Abstract
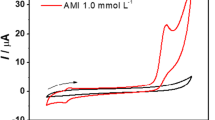
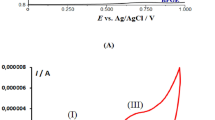
The determination of prilocain, used to manage tonic-clonic seizures, has been carried out at micro gold electrode (Au UME) using continuous fast Fourier transform square wave voltammetry. The Au UME electrode exhibited an effective response towards prilocaine adsorption. The peak current was also found to be significantly increased. The determination was carried out in phosphate containing electrolyte in the pH of 2.0 and a well-defined change on the peak current were noticed. The peak current was found to be linearly dependent on concentration of prilocain in the concentration range 5.0 × 10−7–1.0 × 10−11 M with a detection limit of 5.0 × 10−12 M. This paper describes development of a new analysis system to determine of prilocain by a novel square wave voltammetry method to perform a very sensitive method. The method used for determination of prilocain by measuring the changes in admittance voltammogram of a gold ultramicroelectrode (in 0.05 M H3PO4 solution) caused by adsorption of the prilocain on the electrode surface. Variation of admittance in the detection process is created by inhibition of oxidation reaction of the electrode surface, by adsorbed of prilocain. Furthermore, signal-to-noise ratio has significantly increased by application of discrete Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) method, background subtraction and two-dimensional integration of the electrode response over a selected potential range and time window. Also in this work some parameters such as SW frequency, eluent pH, and accumulation time were optimized. The relative standard deviation at concentration 5.0 × 10−8 M is 5.8% for 5 reported measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Catterall, W. and Mackie, K., The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, Hardman, J., Limbird, L., Molinoff, P., Ruddon, R., and Gilman, A., Eds., New York: McGraw-Hill, 1996, p. 331.
Karcioglu, O., Topacoglu, H., Ayrik, C., Ozucelikl, D.N., and Soysal, S., Croat Med. J., 2003, vol. 44, p. 716.
McQuay, H., Carroll, D., and Moore, R., Pain, 1988, vol. 33, p. 291.
Product information, EMLA, lidocaine/prilocaine, Westborough (MA): Astra Pharmaceutical Products, 1993.
Thompson, D., Computer Software, EMLA Cream-Use for Topical Anesthesia, Denver (CO): Micromedex Inc, 1995.
Moehrle, M. and Breuninger, H., Pediatr. Dermatol., 2001, vol. 18, p. 469.
Gunaydin, B. and Demiryurek, A., Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand., 2001, vol. 45, p. 741.
Janzen, P., Vipond, A., Bush, D., and Hopkins, P., Anesth. Analg., 2001, vol. 93, p. 187.
Uckan, S., Guler, N., Sumer, M., and Ungor, M., Oral Surg., Oral Medicine, Oral Pathol., Oral Radiol. Endodont., 1998, vol. 86, p. 26.
Klimundova, J., Satinsky, D., Sklenarova, H., and Solich, P., Talanta, 2006, vol. 69, p. 730.
Watanabe, T., Namera, A., Yashiki, M., Iwasaki, Y., and Kojima, T., J. Chromatogr., Ser. B, 1998, vol. 709, p. 225.
Koehler, A., Oertel, R., and Kirch, W., J. Chromatogr., Ser. A, 2005, vol. 1088, p. 126.
Taddio, A., Stevens, B., Craig, K., Rastogi, R., Ben David, S., Shennan, A., Mulligan, P., and Koren, G., New Engl. J. Med., 1997, vol. 336, p. 1197.
Kataoka, H., Curr. Pharm. Anal., 2005, vol. 1, p. 65.
Abdel-Rehim, M., J. Chromatogr., Ser. B, 2004, vol. 801, p. 317.
Yu-Chen, T., Barry, A., Coles, R., Compton, G., and Marken, F., Electroanalysis, 2001, vol. 13, p. 639.
Tan, S.H. and Kounaves, S.P., Electroanalysis, 1998, vol. 10, p. 364.
Norouzi, P., Ganjali, M.R., Shirvani-Arani, S., and Mohammadi, A., J. Pharm. Sci., 2007, vol. 95, p. 893.
Norouzi, P., Shirvani-Arani, S., Daneshgar, P., and Ganjali, M.R., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2006, vol. 22, p. 1068.
Norouzi, P., Ganjali, M.R., and Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A., J. Brazil. Chem. Soc., 2007, vol. 18, p. 231.
Norouzi, P., Ganjali, M.R., and Daneshgar, P., Anal. Lett., 2007, vol. 40, p. 547.
Norouzi, P., Ganjali, M.R., and Hajiaghababaei, L., Anal. Lett., 2006, vol. 39, p. 1941.
Norouzi, P., Ganjali, M.R., and Daneshgar, P., Sens. Actuators, Ser. B, 2007, vol. 123, p. 1125.
Norouzi, P., Ganjali, M.R., Daneshgar, P., Alizadeh, T., and Mohammadi, A., Anal. Biochem., 2007, vol. 360, p. 175.
Norouzi, P., Ganjali, M.R., and Daneshgar, P., J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods, 2007, vol. 55, p. 289.
Norouzi, P., Ganjali, M.R., Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A., and Larijani, B., Talanta, 2007, vol. 73, p. 54.
Norouzi, P., Ganjali, M.R., Zare, M., and Mohammadi, A., J. Pharm. Sci., 2007, vol. 96, p. 2009.
Norouzi, P., Ganjali, M.R., and Akbari-Adergani, B., Acta Chim. Slov., 2007, vol. 53, p. 499.
Nabi Bidhendi, G., Norouzi, P., Daneshgar, P., and Ganjali M.R., J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, vol. 143, p. 264.
Norouzi, P., Ganjali, M.R., Labbafi, S., and Mohammadi, A., Anal. Lett., 2007, vol. 40, p. 747.
Norouzi, P., Ganjali, M.R., Daneshgar, P., Dinarvand, P., Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A., and Saboury, A.A., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2007, vol. 590, p. 74.
Norouzi, P., Nabi Bidhendi, G.R., Ganjali, M.R., Sepehri, A., and Ghorbani, M., Microchim. Acta, 2005, vol. 152, p. 123.
Norouzi, P., Ganjali, M.R., Alizadeh, T., and Daneshgar, P., Electroanalysis, 2006, vol. 18, p. 947.
Ganjali, M.R., Norouzi, P., Ghorbani, M., and Sepehri, A., Talanta, 2005, vol. 66, p. 225.
Lipkowski, J. and Stolberg, L., Adsorption of Molecules at Metal Electrodes, New York: VCH, 1992.
Miller, J.C. and Miller, J.N., Statistics for Analytical Chemistry, Chichester: Ellis Horwood, 1984, vol. 22, p. 82.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Norouzi, P., Ganjali, M.R., Dinarvand, R. et al. New adsorptive square wave method for trace determination of prilocain in the flow injection system by a fast fourier analysis. Russ J Electrochem 46, 999–1006 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193510090053
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193510090053