Abstract
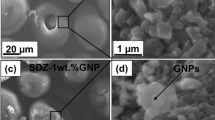
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of press pressure and sintering temperature on the microstructure and electrochemical performance of silver oxide-graphene oxide composite as a novel electrode produced by the powder metallurgy (PM) route. Scanning electron microscopy method used to investigate the microstructure of electrodes and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analysis method was used for point analysis. Potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy methods were used to research the effects of sintering temperature and press pressure on the electrochemical behaviour in the 1.4 wt % KOH solution and electrical discharge test was used for evaluate the ultimate electrical capacity of silver oxide-zinc batteries with electrolyte of the 1.4 wt % KOH solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gregory Zhang, X., Fibrous zinc anodes for high power batteries, J. Power Sources, 2006, vol. 163, pp. 591–597.
Karpinski, A.P., Makovetski, B., Russell, S.J., Serenyi, J.R., and Williams, W.C., Silver-zinc: status of technology and applications, J. Power Sources, 1999, vol. 80, pp. 53–60.
Handbook of Batteries, 2nd ed., Linden, D. and Reddy, T.B., Ed., New York, 1994.
Zinc-Silver Oxide Batteris, Fleischer, A. and Lander, J., New York: Wiley, 1971.
Senthilkumar, M., Satyavani, T., and Srinivas Kumar, A., Effect of temperature and charge stand on electrochemical performance of silver oxide–zinc cell, J. Energy Storage, 2016, vol. 6, pp. 50–58.
Venkatraman, M. and van Zee, J.W., A model for the silver–zinc battery during high rates of discharge, J. Power Sources, 2007, vol. 166, pp. 537–548.
Skelton, J. and Serenyi, R., Improved silver/zinc secondary cells for underwater applications, J. Power Sources, 1997, vol. 65, pp. 39–45.
Lewis, H.L., Danko, T., Himy, A., and Johnson, W., Alternative separation evaluations in model rechargeable silver–zinc cells, J. Power Sources, 1999, vol. 80, pp. 61–65.
Imhof, P., Silver zinc batteries for AUV applications, in Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Technology, 2002.
Xiyan, Z.H. and Yutao, Z.H., A study of the lattice constant of ZrO2 during the oxidation of nanocrystalline zircaloy-4, rare metal, J. Mater. Eng., 2008, vol. 37, pp. 1142–1152.
Gandhimathinathan, S., Optical studies of Ag2O thin film prepared by electron beam evaporation method, Open J. Met., 2013, vol. 3, pp. 57–63.
Dirkset, T.P., The silver oxide electrode, Technical reviews, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1959, vol. 106, pp. 453–457.
Silver–Zinc Battery Phenomena and Design Principles, 1st ed., Himy, A., Ed., New York: Vantage Press, 1986.
Suresh, P., Nagaraju, D.H., Shukla A.K., and Munichandraiah, N., Analysis of ac impedance of AgO–Zn cells: effects of state-of-charge, temperature and cycle-life, Electrochem. Acta, 2005, vol. 50, pp. 3262–3272.
Smith, D.F. and Brown, C., Aging in chemically prepared divalent silver oxide electrodes for silver/zinc reserve batteries, J. Power Sources, 2001, vol. 96, pp. 121–127.
Dallek, S., West, W.A., and Larrick, B.F., Decomposition kinetics of AgO cathode material by thermogravimetry, Electrochem. Soc., 1986, vol. 133, pp. 2451–2454.
Salkind, A.J., Freeman, R.W., Weckesser, J.J., West, W.A., and Dallek, S., Self-decomposition processes in silver electrodes, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1988, vol. 135, pp. 1882–1887.
Gucinski, J.A. and Slack, M., Findings of the rechargeable battery study sponsored by NATIBO (North American technology and industrial base organization), J. Power Sources, 2001, vol. 96, pp. 246–251.
Torabi, F. and Aliakbar, A., A single-domain formulation for modeling and simulation of zinc–silver oxide batteries and energy storage, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2012, vol. 159, pp. A1986–A1922.
Mclarnon, F.R. and Cairns, E.J., The secondary alkaline zinc electrode, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1991, vol. 138, pp. 645–656.
Choi, K.W., Bennion, D.N., and Newman, J., Engineering analysis of shape change in zinc secondary electrodes. I. Theoretical, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1976, vol. 123, pp. 1616–1627.
Stachurski, Z. and Dalin, G.A., Investigation and Improvements of Zinc Electrodes for Electrochemical Cells, Final Report, New York, NY: Yardney Electric Corp., 1965, pp. 150–159.
