Abstract
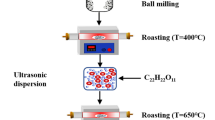
Olivine-structured LiFe0.97Ni0.03PO4/C/Ag nanomaterials of varying dispersibility are prepared by using sol–gel synthesis with subsequent milling. The materials are certified using X-ray diffraction analysis, scanning electron microscopy, low-temperature nitrogen adsorption, and electrochemical testing under the lithium-ion battery operating conditions. The LiFe0.97Ni0.03PO4/C/Ag cathode material primary particles’ size was shown to decrease, under the intensifying of ball-milling, from 42 to 31 nm, while the material’s specific surface area increased from 48 to 65 m2/g. The discharge capacity, under slow charging–discharging (C/8), approached a theoretical one for all materials under study. It was found that under fast charging–discharging (6 C and 30 C) the discharge capacity is inversely proportional to the particles’ mean size. The discharge capacity under the 6 С current came to 75, 94, 97, and 106 mA h/g for the initial material and that milled at a rotation velocity of 300, 500, and 700 rpm, respectively. An increase in the lithium diffusion coefficient upon the samples’ intense milling is noted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Padhi, A.K., Nanjundaswamy, K.S., and Goodenough, J.B., Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1997, vol. 144, p. 1188.
Yang, Zh., Dai, Y., Wang, Sh., and Yu, J., How to make lithium iron phosphate better: a review exploring classical modification approaches in-depth and proposing future optimization methods, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, vol. 4, p. 18210.
Eftekhari, A., LiFePO4/C nanocomposites for lithium-ion batteries, J. Power Sources, 2017, vol. 343, p.395.
Benoit, C. and Franger, S., Chemistry and electrochemistry of lithium iron phosphate, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2008, vol. 12, p.987.
Amin, R., Maier, J., Balaya, P., Chen, D.P., and Lin, C.T., Ionic and electronic transport in single crystalline LiFePO4 grown by optical floating zone technique, Solid State Ionics, 2008, vol. 179, p. 1683.
Safronov, D.V., Novikova, S.A., Skundin, A.M., and Yaroslavtsev, A.B., Lithium intercalation and deintercalation processes in Li4Ti5O12 and LiFePO4, Inorg. Mater., 2012, vol. 48, p.57.
Chen, Z.-Y., Zhu, H.-L., Ji, S., Fakir, R., and Linkov, V., Influence of carbon sources on electrochemical performances of LiFePO4/C composites, Solid State Ionics, 2008, vol. 179, p. 1810.
Safronov, D.V., Pinus, I.Yu., Profatilova, I.A., Tarnopol’skii, V.A., Skundin, A.M., and Yaroslavtsev, A.B., Kinetics of lithium deintercalation from LiFePO4, Inorg. Mater., 2011, vol. 47, p.303.
Li, H. and Zhou, H., Enhancing the performances of Li-ion batteries by carbon-coating:present and future, Chem. Commun., 2012, vol. 48, p. 1201.
Gryzlov, D., Novikova, S., Kulova, T., Skundin, A., and Yaroslavtsev, A., Behavior of LiFePO4/CPVDF/Agbased cathode materials obtained using polyvinylidene fluoride as the carbon source, Materials Design, 2016, vol. 104, p.95.
Tu, X., Zhou, Y., and Song, Y., Freeze-drying synthesis of three-dimensional porous LiFePO4 modified with well-dispersed nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes for high-performance lithium-ion batteries, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, vol. 400, p.329.
Ornek, A., Bulut, E., Can, M., and Ozacar, M., Characteristics of nanosized LiNixFe1 -xPO4/C (x = 0.00–0.20) composite material prepared via sol–gel-assisted carbothermal reduction method, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2013, vol. 17, p. 3101.
Novikova, S., Yaroslavtsev, S., Rusakov, V., Kulova, T., Skundin, A., and Yaroslavtsev, A., LiFe1 -xMx IIPO4/C (MII = Co, Ni, Mg) as cathode materials for lithiumion batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2014, vol. 122, p.180.
Liu, W., Huang, Q., and Hu, G., A novel preparation route for multi-doped LiFePO4/C from spent electroless nickel plating solution, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, vol. 632, p.185.
