Abstract
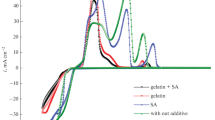
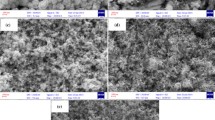
The present work details optimization of a stable acid chloride bath for electroplating of bright Zn-Co alloy on mild steel using gelatin and glycine as additives. It was found that the addition of gelatin along with glycine changed the deposition pattern markedly. A suitable bath has been formulated using conventional Hull cell experiments. The bath under plating conditions were found to exhibit anomalous codeposition with preferential deposition of less noble (zinc) over more noble (cobalt) as characterized by Zn-Fe group metal alloys. Investigation revealed that the current density (c.d.), temperature, and pH of the bath have strong effect on the composition of the deposit. Influence of bath constituents and operating parameters on appearance and composition of deposits were studied as measure of their performance against corrosion. A variety of deposits were obtained and their corrosion resistances were measured by Tafel method with/without chrome passivation. Experimental results demonstrated the fact that the corrosion resistances of Zn-Co alloys increased with percent of Co in the deposit except at very high c.d. This is due to the fact at very high c.d. the deposit becomes very porous and thick as evidenced by SEM image. The formation of Zn-Co alloy is confirmed by EDAX analysis. A stable chloride bath for Zn-Co alloy deposition has been proposed and discussed. The formation of passive film on chromatization is indicated by almost same E corr value of all Zn-Co electroplates irrespective of the current densities at which they have been deposited.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malathy, P., Bulletin Electrochem., 2000, vol. 16(12), p. 559.
Crotty, D, Metal Finish., 1996, vol. 94, p. 54.
Brenner, A., Electrodeposition of Alloys, New York: Academic, 1963, vol. 1.
Andricose, P.C. and Romankiw, L.T., Advances in Electrochemical Secience and Engineering, 1994, vol. 3, p. 226.
Zech, N., Podlaha, E.J., and Landolt, D., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1999, vol. 146, no. 8, p. 2886.
Sriveeraghavan, Krishnan R.M. and Natarajan, S.R., Bull. Electrochem., 1996, vol. 12, nos. 5–6, p. 259.
Dini, J. and Johnson, H., Metal Finish, 1979, vol. 77(17), p. 53.
Hsu, G.H., Plating Surf. Finish, 1979, vol. 71, no. 4, p. 52.
Malathy, P., Raman V., Jayakrishnan, S.T., and Shenoy, B.A., Metal Finish, 1983, vol. 81, p. 81.
Vogel, A.I., Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, London: Longmans Green and Co, 1951.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Elektrokhimiya, 2009, Vol. 45, No. 7, pp. 811–816.
The text is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chitharanjan Hegde, A., Thangaraj, V. Electrodeposition and characterization Zn-Co alloy. Russ J Electrochem 45, 756–761 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193509070076
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193509070076