Abstract
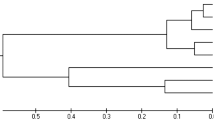
Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus) is a rare amphibian species in the world. Microsatellite markers are a promising tool for accurate estimation population structure and genetic diversity. In this paper, we isolated novel microsatellite marker for Chinese giant salamander using fast isolation by AFLP of sequences containing repeats (FIASCO) method. More than 50% sequences in 132 clones had repeat number over ten times with di or trinucleeotide repeat except of (GA)12. Seventy pairs of primers were designed and eleven polymorphic microsatellite loci were characterized for wild and cultivated Chinese giant salamander populations. The allele number was from 3 to 9 in different loci. Polymorphism information content was from 0.544 to 0.702 in cultivated population. The results implied more alleles and PIC were in the wild population than cultivated population. The observed heterozygosities in two populations were higher than 0.553. The data analysis suggested that the cultivated population has lower genetic diversity than wild population, which it’s perhaps owing to inbreeding in artificial breeding. To our knowledge, it’s the first time to isolated microsatellite markers for Chinese giant salamander. The result indicated that the markers were suitable for the population genetic analysis of Chinese giant salamander.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao, E.M., China Red Data Book of Endangered Animals: Amphibians and Reptiles, Beijing: Science Press, 1998.
Hou, J.H., Zhu, B.C., Dong, Y.W., et al., Research Advances of Chinese Giant Salamander, Andrias davidianus, Sichuan J. Zool., 2004, vol. 22, pp. 262–267.
Lin, M., Huang, J., Li, Z., et al., RAPD Analysis on the Wild Parents and Second Filial Generation of Artificial Breeding of Andrias davidianus, J. Shanghai Fish. Univ., 2003, vol. 12,suppl., pp. 20–23.
Lukas, F.K. and Donald, M.W., Inbreeding Effects in Wild Populations, Trends Ecol. Evol., 2002, vol. 17, pp. 230–241.
Liu, Y.G., Guo, Y.H., Hao, J., and Liu, L.X., Genetic Diversity of Swimming Crab (Portunus trituberculatus) Populations from Shandong Peninsula as Assessed by Microsatellite Markers, Biochem. Syst. Ecol., 2012, vol. 41, pp. 91–97.
Fang, Y.L., Zhang, Y., Yang, Y.Q., and Xiao, H.B., Genetic Diversity Analysis of Domesticated Chinese Giant Salamander (Andrias davidianus Blanchard), Freshwater Fish., 2006, vol. 36, pp. 8–11.
Tao, F.Y., Wang, X.M., and Zheng, H.X., Analysis of Complete Cytochrome b Sequences and Genetic Relationship among Chinese Giant Salamanders (Andrias davidianus) from Different Areas, Acta Hydrobiol. Sin., 2006, vol. 36, pp. 8–11.
Murphy, R.W., Fu, J.Z., Upton, D.E., et al., Genetic Variability among Endangered Chinese Giant Salamanders, Andrias davidianus Mol. Ecol., 2000, vol. 9, pp. 1539–1547.
Vera, N.S., Chiappero, M.B., Priotto, J.W., and Gardenal, C.N., Isolation of Microsatellite Loci in Akodon azarae (Muridae, Sigmodontinae) and Cross-Amplifcation in other Akodontini Species, J. Genet., 2011, vol. 90, pp. 25–29.
Takezaki, N. and Nei, M., Genetic Distances and Reconstruction of Phylogenic Tree from Microsatellite DNA, Genetics, 1996, vol. 144, pp. 389–399.
Goldstein, D.B. and Schlotterer, C., Microsatellites: Evolution and Applications, Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press, 1999.
Knopp, T. and Merila, J., Microsatellite Variation and Population Structure of the Moor Frog (Rana arvalis) in Scandinavia. Mol. Ecol., 2009, vol. 18, pp. 2996–3009.
Rice, A.M., Pearse, D.E., Becker, T., et al., Development and Characterization of Nine Polymorphic Microsatellite Markers for Mexican Spadefoot Toads (Spea multiplicata) with Cross-Amplification in Plains Spadefoot Toads (S. bombifrons), Mol. Ecol. Resour., 2008, vol. 8, pp. 1386–1389.
Aurelie, J., Damien, P., Trenton, W.J.G., et al., Characterization of Microsatellite Loci in Two Closely Related Lissotriton Newt Species, Conserv. Genet., 2009, vol. 10, pp. 1903–1906.
Taggart, J.B., Hynes, R.A., Prodoh, P.A., and Ferguson, A., A Simplified Protocol for Routine Total DNA Isolation from Salmonid Fishes, J. Fish Biol., 1992, vol. 40, pp. 963–965.
Zane, L., Bargelloni, L., and Patarnello, T., Strategies for Microsatellite Isolation: A Review, Mol. Ecol., 2002, vol. 11, pp. 1–16.
Benson, G., Tandem Repeats Finder: A Program to Analyze DNA Sequences, Nucleic Acids Res., 1999, vol. 27, pp. 573–580.
Zhang, P., Chen, Y.Q., Liu, Y.F., et al., The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Chinese Giant Salamander, Andrias davidianus (Amphibia: Caudata), Gene, 2003, vol. 311, pp. 93–98.
Tao, F.Y., Wang, X.M., Zheng, H.X., and Fang, S.G., Genetic Structure and Geographic Subdivision of Four Populations of the Chinese Giant Salamander (Andrias davidianus), Zool. Res., 2005, vol. 6, pp. 162–167.
Rallo, P., Dorado, G., and Martin, A., Development of Simple Sequence Repeats (SSRs) in Olive Tree (Olea europaea L.), Theor. Appl. Genet., 2000, vol. 101, pp. 984–989.
Johnson, J.R., Faries, K.M., Rabenold, J.J., et al., Polymorphic Microsatellite Loci for Studies of the Ozark Hellbender (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis bishop), Conserv. Genet., 2009, vol. 10, pp. 1759–1797.
Yoshikama, N., Kaneko, S., Kumabara, K., et al., Development of Microsatellite Markers for the Two Giant Salamander Species (Andrias japonicas and A. davidianus), Curr. Herpetol., 2011, vol. 30, pp. 177–180.
Matsui, M., Tominaga, A., Liu, W.Z., and Ueno, T.T., Reduced Genetic Variation in the Japanese Giant Salamander, Andrias japonicas (Amphibia: Caudata), Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 2008, vol. 49, pp. 318–326.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Y., Zhang, Y., Liang, H.W. et al. Genetic diversity of Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus) based on the novel microsatellite markers. Russ J Genet 48, 1227–1231 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S102279541212006X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S102279541212006X