Abstract
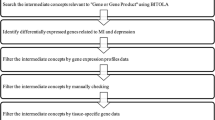
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is an important problem in psychophysical health and well-being of society in Russia and worldwide. In the present work, the role of apoptosis in the associative gene network of MDD was studied. The methods of prioritization were analyzed and candidate genes for further research were predicted. The quality of prioritization methods and their combinations was tested, and the most effective methods were selected. Prioritization was carried out for genes of the extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway considering their role in the structure of the associative genetic network of MDD, since the external pathway of apoptosis is important for drug development. The methods of the ANDSystem, a computer system for reconstruction of gene networks on the basis of automatic data retrieval from scientific publications, were considered and used for gene prioritization. As a result of prioritization, some candidate genes were suggested for the further experimental study of their role in MDD pathogenesis, including CAV1, FYN, JAK2, PTEN, RAF1, RELA and SRC.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ehret, AM., Kowalsky, J., Rief, W., et al., Reducing symptoms of major depressive disorder through a systematic training of general emotion regulation skills: protocol of a randomized controlled trial, BMC Psychiatry, 2014, vol. 14, p. 20. doi 10.1186/1471-244X-14-20
Ferrari, A.J., Charlson, F.J., Norman, R.E., et al., Burden of depressive disorders by country, sex, age, and year: findings from the global burden of disease study 2010, PLoS Med., 2013, vol. 10, no. 11, p. 1001547. doi 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001547
Cuijpers, P., Berking, M., Andersson, G., et al., A meta-analysis of cognitive-behavioural therapy for adult depression, alone and in comparison with other treatments, Canad. J. Psychiatry, 2013, vol. 58, no. 7, pp. 376-385.
Borges, S., Chen, Y.F., Laughren, T.P., et al., Review of maintenance trials for major depressive disorder: a 25-year perspective from the US Food and Drug Administration, J. Clin. Psychiatry, 2014, vol. 75, no. 3, pp. 205-214. doi 10.4088/JCP.13r08722
Kendler, K.S., The phenomenology of major depression and the representativeness and nature of DSM criteria, Am. J. Psychiatry, 2016, vol. 173, no. 8, pp. 771-780.
McKernan, D.P., Dinan, T.G., and Cryan, J.F., “Killing the Blues”: a role for cellular suicide (apoptosis) in depression and the antidepressant response?, Prog. Neurobiol., 2009, vol. 88, no. 4, pp. 246-263. doi 10.16/j.pneurobio.2009.04.006
Leonard, B. and Maes, M., Mechanistic explanations how cell-mediated immune activation, inflammation and oxidative and nitrosative stress pathways and their sequels and concomitants play a role in the pathophysiology of unipolar depression, Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 2012, vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 764-785. doi 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2011.12.005
Chen, J., Aronow, B.J., and Jegga, A.G., Disease candidate gene identification and prioritization using protein interaction networks, BMC Bioinf., 2009, vol. 10, p. 73. doi 10.1186/1471-2105-10-73
Tranchevent, L.C., Ardeshirdavani, A., ElShal, S., et al., Candidate gene prioritization with Endeavour, Nucleic Acids Res., 2016, vol. 44, no. W1, pp. W117-W121. doi 10.1093/nar/gkw365
Saik, O.V., Demenkov, P.S., Ivanisenko, T.V., et al., Novel candidate genes important for asthma and hypertension comorbidity revealed from associative gene networks, BMC Med. Genomics, 2018, vol. 11(S1), no. 15, pp. 61-76. doi 10.1186/s12920-018-0331-4
Yankina, M.A., Saik, O.V., Demenkov, P.S., et al., Analysis of the interactions of neuronal apoptosis genes in the associative gene network of Parkinson’s disease, Vavilovskii Zh. Genet. Sel., 2018, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 153-160. https://doi.org/10.18699/VJ18.343.
