensitized solar cells, Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, vol. 5, p. 8506.
Ma, Z., Li, Z., Liu, K., Ye, C., and Sorger, V.J., Indium-tin-oxide for high-performance electro-optic modulation, Nanophotonics, 2015, vol. 4, p. 198.
Liau, L.C.-K. and Chen, Y.-P., Effects of voltage operating strategy on electrophoretic self-assembly deposition of spherical SiO2 particles in water, Colloids Surf. A, 2013, vol. 429, p. 121.
Aydin, E.B. and Sezginturk, M.K., Indium tin oxide (ITO): a promising material in biosensing technology, Trends Anal. Chem., 2017, vol. 97, p. 309.
van den Meerakker, J.E.A., Baarslag, M.P.C., Walrave, W., Vink, T.J., and Daams, J.L.C., On the homogeneity of sputter-deposited ITO films Part II. Etching behavior, Thin Solid Films, 1995, vol. 266, p. 152.
van den Meerakker, J.E.A.M. and ter Veen, W.R., Reductive corrosion of ITO in contact with Al, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1992, vol. 139, p. 385.
Huang, C.J., Su, Y.K., and Wu, S.L., The effect of solvent on the etching of ITO electrode, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2004, vol. 84, p. 146.
Senthilkumar, M., Mathiyarasu, J., Joseph, J., Phani, K.L.N., and Yegnaraman, V., Electrochemical instability of indium tin oxide (ITO) glass in acidic pH range during cathodic polarization, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2008, vol. 108, p. 403.
Spada, E.R., Paula, F.R. de, Plá Cid, C.C., Candiotto, G., Faria, R.M., and Sartorelli, M.L., Role of acidic and basic electrolytes on the structure and morphology of cathodically reduced indium tin oxide (ITO) substrates, Electrochim. Acta, 2013, vol. 108, p. 520.
Mammana, S.S., Greatti, A., Luiz, F.H., Costa, F.I. da, Mammana, A.P., Calligaris, G.A., Cardoso, L.P., Mammana, C.I.Z., and Engelsen, D., Study of wet etching thin films of indium tin oxide in oxalic acid by monitoring the resistance, Thin Solid Films, 2014, vol. 567, p. 20.
Liu, L., Yellinek, S., Valdinger, I., Donval, A., and Mandler, D., Important implications of the electrochemical reduction of ITO, Electrochim. Acta, 2015, vol. 176, p. 1374.
Belobaba, A.G., Zelinskiy, A.G., Gusev, A.A., and Masliy, A.I., Electrochemical stability of indium-tin oxide, Chem. Sustainable Dev., 2014, vol. 22, p. 401.
Charlot, A., Deschanels, X., and Toquer, G., Submicron coating of SiO2 nanoparticles from electrophoretic deposition, Thin Solid Films, 2014, vol. 553, p. 148.
Zill, D.G. and Wright, W.S., Advanced Engineering Mathematics, Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning, 2014, 5th ed.
Funding
This work is partially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, R.O.C. under grant MOST106-2221-E-155-047. The financial support is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leo Chau-Kuang Liau, Jhan, JL. & Kuo, PW. Evolution of the Electrochemical Reduction of Indium Tin Oxide in an Aqueous Solution of Silica Particles. Russ J Electrochem 55, 1373–1380 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193519130032
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193519130032