Abstract
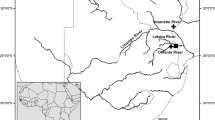
Genetic and morphological analysis of endemic sponges of the Lubomirskiidae family from Lake Baikal and the upper reaches of the Angara River was performed. Various sponge species acquired a number of similar morphological traits after the transition from the lake into the river. These traits enabled an increase of sponge skeleton strength under the conditions of elevated hydrodynamic activity. The changes significantly impeded morphology-based species identification of Angara sponges. Phylogenetic analysis of ITS regions and noncoding mitochondrial DNA fragments confirmed that the Angara sponges belonged to the Baikalian Lubomirskiidae family and demonstrated the polyphyletic origin of the sponges. The use of combined molecular and morphological data allowed for the clustering of some sponge samples into groups that corresponded to individual species. The absence of genetic isolation between the Baikalospongia intermedia and Lubomirskia baicalensis species was demonstrated, whereas the B. intermedia profundalis subspecies was well separated from B. intermedia. This finding pointed to the necessity of further studies for the clarification of the taxonomic status of this subspecies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kozhov, M.M., Biologiya ozera Baikal (Biology of Lake Baikal), Moscow: Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1962.
Kozhov, M.M., About the benthos of Southern Baikal, Bentos i plankton Yuzhnogo Baikala (Benthos and Plankton of Southern Baikal), Izv. Irkutsk. Gos. Univ., Ser. Biol. Ecol., 1970, vol. 23, issue 1, pp. 3–12.
Efremova, S.M., Sponges, in Annotirovannyi spisok fauny ozera Baikal i ego vodosbornogo basseina (An Annotated List of the Fauna of Lake Baikal and Its Catchment Area), Timoshkin, O.A., Ed., Novosibirsk: Nauka, 2001, vol. 1, pp. 177–190.
Efremova, S.M., New genus and new species of sponges from the family Lubomirskiidae Rezvoj, 1936, in Annotirovannyi spisok fauny ozera Baikal i ego vodosbornogo basseina (An Annotated List of the Fauna of Lake Baikal and Its Catchment Area), Timoshkin, O.A., Ed., Novosibirsk: Nauka, 2004, vol. 1, book 2, pp. 1261–1278.
Manconi, R. and Pronzato, R., Global diversity of sponges (Porifera: Spongillina) in freshwater, Hydrobiologia, 2008, vol. 595, no. 1, pp. 27–33.
Harcet, M., Bilandzija, H., Bruvo-Madaric, B., and Cetkovic, H., Taxonomic position of Eunapius subterraneus (Porifera, Spongillidae) inferred from molecular data—a revised classification needed?, Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 2010, vol. 54, pp. 1021–1027.
Schronberg, C.H.L. and Barthel, D., Unreliability of demosponge skeletal characters: the example of Halichondria panacea, in Sponge Sciences, Watanabe, Y. and Fusetani, N., Eds., Tokyo: Springer-Verlag, 1998, pp. 41–54.
Maldonado, M., Carmona, M.C., Uriz, M.J., and Cruzado, A., Decline in Mesozoic reef-building sponges explained by silicon limitation, Nature, 1999, vol. 401, pp. 785–788. doi 10.1038/44560
Bell, J., Barnes, D., and Turner, J., The importance of micro and macro morphological variation in the adaptation of a sublittoral demosponge to current extremes, Mar. Biol., 2002, vol. 140, pp. 75–81.
Van Soest, R., Boury-Esnault, N., Vacelet, J., et al., Global diversity of sponges (Porifera), PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7: e35105. doi 10.1371/journal.pone.0035105
Manconi, R. and Pronzato, R. Suborder Spongillina subord. nov.: freshwater sponges, in Systema Porifera: A Guide to the Classification of Sponges, vol. 1, Hooper, J.N.A. and Van Soest, R.W.M., Eds., Dordrecht: Kluwer, 2002, pp. 921–1020.
Castellani, C., Maas, A., Haug, C., et al., Isolated sponges spicules from the late Cambrian Alum Shale Formation (‘Orsten’ nodules) of Sweden, Bull. Geosci., 2012, vol. 87, no. 3, pp. 443–460.
Veinberg, E.V., Spongiofauna of the Pliocene—Quaternary deposits of Lake Baikal, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. Dissertation, St. Petersburg, 2005.
Maikova, O., Khanaev, I., Belikov, S., and Sherbakov, D., Two hypotheses of the evolution of endemic sponges in Lake Baikal (Lubomirskiidae), J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res., 2015, vol. 53, no. 2, pp. 175–179.
Schroder, H.C., Efremova, S.M., Itskovich, V.B., et al., Molecular phylogeny of the freshwater sponges in Lake Baikal, J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res., 2002, vol. 40, pp. 1–7.
Itskovich, V., Belikov, S., Efremova, S., et al., Phylogenetic relationships between freshwater and marine Haplosclerida (Porifera, Demospongiae) based on the full length 18S rRNA and partial COXI gene sequences, in Porifera Research—Biodiversity, Innovation and Sustainability, 2007, pp. 1–9.
Boury-Esnault, N., Lavrov, D.V., Ruiz, C.A., and Perez, T., The integrative taxonomic approach applied to Porifera: a case study of the Homoscleromorpha, Integr. Comp. Biol., 2013, vol. 53, no. 3, pp. 416–427.
Rezvoi, P.D., Freshwater sponges (families Spongillidae and Lubomirskiidae), in Fauna SSSR (Fauna of the Soviet Union), Moscow: Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1936, vol. 2, pp. 90–101.
