Abstract
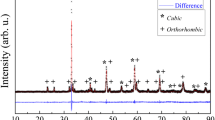
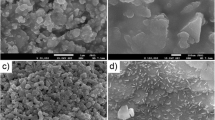
The electric and electrochemical characteristics of cathodes made of La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Co0.2O3−δ (LSFC) and intended for fuel cells with electrolytes based on ceric oxide are studied. Adding cupric oxide into the LSFC cathode is shown to exert a favorable effect of the properties of the LSFC-CuO/SDC electrode system, where SDC stands for the CeO2-Sm2O3 electrolyte. The effect produced by cupric oxide when added in the form of nanopowder is perceptibly greater than in the case of micropowdered CuO. Adding a mere 0.5 wt % of nanopowdered CuO reduces the LSFC cathode resistance nearly tenfold. The cathode’s adhesion to the electrolyte substantially improves as well, which makes it possible to lower the cathode’s firing temperature by 100°C. The maximum of electrochemical activity is intrinsic to cathodes containing 2 wt % CuO, with the caking temperature of 1000°C. According to a 2011-h life test of the LSFC-SDC composite cathodes containing nanopowdered CuO, temporal stability of their electrochemical characteristics improves with the SDC content. The time dependences of the polarization resistance of cathodes containing 40–50 wt % SDC look like decaying exponential curves. The steady-state polarization resistance, calculated on the basis of this, is equal to 0.1–0.2 ohm cm2. At an overvoltage of less than 100 mV, the cathodes may provide for a current density of 0.5–1.0 A cm−2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alder, B., Lane, J.A., and Steele, B.C.H., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1996, vol. 143, p. 3554.
Qiu, L., Ichikawa, T., Hirano, A., Imanishi, N., and Takeda, Y., Solid State Ionics, 2003, vol. 158, p. 55.
Wang, W.G. and Mogensen, M., Solid State Ionics, 2005, vol. 176, p. 457.
Hwang, H.J., Moon, J.W., Lee, S., and Lee, E.A., J. Power Sources, 2005, vol. 145, p. 243.
Zhang, J., Ji, Y., Gao, H., He, T., and Liu, J., J. Alloys Compd., 2005, vol. 395, p. 322.
Dusastre, V. and Kilner, J.A., Solid State Ionics, 1999, vol. 126, p. 163.
Bae, J.-M. and Steele, B.C.H., Solid State Ionics, 1998, vol. 106, p. 247.
Bae, J.-M. and Steele, B.C.H., Solid State Ionics, 1998, vol. 106, p. 255.
Tai, L.-W., Nasrallah, M.M., Anderson, H.U., Sparlin, D.M., and Sehlin, S.R., Solid State Ionics, 1995, vol. 76, p. 273.
Stevenson, J.W., Armstrong, T.R., Carneim, R.D., Pederson, L.R., and Weber, W.J., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1996, vol. 143, p. 2722.
Kostogloudis, G.Ch. and Ftikos, Ch., Solid State Ionics, 1999, vol. 126, p. 143.
Mineshige, A., Izutsu, J., Nakamura, M., Nigaki, K., Abe, J., Kobune, M., Fujii, S., and Yazawa, T., Solid State Ionics, 2005, vol. 176, p. 1145.
Chen, C.C., Nasrallah, M.M., and Anderson, H.U., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1995, vol. 142, p. 491.
Petric, A., Huang, P., and Tietz, F., Solid State Ionics, 2000, vol. 135, p. 719.
Mogensen, M., Lindegaard, Th., and Hansen, U.R., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1994, vol. 141, p. 2122.
Kharton, V.V., Figueiredo, F.M., Navarro, L., Naumovich, E.N., Kovalevsky, A.V., Yaremchenko, A.A., Viskup, A.P., Carneiro, A., Marques, F.M.B., and Frade, J., J. Mater. Sci., 2001, vol. 36, p. 1105.
Wang, Sh., Katsuki, M., Hashimoto, T., and Dokiya, M., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2003, vol. 150, p. A952.
Murray, E.P., Sever, M.J., and Barnett, S.A., Solid State Ionics, 2002, vol. 148, p. 27.
Neuimin, A.D., Fedin, V.V., Zhuravlev, B.V., Kozhevnikova, T.P., Bogdanovich, N.M., Maizner, E.A., and Khomyakova, N.G., RF Patent 1 825 575, 1990.
Kozhevnikova, T.R., Bogdanovich, N.M., Neuimin, A.D., and Zhuravlev, B.V., in Sb. nauch. trudov “Ionika tverdogo tela” (A Compilation of Scientific Works “Solid State Ionics”), Yekaterinburg: UI Nauka, 1993, p. 65.
Wang, Sh., Kato, T., Nagata, S., Honda, T., Kaneko, T., Iwashita, N., and Dokiya, M., Solid State Ionics, 2002, vol. 146, p. 203.
Kuzin, B.L., Demin, A.K., and Komarova, N.Yu., Abstracts of Papers, 2-i Vsesoyuz. simp. “Tverdye elektrolity i ikh analiticheskoe primenenie” (2nd All-Union Symp. “Solid Electrolytes and Their Analytical Application), Sverdlovsk: UNTs AN SSSR, 1985, p. 153.
Waller, D., Lane, J.A., Kilner, J.A., and Steele, B.C.H., Solid State Ionics, 1996, vol. 86–88, p. 767.
Liu, J., Co, A.C., Paulson, S., and Birss, V.I., Solid State Ionics, 2006, vol. 177, p. 377.
Esquirol, A., Brandon, N.P., Kilner, J.A., and Mogensen, M., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2004, vol. 151, p. A1847.
Sahibzada, M., Benson, S.J., Rudkin, R.A., and Kilner, J.A., Solid State Ionics, 1998, vol. 113–115, p. 285.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © B.L. Kuzin, N.M. Bogdanovich, D.I. Bronin, I.Yu. Yaroslavtsev, G.K. Vdovin, Yu.A. Kotov, A.V. Bagazeev, A.I. Medvedev, A.M. Murzakaev, O.P. Timoshenkova, A.K. Stol’ts, 2007, published in Elektrokhimiya, 2007, Vol. 43, No. 8, pp. 968–977.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuzin, B.L., Bogdanovich, N.M., Bronin, D.I. et al. Electrochemical properties of cathodes made of (La,Sr)(Fe,Co)O3 containing admixtures of nanoparticles of cupric oxide and intended for fuel cells with a solid electrolyte based on ceric oxide. Russ J Electrochem 43, 920–928 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193507080101
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193507080101