Yankina, M.A., Saik, O.V., Demenkov, P.S., et al., Search for candidate genes associated with anxiety neurosis, based on the automatic analysis of scientific texts with ANDSystem, Alleya Nauki, 2017, vol. 2, no. 14, pp. 712-720.
Lavrik, I.N., Ivanisenko, V.A., Demenkov, P.S., et al., Prioritization of neuronal apoptosis genes by their structural role in the associative gene network of autism disorders using the ANDSystem, Mezhdunar. Zh. Gumanitar. Estestv. Nauk, 2017, no. 9, pp. 5-11.
Ivanisenko, V.A., Saik, O.V., Ivanisenko, N.V., et al., ANDSystem: an Associative Network Discovery System for automated literature mining in the field of biology, BMC Syst. Biol., 2015, vol. 9, no. 2, p. S2. doi 10.1186/1752-0509-9-S2-S2
Demenkov, P.S., Ivanisenko, T.V., Kolchanov, N.A., and Ivanisenko, V.A., ANDVisio: a new tool for graphic visualization and analysis of literature mined associative gene networks in the ANDSystem, In Silico Biol., 2011-2012, vol. 11, nos. 3-4, pp. 149-161. doi 10.3233/ISB-2012-0449
Ashburner, M., Ball, C.A., Blake, J.A., et al., Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium, Nat. Genet., 2000, vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 25-29. doi 10.1038/75556
Rappaport, N., Twik, M., Plaschkes, I., et al., MalaCards: an amalgamated human disease compendium with diverse clinical and genetic annotation and structured search, Nucleic Acids Res., 2017, vol. 45, no. D1, pp. D877-D887. doi 10.1093/nar/gkw1012
Pinero, J., Bravo, A., Queralt-Rosinach, N., et al., DisGeNET: a comprehensive platform integrating information on human disease-associated genes and variants, Nucleic Acids Res., 2017, vol. 45, no. D1, pp. D833-D839. doi 10.1093/nar/gkw943
Huang da, W., Sherman, B.T. and Lempicki, R.A., Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources, Nat. Protoc., 2009, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 44-57. doi 10.1038/nprot.2008.211
Maletic, V., Robinson, M., Oakes, T., et al., Neurobiology of depression: an integrated view of key findings, Int. J. Clin. Pract., 2007, vol. 61, no. 12, pp. 2030-2040. doi 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01602.x
Yu, S., Holsboer, F., and Almeida, O.F., Neuronal actions of glucocorticoids: focus on depression, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., 2008, vol. 108, pp. 300-309. doi 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.09.01
Rotwein, P., Variation in Akt protein kinases in human populations, Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol., 2017, vol. 313, no. 6, pp. R687-R692. doi 10.1152/ajpregu.00295.2017
Kajdaniuk, D., Marek, B., Borgiel-Marek, H., and Kos-Kudła, B., Transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1) in physiology and pathology, Endokrynol. Pol., 2013, vol. 64, no. 5, pp. 384-396. doi 10.5603/EP.2013.0022
Hopkins, B.D., Hodakoski, C., Barrows, D., et al., PTEN function, the long and the short of it, Trends Biochem. Sci., 2014, vol. 39, no. 4, pp. 183-190. doi 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.02.006
Ma, Y.C. and Huang, X.Y., Novel regulation and function of Src tyrosine kinase, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 2002, vol. 59, no. 3, pp. 456-462.
Samoilov, M.O., Churilova, A.V., Glushchenko, T.S., and Baranova, K.A., Pattern of neuronalexpression of transcription factors NF-kappaB under different modes of hypobarichypoxia, Fiziol. Zh., 2013, vol. 59, no. 6, pp. 132-140.
