Abstract
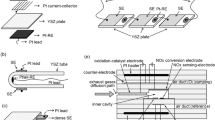
A zirconia-based (0.9ZrO2 · 0.1Y2O3) high-temperature electrochemical reactor with three-electrode connection circuit was shown promising if used as a chromatographic sensor for quantitative organic gas detection as well as an organic gas sample preparation device for carbon isotopic analysis. The optimized parameters and working mode of the herein proposed solid electrolyte reactor provided complete organic gas oxidation to stoichiometric oxides without oxygen addition to the carrier gas flow at the temperature of 900 to 950°C. The maximum hydrocarbon gas sample amount was calculated for complete oxidation in the designed reactor. Due to its simple and reliable design, the solid electrolyte reactor can be used instead of a standard oxidizing reactor in an isotopic mass spectrometer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zuev, B.K. and Olenin, A.Yu., Zhurn. Analyt. Khimii, 2005, vol. 60, no. 12, p. 1.
Sundmacher, K., Rihko-Struckmann, L.K., and Galvita, V., Catalysis Today, 2005, p. 185.
Maskell, W. S., Solid State Ionics, 2000, vol. 134, p. 43.
Schmidt-Zhang, P. and Guth, U., Sensors and Actuators, 2004, vol. B99, p. 258.
Perfil’ev, M.V., Demin, A.K., Kuzin, B.L., and Lipiluin, A.S., Vysokotemperaturnyi elektroliz gazov (High-Temperature Electrolysis of Gases), Moscow: Nauka, 1988.
Vecher, A.A. and Vecher, D.V., Tverdye elektrolity (Solid Electrolytes), Minsk: Universitetskoe, 1998.
Sevast’yanov, V.S., Galimov, E.M., Babulevich, N.E., and Arzhannikov, A.A., Elektrokhimiya, 2007, vol. 43, p. 172.
Talanchuk, P.M., Shmatko, B.A., Zaika, L.S., and Tsvetkova, O.E., Poluprovodnikovye i tverdotel’nye sensory (Semiconductor and Solid Electrolyte Sensors), Kiev: Tekhnika, 1992.
Shkerin, S.N. and Perfil’ev, M.V., Elektrokhimiya, 1990, vol. 26, p. 1461.
Somov, S.I., Reinhardt, G., Guth, U., and Gopel, W., Solid State Ionics, 2000, vols. 136–137, p. 543.
Handbook of Stable Isotope Analytical Techniques, vol. 1, Groot, P.A., Ed., Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2004.
Matthews, D.E. and Hayes, J.M., Anal. Chem., 1978, vol. 50, p. 1465.
Tokarev, M.I., Fainberg, V.S., and Khodeev, Yu.S., Mass-spektrometriya, 2004, no. 1, p. 179.
Metcalfe, I.S., Proceedings of the 26-th Ris0 International Symposium on Materials Science: Solid State Electrochemistry, Denmark, Roskild: Technical University, 2005, p. 39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.S. Sevast’yanov, E.M. Galimov, N.E. Babulevich, E.N. Tyurina, A.A. Arzhannikov, 2009, published in Elektrokhimiya, 2009, Vol. 45, No. 6, pp. 705–711.
Published by report at IX Conference “Fundamental Problems of Solid State Ionics”, Chernogolovka, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sevast’yanov, V.S., Galimov, E.M., Babulevich, N.E. et al. Optimizing zirconia-based solid electrolyte cell operated as oxidizing reactor and chromatographic sensor. Russ J Electrochem 45, 662–667 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S102319350906007X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S102319350906007X