Hamby, D. and Wirkkala, J., Further experimental tests of the convective flow theory of Zn secondary electrode shape change, I, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1978, vol. 125, pp. 1020–1026.
Sunu, W.G., Transient and failure analyses of the porous zinc electrode. I. Theoretical, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1980, vol. 127, pp. 2007–2016.
Kwak, W., Jung, J., Lee, H.G., Park, S.H., Aurbach, J.B., and Suna, Y.K., Silver nanowires as catalytic cathodes for stabilizing lithium-oxygen batteries, J. Power Sources, 2016, vol. 311, pp. 49–56.
Marcano, D.C., Kosynin, D.V., and Berlin, J.M., Improved synthesis of graphene oxide, ACS Nano, 2010, vol. 4, pp. 4806–4814.
ASTM B962-14, Standard Test Methods for Density of Compacted or Sintered Powder Metallurgy (PM) Products Using Archimedes’ Principle, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, 2014.
Lopez, M., Vilche, J.R., and Arvia, A.J., Comparative voltammetric behaviour of the silver/silver oxide electrode prepared on vitreous carbon and silver substrates, J. Appl. Electrochem., 1988, vol. 18, pp. 691–698.
Pierson, J.F. and Rousselot, C., Stability of reactively sputtered silver oxide films, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2005, vol. 200, pp. 276–279.
Murray, B.J., Li, Q., and Newberg, J.T., Shape and size-selective electrochemical synthesis of dispersed silver(I) oxide colloids, Nano Lett., 2005, vol. 5, pp. 2319–2324.
Mellor, J.V., Comprehensive Treatise on Inorganic and Theoretical Chemistry, London, U.K.: Longmanas, Green and Co., vol. 3, p. 457.
Murray, B.J., Li, Q., Newberg, J.T., Menke, E.J., Hemminger, J.C., and Penner, R.M., Silver oxide microwires, Chem. Mater., 2005, vol. 17, pp. 6611–6618.
US Patent 2738375, 1956.
Breyfogle, B.E., Hung, C., Shumsky, M.G., and Switzer, J.A., Electrodeposition of silver(II) oxide films, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1996, vol. 143, pp. 2741–2746.
Riedel, A.R., Quality Control for Missile Batteries, Proc. 15th Annual Power Source Conf., 1961, pp. 86–89.
Parkhurst, W.A., Dallek, S., and Larrick, B.F., Thermogravimetry— Evolved gas analysis of silver oxide cathode material, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1984, vol. 131, pp. 1739–1742.
Sanghi, I. and Feischmann, F., Electrochemical behaviour of zinc in alkaline solutions, Proc. Math. Sci., 1959, vol. 49A, pp. 6–24.
Smith, D.F. and Gucins J.A., Synthetic silver oxide and mercury-free zinc electrodes for silver–zinc reserve batterieski, J. Power Sources, 1999, vol. 80, pp. 66–71.
Johansen, J.F and Farell, T.W., Modeling the stepped potential discharge of primary alkaline battery cathodes, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2011, vol. 158, pp. A6–A13.
Bode, H. and Oliapuram, A., Elektrochemische potentiale von zinkeinkristallen in wässrigen elektrolyten, Electrochim. Acta, 1968, vol. 13, pp. 71–80.
Zhutaeva, G.V., Merkulova, N.D., Shumilova, N.A., and Bagotskii, V.S., The kinetics of individual stages in the reduction of oxygen. II. Reduction of oxygen on silver in alkaline solutions, Soviet Electrochem., vol. 4, pp. 1136–1138.
Farr, J.P.G. and Hampson, N.A., Reactions at solid metal electrodes. Part 1: Faradaic impedance of zinc electrodes in alkaline solution, Trans. Faraday Soc., 1966, vol. 62, pp. 3493–3501.
Wales, C.P. and Burbank, J., Oxides on the silver electrode. II. X-ray diffraction studies of the working silver electrode, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1965, vol. 112, pp. 13–16.
Wilburn, N.T., Reliability program on high-rate zincsilver oxide batteries, Proc. 15th Annual Power Sources Conf., 1961.
Poa, S.P. and Lee, S.J., Experimental optimization of alkaline zinc-silver oxide primary cell with respect to the zinc electrode preparation and composition, J. Appl. Electrochem., 1979, vol. 9, pp. 307–313.
Chen, J.S. and Wang, L.F., Evaluation of calcium-containing zinc electrodes in zinc/silver oxide cells, J. Appl. Electrochem., 1996, vol. 26, pp. 227–227.
