Abstract
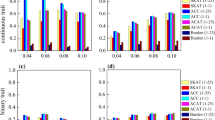
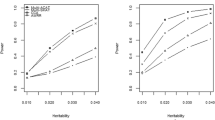
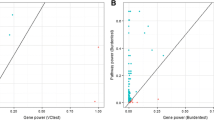
Set-based association analysis has emerged as a popular tool for testing the association of rare variants within a genomic region with complex diseases. However, when only a small proportion of variants are causal, combining the association signals of multiple markers within a genomic region may cause noise due to the inclusion of non-causal variants, which usually decreases the power of a test. Besides, the existing set-based methods are sensitive to the genetic architecture. Therefore, we extend the aggregated Cauchy association test (ACAT) and propose an adaptive Cauchy-variable combination method (AAC). The AAC method adaptively combines Cauchy-variables transformed from variant-level P-values by using the optimal number of P-values that is determined by the data; the AAC method can remove variants with larger P-values. Extensive simulation studies and Genetic Analysis Workshop 19 real data analysis show that AAC is more powerful than the other comparative methods when only a small proportion of variants are causal. And AAC is robust to the varied genetic architecture. In addition, the AAC method may use summary statistics, without requiring the original genotypic and phenotypic data.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Visscher, P.M., Brown, M.A., McCarthy, M.I., and Yang, J., Five years of GWAS discovery, Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2012, vol. 90, no. 1, pp. 7—24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.029
Welter, D., MacArthur, J., Morales, J., et al., The NHGRI GWAS catalog, a curated resource of SNP-trait associations, Nucleic Acids Res., 2018, vol. 42, no. D1, pp. D1001—D1006. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1229
Lee, J.C. and Parkes, M., Genome-wide association studies and Cohn’s disease, Briefings Funct. Genomics, 2011, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 71—76. https://doi.org/10.1093/bfgp/elr009
Willer, C.J., Speliotes, E.K., Loos, R.J.F., et al., Six new loci associated with body mass index highlight a neuronal influence on body weight regulation, Nat. Genet., 2009, vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 25—34. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.287
Maher, B., Personal genomes: the case of the missing heritability, Nature, 2008, vol. 456, no. 7218, pp. 18—21. https://doi.org/10.1038/456018a
McCarthy, M.I., Abecasis, G.R., Cardon, L.R., et al., Genome-wide association studies for complex traits: consensus, uncertainty and challenges, Nat. Rev. Genet., 2008, vol. 9, no. 5, pp. 356—369. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2344
Pritchard, J.K. and Cox, N.J., The allelic architecture of human disease genes: common disease—common variant… or not?, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2002, vol. 11, no. 20, pp. 2417—2423. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/11.20.2417
Manolio, T.A., Collins, F.S., Cox, N.J., et al., Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases, Nature, 2009, vol. 461, no. 7265, pp. 747—753. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08494
Dering, C., Hemmelmann, C., Pugh, E., and Ziegler, A., Statistical analysis of rare sequence variants: an overview of collapsing methods, Genet. Epidemiol., 2011, vol. 35, no. S1, pp. S12—S17. https://doi.org/10.1002/gepi.20643
Svishcheva, G.R., Belonogova, N.M., Zorkoltseva, I.V., et al., Gene-based association tests using GWAS summary statistics, Bioinformatics, 2019, vol. 35, no. 19, pp. 3701—3708 https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz172
Chapman, J. and Whittaker, J., Analysis of multiple SNPs in a candidate gene or region, Genet. Epidemiol., 2008, vol. 32, no. 6, pp. 560—566. https://doi.org/10.1002/gepi.20330
Fan, R., Wang, Y., Mills, J., et al., Functional linear models for association quantitative traits, Genet. Epidemiol., 2013, vol. 37, no. 7, pp. 726—742. https://doi.org/10.1002/gepi.21757
Svishcheva, G.R., Belonogova, N.M., and Axenovich, T.I., Region-based association test for familial data under functional linear models, PLoS One, 2015, vol. 10, no. 6, pp. e0128999. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128999
Chen, H., Meigs, J.B., and Dupuis, J., Sequence kernel association test for quantitative traits in family samples, Genet. Epidemiol., 2012, vol. 37, no. 2, pp. 196—204. https://doi.org/10.1002/gepi.21703
Wu, M.C., Lee, S., Cai, T., et al., Rare-variant association testing for sequencing data with the sequence kernel association test, Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2011, vol. 89, no. 1, pp. 82—93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.05.029
Lee, S., Emond, M.J., Bamshad, M.J., et al., Optimal unified approach for rare-variant association testing with application to small-sample case—control whole-exome sequencing studies, Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2012, vol. 91, no. 2, pp. 224—237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.06.007
Wu, B., Guan, W., and Pankow, J.S., On efficient and accurate calculation of significance p-values for sequence kernel association testing of variant set, Ann. Hum. Genet., 2016, vol. 80, no.2, pp. 123—135. https://doi.org/10.1111/ahg.12144
Svishcheva, G.R., A generalized model for combining dependent SNP-level summary statistics and its extensions to statistics of other levels, Sci. Rep., 2019, vol. 9, no. 5461. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-41827-5
Liu, Y., Chen, S., Li, Z., et al., ACAT: a fast and powerful p value combination method for rare-variant analysis in sequencing studies, Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2019, vol. 104, no. 3, pp. 410—421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.01.002
Lee, S., Teslovich, T.M., Boehnke, M., and Lin, X., General framework for meta-analysis of rare variants in sequencing association studies, Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2013, vol. 93, no. 1, pp. 42—53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.05.010
Sha, Q., Wang, X., Wang, X., and Zhang, S., Detecting association of rare and common variants by testing an optimally weighted combination of variant, Genet. Epidemiol., 2012, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 561—571. https://doi.org/10.1002/gepi.21649
Chen, L., Wang, Y., and Zhou, Y., Association analysis of multiple traits by an approach of combining P values, J. Genet., 2018, vol. 97, no. 1, pp. 79—85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-018-0885-0
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China (LH2019A020), and basic research expenditure of universities in Heilongjiang Province, special fund of Heilongjiang University (KJCX201803 and KJCX201804). The Genetic Analysis Workshops are supported by GAW grant R01 GM031575 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. Preparation of the Genetic Analysis Workshop 17 Simulated Exome Dataset was supported in part by NIH R01 MH059490 and used sequencing data from the 1000 Genomes Project (http://www.1000genomes.org). The GAW19 unrelated data were provided by Type 2 Diabetes Genetic Exploration by Next-generation sequencing in Ethnic Samples (T2D-GENES) Project 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Y., Zhou, Y., Chen, L. et al. A Powerful Adaptive Cauchy-Variable Combination Method for Rare-Variant Association Analysis. Russ J Genet 57, 238–245 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795421020125
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795421020125