Bazikalova, A., About amphipoda of Angara River, Proc. Baikal Limnol. Stat., 1957, vol. 15, pp. 377–387.
Golyshkina, R., Benthos of Irkutsk Reservoir in first years of its existence (1957–1961), Proc. IBIW AN SSSR, 1963, vol. 6, no. 9, pp. 91–104.
Masuda, Y., Studies on the taxonomy and distribution of freshwater sponges in Lake Baikal, Prog. Mol. Subcell. Biol., 2009, vol. 47, pp. 81–110.
Wetzel, R.G. and Likens, G.E., Limnological Analyses, New York: Springer-Verlag, 1991.
Baram, G.I., Vereshchagin, A.L., and Golobokova, L.P., Application of microcolumn HPLC with UV detection to analysis of anions in environmental objects, Zh. Anal. Khim., 1999, p. 54.
Boeva, L., Rukovodstvo dlya khimicheskogo analiza poverkhnostnykh vod (Guidelines for the Chemical Analysis of Surface Waters), Rostov-on-Don: RosGidromet, 2009.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F., and Sambrook, J., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Lab., 1982.
Maikova, O.O., Stepnova, G.N., and Belikov, S.I., Variations in noncoding sequences of the mitochondrial DNA in sponges from family Lubomirskiidae, Dokl. Biol. Sci., 2012, vol. 442, nos. 1–6, pp. 1–3.
Itskovich, V., Gontcharov, A., Masuda, Y., et al., Ribosomal its sequences allow resolution of freshwater sponge phylogeny with alignments guided by secondary structure prediction, J. Mol. Evol., 2008, vol. 67, no. 6, pp. 608–620.
Katoh, K. and Toh, H., Recent developments in the mafft multiple sequence alignment program, Briefings Bioinf., 2008, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 286–298.
Ronquist, F. and Huelsenbeck, J.P., MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models, Bioinformatics, 2003, vol. 19, no. 12, pp. 1572–1574.
Newton, M. and Raftery, A., Approximate Bayesian inference with the weighted likelihood bootstrap (with discussion), J. R. Stat. Soc., Ser. B, 1994, vol. 56, p. 348.
Suchard, M., Weiss, R., and Sinsheimer, J., Bayesian selection of continuous-time Markov chain evolutionary models, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2001, vol. 18, pp. 1001–1013.
Timoshkin, O.A., Samsonov, D.P., and Yamamuro, M., Rapid ecological change in the coastal zone of Lake Baikal (East Siberia): is the site of the world’s greatest freshwater biodiversity in danger?, J. Great Lakes Res., 2016, vol. 42, pp. 487–497.
Lavrov, D., Rapid proliferation of repetitive palindromic elements in mtDNA of the endemic Baikalian sponge Lubomirskia baicalensis, Mol. Biol Evol., 2010, vol. 27, pp. 757–760.
Itskovich, V.B., Kalyuzhnaya, O.V., and Belikov, S.I., Investigation of nuclear and mitochondrial DNA polymorphism in closely related species of endemic Baikal sponges, Russ. J. Genet., 2013, vol. 49, no. 8, pp. 966–974.
Bukshuk, N.A. and Timoshkin, O.A., Morphology and vertical distribution of Baikalospongia intermedia (Spongia: Lubomirskiidae) in the deep-water zone of Lake Baikal, Izv. Irkutsk Gos. Univ., Ser. Biol. Ekol., 2013, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 128–131.
Maikova, O.O., Itskovich, V.B., Semiturkina, N.A., et al., Phylogenetic position of sponges from Chagatai and Tore-Khol lakes, Russ. J. Genet., 2010, vol. 46, no. 12, pp. 1670–1677.
Itskovich, V., Kaluzhnaya, O., Ostrovsky, I., and McCormack, G., The number of endemic species of freshwater sponges (Malawispongiidae; Spongillina; Porifera) from Lake Kinneret is overestimated, J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res., 2013, vol. 51, no. 3, pp. 252–257.
Kelly-Borges, M. and Pomponi, S., Phylogeny and classification of lithistid sponges (Porifera, Demospongiae): a preliminary assessment using ribosomal DNA sequence comparisons, Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotech., 1994, vol. 3, pp. 87–103.
Borchiellini, C., Manuel, M., Alivon, E., et al., Sponge paraphyly and the origin of Metazoa, J. Evol. Biol., 2001, vol. 14, pp. 171–179.
Erpenbeck, D. and Worheide, G., On the molecular phylogeny of sponges (Porifera), Linnaeus Tercentenary: Progress in Invertebrate Taxonomy, Zhang, Z.-Q. and Shear, W.A., Eds., Zootaxa, 2007, vol. 1668, pp. 107–126.
Vargas, S., Schuster, A., Sacher, K., et al., Barcoding sponges: an overview based on comprehensive sampling, PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7, no. 7: e39345. doi 10.1371/journal.pone.0039345
Lavrov, D.V., Maikova, O.O., Pett, W., and Belikov, S.I., Small inverted repeats drive mitochondrial genome evolution in Lake Baikal sponges, Gene, 2012, vol. 505, pp. 91–99.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O.O. Maikova, N.A. Bukshuk, V.B. Itskovich, I.V. Khanaev, I.A. Nebesnykh, N.A. Onishchuk, D.Yu. Sherbakov, 2017, published in Genetika, 2017, Vol. 53, No. 12, pp. 1419–1426.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maikova, O.O., Bukshuk, N.A., Itskovich, V.B. et al. Transformation of Baikal sponges (family Lubomirskiidae) after penetration into the Angara River. Russ J Genet 53, 1343–1349 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795417120092
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795417120092