Sebborn, W.S., The nature of spongy zinc deposits, obtained by the electrolysis of aqueous solutions of zinc sulphate, Trans. Faraday Soc., 1933, vol. 29, pp. 825–829.
ACI 222R-01, Protection of Metals in Concrete against Corrosion, American Concrete Institute, Michigan, USA, 2001.
Jones, D.A., Principles and Prevention of Corrosion, Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1996.
Groysman, A., Corrosion for Everybody, Springer, 2010.
Stern, M. and Geary, A., The mechanism of passivating-type inhibitors, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1958, vol. 105, pp. 638–647.
Barsoukov, E. and Macdonald, J.R., Impedance Spectroscopy, Theory, Experiment, and Applications, 2nd ed., NY: Wiley, 2005.
Li, Y.H., Rao, G.B., Rong, L., Li, Y., and Ke, W., Effect of pores on corrosion characteristics of porous NiTi alloy in simulated body fluid, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2003, vol. 363, pp. 356–359.
Kazemi, A., Faghihi-Sani, M.A., Nayyeri, M.J., Mohammadi, M., and Hajfathalian, M., Effect of zircon content on chemical and mechanical behavior of silica-based ceramic cores, Ceram. Int., 2014, vol. 40, pp. 1093–1098.
Frank, H.A., Long, W.L., and Uchiyama, A.A., Impedance of silver oxide-zinc cells, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1971, vol. 123, pp. 1–9.
Brug, G.J., Eden, A.L.G., Rehbach, M.S., and Sluyters, J.H., The analysis of electrode impedances complicated by the presence of a constant phase element, J. Electroanal. Chem., 1984, vol. 176, pp. 275–295.
Lasia, A., Study of electrode activities towards the hydrogen evolution reaction by a.c. impedance spectroscopy, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 1993, vol. 18, pp. 557–560.
Roberge, P.A., Handbook of Corrosion Engineering, 2nd ed., 2012, pp. 751–643.
Bentiss, F., Lebrini, M., Lagrenee, M., Traisnel, M., Elfarouk, A., and Vezin, H., The influence of some new 2,5-disubstituted 1,3,4-thiadiazoles on the corrosion behaviour of mild steel in 1M HCl solution: AC impedance study and theoretical approach, J. Electrochim. Acta, 2007, vol. 52, pp. 6865–6872.
Ashassi, H., Seifzadeh, D., and Hosseini, M.G.E.N., EN, EIS and polarization studies to evaluate the inhibition effect of 3H-phenothiazin-3-one, 7-dimethylamin on mild steel corrosion in 1M HCl solution, J. Corros. Sci., 2008, vol. 50, pp. 3363–3370.
El Achouri, M., Kertit, S., Gouttaya, H.M., Nciri, B., Bensouda, Y., Perez, L., Infante, M.R., and Elkacemi, K., Corrosion inhibition of iron in 1M HCl by some gemini surfactants in the series of alkanediyl-α,ω-bis-(dimethyl tetradecyl ammonium bromide), Prog. Org. Coat., 2001, vol. 43, pp. 267–273.
Ramesh, S. and Rajeswari, S., Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in neutral aqueous solution by new triazole derivatives, J. Electrochim. Acta, 2004, vol. 49, pp. 811–820.
Tsai, S.W. and Hahn, H.T., Introduction to Composite Materials, CT, Technomic Publishing Co., 1980.
Haghi, A.K., Oluwafemi, O.S., Jose, J.P., and Maria, H.J., Composites and nanocomposites, Adv. Mater Sci., 2013, vol. 4, pp. 119–125
McBreen, J., Investigation of Zinc shape Change and Low Rate Capacity Loss in Silver Positives, Internal Report, Yardney Electric Co., 1966.
Park, S.M. and Yoo, J.S., Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for better electrochemical measurements, Anal. Chem., 2003, vol. 75, pp. 455–461.
Nagy, G.D., The anodic behavior of silver in alkaline solutions, PhD Thesis, Toronto: Univ. of Toronto, 1964.
Orgel, E. and Dunitz, J.D., Stereochemistry of cupric compounds, Nature, 1957, vol. 179, pp. 462–465.
Oxley, J.E., Improvement of Zinc Electrodes for Electrochemical Cells, Final Report, 1965.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Elektrokhimiya, 2018, Vol. 54, No. 7S, pp. S11–S24.
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pourfarzad, H., Olia, M.H., Shirojan, A. et al. Effects of Sintering Temperature and Press Pressure on the Microstructure and Electrochemical Behaviour of the Ag2O/GO Nanocomposite. Russ J Electrochem 54, 1053–1066 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193518120078
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193518120078