Oliveira-Paula, G.H., Lacchini, R., and Tanus-Santos, J.E., Endothelial nitric oxide synthase: from biochemistry and gene structure to clinical implications of NOS3 polymorphisms, Gene, 2016, vol. 575, no. 2, part 3, pp. 584-599. doi 10.1016/j.gene.2015.09.061
Wijeyewickrema, L.C., Gardiner, E.E., Gladigau, E.L., et al., Nerve growth factor inhibits metalloproteinase-disintegrins and blocks ectodomain shedding of platelet glycoprotein VI, J. Biol. Chem., 2010, vol. 285, no. 16, pp. 11793-11799. doi 10.1074/jbc.M110.100479
Lester, K.J., Hudson, J.L., Tropeano, M., et al., Neurotrophic gene polymorphisms and response to psychological therapy, Transl. Psychiatry, 2012, vol. 2, no. 5. e108. doi 10.1038/tp.2012.33
Zode, G.S., Sethi, A., Brun-Zinkernagel, A.M., et al., Transforming growth factor-β2 increases extracellular matrix proteins in optic nerve head cells via activation of the Smad signaling pathway, Mol. Vision, 2011, vol. 17, pp. 1745-1758.
Amare, A.T., Schubert, K.O., and Baune, B.T., Pharmacogenomics in the treatment of mood disorders: strategies and opportunities for personalized psychiatry, EPMA J., 2017, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 211-227. doi 10.1007/s13167-017-0112-8
Seavey, M.M. and Dobrzanski, P., The many faces of Janus kinase, Biochem. Pharmacol., 2012, vol. 83, no. 9, pp. 1136-1145. doi 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.12.024
Tanowitz, H.B., Machado, F.S., Avantaggiati, M.L., and Albanese, C., An expanded role for Caveolin-1 in brain tumors, Cell Cycle, 2013, vol. 12, no. 10, pp. 1485-1486. doi 10.4161/cc.24855
Kangussu, L.M., Almeida-Santos, A.F., Bader, M., et al., Angiotensin-(1-7) attenuates the anxiety and depression-like behaviors in transgenic rats with low brain angiotensinogen, Behav. Brain Res., 2013, vol. 257, pp. 25-30. doi 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.09.003
Sinclair, C.S., Rowley, M., Naderi, A., and Couch, F.J., The 17q23 amplicon and breast cancer, Breast Cancer Res. Treat., 2003, vol. 78, no. 3, pp. 313-322.
Kim, J., Yum, S., Kang, C., and Kang, S.J., Gene—gene interactions in gastrointestinal cancer susceptibility, Oncotarget, 2016, vol. 7, no. 41, pp. 67612-67625. doi 10.18632/oncotarget.11701
Dwivedi, Y., Rizavi, H.S., Conley, R.R., and Pandey, G.N., ERK MAP kinase signaling in post-mortem brain of suicide subjects: differential regulation of upstream Raf kinases Raf-1 and B-Raf, Mol. Psychiatry, 2006, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 86-98. doi 10.1038/sj.mp.4001744
Xia, H., Khalil, W., Kahm, J., et al., Pathologic caveolin-1 regulation of PTEN in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, Am. J. Pathol., 2010, vol. 176, no. 6, pp. 2626-2637. doi 10.2353/ajpath.2010.091117
Hamdan, F.F., Gauthier, J., Araki, Y., et al., Excess of de novo deleterious mutations in genes associated with glutamatergic systems in nonsyndromic intellectual disability, Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2011, vol. 88, no. 3, pp. 306-316. doi 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.02.001
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The development of gene prioritization criteria was supported by the Russian Science Foundation “Programmed Cell Death Induced via Apoptotic Receptors: Identification of Molecular Mechanisms of Apoptosis Initiation Using Molecular Modeling” (no. 14-44-00011). Genetic network analysis was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (RFBR-ofi-m) “Genomics of Aggressive and Depressive Behavior in Humans” (no. 17-29-02195).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by A. Kazantseva
Supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yankina, M.A., Saik, O.V., Ivanisenko, V.A. et al. Evaluation of Prioritization Methods of Extrinsic Apoptotic Signaling Pathway Genes for Retrieval of the New Candidates Associated with Major Depressive Disorder. Russ J Genet 54, 1366–1374 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795418110170
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795418110170