Abstract
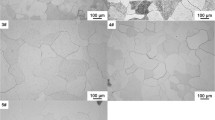
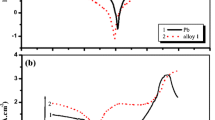
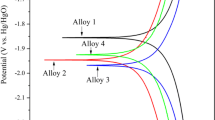
The electrochemical polarization potential of oxygen evolution at the surface of lead-antimony-tin alloy is varied in different casting temperature of electrode production, which is used in the most of battery manufacturer. Effect of the casting temperature on the polarization potential of oxygen evolution and electrochemical behavior of lead-antimony-tin alloy in low antimony grid (1.7%) of lead acid battery is studied by using cyclic voltammetry and linear sweep voltammetry in aqueous sulfuric acid solution. The grid morphology is studied by using scanning electron microscopy and optical microscopy at the different casting temperatures. Cyclic voltammograms of the Pb-Sb-Sn and lead-antimony electrodes are similar, and both alloys show the anodic excursion peak under the same experimental conditions. The oxidation of tin is done at the formation potential of PbO. The results show the polarization potential for oxygen gas evolution to vary with casting temperature for production of lead-antimony electrodes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hunsen, M. and Anderko, K., Constitution of Binary Alloys, New York: McGraw-Hill, 1958, p. 1100.
Shapiro, H. and Frey, F.W., The Organic Compounds of Lead, New York: Interscience, 1968.
Danel, V. and Plichon, V., Electrochim. Acta, 1983, vol. 28, p. 785.
Hammenoja, E., Laitinen, T., Sundholm, G., and Yli-Pentti, A., Electrochim. Acta, 1989, vol. 34, p. 233.
Laihanen, S., Laitinen, T., and Yli-Pentti, A., Electrochim. Acta, 1990, vol. 35, p. 229.
Hirasawa, T., Sasaki, K., Taguchi, M., and Kanecho, H., J. Power Sources, 2000, vol. 85, p. 44.
Manahov, B. and Pavlov, D., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1994, vol. 141, p. 2316.
Pavlov, D., J. Power Sources, 1993, vol. 46, p. 171.
Ball, R.J., Kurian, R., Evans, R., and Stevens, R., J. Power Sources, 2002, vol. 111, p. 23.
Hou Tiana, L., Jionga, Y., Hai-Hea, L., Ji-Huaaa, Z., and Wei-Fanga, Z., J. Power Sources, 2001, vol. 93, p. 230.
Peterson, I. and Ahlberg, E., J. Power Sources, 2000, vol. 91, p. 143.
Babic, R., Melikos-Hukoric, M., Lajqy, N., and Brinic, S., J. Power Sources, 1994, vol. 52, p. 17.
Omae, T., Osumi, S., Takahashi, K., and Tsubota, M., J. Power Sources, 1997, vol. 65, p. 65.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Published in Russian in Elektrokhimiya, 2006, Vol. 42, No. 4, pp. 401–405.
The text was submitted by the author in English.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezaei, B. Effects of casting temperature of Pb-Sb-Sn grid alloy on the polarization potential of oxygen evolution of lead acid batteries. Russ J Electrochem 42, 350–354 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193506040100
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193506040100