Novikova, S., Yaroslavtsev, S., Rusakov, V., Chekannikov, A., Kulova, T., Skundin, A., and Yaroslavtsev, A., Behavior of LiFe1–yMnyPO4/C cathode materials upon electrochemical lithium intercalation/deintercalation, J. Power Sources, 2015, vol. 300, p.444.
Liu, Q., Liu, W., Li, D., and Wang, Z., Synthesis and characterization of grape-like LiFe0.97M0.03PO4/C (M = Ni, CO, Mn) composites, Mater. Lett., 2016, vol. 162, p.87.
Zaghib, K., Guerfi, A., Hovington, P., Vijh, A., Trudeau, M., Mauger, A., Goodenough, J.B., and Julien, C.M., Review and analysis of nanostructured olivine-based lithium recheargeable batteries: status and trends, J. Power Sources, 2013, vol. 232, p.357.
Yaroslavtsev, A.B., Kulova, T.L., and Skundin, A.M., Electrode nanomaterials for lithium-ion batteries, Russ. Chem. Rev., 2015, vol. 84, p.826.
Wang, K.-X., Li, X.-H., and Chen, J.-Sh., Surface and interface engineering of electrode materials for lithiumion batteries, Adv. Mater., 2015, vol. 27, p.527.
Chekannikov, A., Kapaev, R., Novikova, S., Tabachkova, N., Kulova, T., Skundin, A., and Yaroslavtsev, A., Na3V2(PO4)3/C/Ag nanocomposite materials for Naion batteries obtained by the modified Pechini method, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2017, vol. 21, p. 1615.
Rise, S.A., Diffusion-limited Reactions, Elsevier, 1985, p.351.
Kapaev, R., Novikova, S., Kulova, T., Skundin, A., and Yaroslavtsev, A., Conductivity and electrochemical behavior of Li1–xFe1–2x(MIIMIII)xPO4 with olivine structure, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2015, vol. 19, p. 2793.
Christmann, K., Introduction to Surface Physical Chemistry, Darmstadt: Springer, 1991.
Andersson, A. and Thomas, J.O., The source of firstcycle capacity loss in LiFePO4, J. Power Sources, 2001, vol. 97, p.498.
Kim, D.-H. and Kim, J., Synthesis of LiFePO4 nanoparticles in polyol medium and their electrochemical properties, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett., 2006, vol. 9, p. A439.
Zhang, Y., Wu, L., Zhao, J., and Yu, W., A facile precursor-separated method to synthesize nano-crystalline LiFePO4/C cathode materials, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2014, vol. 719, p.1.
Oh, S.W., Myung, S.-T., Bang, H.J., Yoon, C.S., Amine, K., and Sun, Y.-K., Nanoporous structured LiFePO4 with spherical microscale particle having high volumetric capacity for lithium batteries, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett., 2009, vol. 12, p. A181.
Wen, L., Hu, X., Luo, H., Li, F., and Cheng, H., Openpore LiFePO4/C microspheres with high volumetric energy density for lithium ion batteries, Particuology, 2015, vol. 22, p.24.
Tabassam, L., Giuli, G., Moretti, A., Nobili, F., Marassi, R., Minicucci, M., Gunnella, R., Olivi, L., and Di Cicco, A., Structural study of LiFePO4/C–LiNiPO4 solid solutions, J. Power Sources, 2012, vol. 213, p.287.
Qing, R., Yang, M.-Ch., Meng, Y.Sh., and Sigmund, W., Synthesis of LiNixFe1 -xPO4 solid solution as cathode materials for lithium ion batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2013, vol. 108, p.827.
Wilcox, J.D., Doeff, M.M., Marcinek, M., and Kostecki, R., Factors influencing the quality of carbon coatings on LiFePO4, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2007, vol. 154, p. A389.
Vidano, R.P. and Fishbach, D.B., Observation of raman band shifting with excitation wavelength for carbons and graphites, Solid State Commun., 1981, vol. 39, p.341.
Stenina, I. A., Bukalov, S. S., Kulova, T. L., Skundin, A. M., Tabachkova, N.Yu., and Yaroslavtsev, A.B., Influence of a Carbon Coating on the Electrochemical Properties of Lithium-Titanate-Based Nanosized Materials, Nanotechnologies in Russia, 2015, vol. 10, p.865.
Smecellato, P.C., Davoglio, R.A., Biaggio, S.R., Bocchi, N., and Rocha-Filho, R.C., Alternative route for LiFePO4 synthesis: carbothermal reduction combined with microwave-assisted solid-state reaction, J. Power Sources, 2003, vol. 119–121, p.252.
Tian, X., Zhou, Y., Wu, G., and Wang, P.J., Chen controllable synthesis of porous LiFePO4 for tunable electrochemical li-insertion performance, Electrochim. Acta, 2017, vol. 229, p.316.
Boldyrev, V.V., Mechanochemistry and mechanical activation of solids, Russ. Chem. Rev., 2006, vol. 75, no. 3, p. 177–189.
Maier, J., Defect chemistry and ion transport in nanostructured materials: part II. Aspects of nanoionics, Solid State Ionics, 2003, vol. 157, p.327.
Maier, J., Nanoionics: ion transport and electrochemical storage in confined systems, Nat. Mater., 2005, vol. 4, p.805.
Novikova, S.A., Yurkov, G.Yu., and Yaroslavtsev, A.B., Synthesis and transport properties of membrane materials with incorporated metal nanoparticles, Mend. Comm., 2010, vol. 20, p.89.
Lu, C.Z., Fey, G.T.K., and Kao, H.M., Study of LiFePO4 cathode materials coated with high surface area carbon, J. Power Sources, 2009, vol. 189, p.155.
Liu, Y., Gu, J., Zhang, J., Wang, J., Nie, N., Fu, Y., Li, W., and Yu, F., Controllable synthesis of nano-sized LiFePO4/C via a high shear mixer facilitated hydrothermal method for high rate Li-ion batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2015, vol. 173, p.448.
Shen, W., Wang, Y., Yan, J., Wu, H., and Guo, Sh., Enhanced electrochemical performance of lithium iron(II) phosphate modified cooperatively via chemically reduced graphene oxide and polyaniline, Electrochim. Acta, 2015, vol. 173, p.310.
Liu, T., Xia, Q., Lu, W., Xu, J., and Wu, X., A novel method of preparing LiMPO4-C nano particles with organic P source, Electrochim. Acta, 2015, vol. 174, p.120.
Liu, Y., Zhang, M., Li, Y., Hu, Y., Zhu, M., Jin, H., and Li, W., Nano-sized LiFePO4/C composite with core–shell structure as cathode material for lithium ion battery, Electrochim. Acta, 2015, vol. 176, p.689.
He, J., Wang, J., Zhong, H., Ding, J., and Zhang, L., Cyanoethylated carboxymethyl chitosan as water soluble binder with enhanced adhesion capability and electrochemical performances for LiFePO4 cathode, Electrochim. Acta, 2015, vol. 182, p.900.
Garino, N., Bedini, A., Chiappone, A., and Gerbaldi, C., Ultrafast, low temperature microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis of nanostructured lithium iron phosphate optimized by a chemometric approach, Electrochim. Acta, 2015, vol. 184, p.381.
Bai, N., Xiang, K., Zhou, W., Lu, H., Zhao, X., and Chen, H., LiFePO4/carbon nanowires with 3D nanonetwork structure as potential high performance cathode for lithium ion batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2016, vol. 191, p.23.
Yang, X., Tu, J., Lei, M., Zuo, Z., Wu, B., and Zhou, H., Selection of carbon sources for enhancing 3D conductivity in the secondary structure of LiFePO4/C cathode, Electrochim. Acta, 2016, vol. 193, p.206.
Maier, J., Nano-ionics: trivial and non-trivial size effects on ion conduction in solids, Z. Phys. Chem., 2003, vol. 217, p.415.
Yaroslavtsev, A.B., Mirak’yan, A.L., Chuvaev, V.F., and Sokolova, L.N., Proton Mobility on the Surface of Some Acid Salt Crystal Hydrates, Russ. J. Inorg. Chem., 1997, vol. 42, p. 806.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.Yu. Gryzlov, S.A. Novikova, T.L. Kulova, A.M. Skundin, A.B. Yaroslavtsev, 2018, published in Elektrokhimiya, 2018, Vol. 54, No. 5, pp. 507–516.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gryzlov, D.Y., Novikova, S.A., Kulova, T.L. et al. The Effect of Particle Size on the Processes of Charging and Discharging of the LiFe0.97Ni0.03PO4/C/Ag Cathode Material. Russ J Electrochem 54, 442–450 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193518050038
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193518050038