Abstract
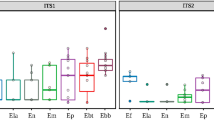
The ITS1-5.8S rDNA-ITS2 regions of 33 accessions belonging to 16 species and five natural and garden interspecific hybrids of the genus Paeonia L. were sequenced. Chromatograms of the peony hybrids demonstrated the presence of the signals, corresponding to two different nucleotides at the positions differing in the parents, indicating that in the hybrids, no rDNA isogenization usually occurred, and they preserved rDNA of both parents. Analysis of these polymorphic sites (PS) showed that P. × majkoae was interspecific hybrid between P. tenuifolia and P. caucasica. The ITS of P. hybrida differs from ITS of P. × majkoae in 19 mutations. Because of this, P. × majkoae is definitely not synonymous to P. hybrida. Comparative analysis of ITS1-5.8S rDNA-ITS2 showed that species diversity in section Paeonia was based on recombination as a result of intraspecific hybridization of three haplotype families. Specifically, haplotypes A, typical of the P. tenuifolia and P. anomala genomes, haplotypes B, typical of P. mlokosewitschii and P. obovata, and haplotypes of family C, currently represented in rDNA of diploid and tetraploid forms of some Caucasian and Mediterranean species. The ITS regions many diploid peonies contain no dimorphic sites, while P. oreogeton, P. cambessedesii, P. rhodia, and P. daurica carry from 10 to 17 PS, and supposed to be the interspecific hybrids. Most of the tetraploid peonies contain from 6 to 18 PS in the ITS regions. These are alloploids with one of the parental genomes similar to that of P. mlokosewitschii (B1), or P. obovata (B3). The second parental genome in P. banatica, P. peregrina, and P. russii is represented by the genome, close to that of P. tenuifolia (A). P. macrophylla, P. mascula, P. coriacea, P. wittmanniana, and P. tomentosa carry genome of series B and genome of series C, which slightly resembles genome A.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grant, V., Plant Speciation, New York: Columbia Univ. Press, 1981, 2nd ed.
Soltis, P.S. and Soltis, D.E., The Role of Genetic and Genomic Attributes in the Success of Polyploids, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2000, vol. 97, pp. 7051–7057.
Anderson, E. and Stebbins, G.L., Hybridization as an Evolutionary Stimulus, Evolution, 1954, vol. 8, pp. 378–388.
Punina, E.O., Karyological Study of Species of the Genus Paeonia (Paeoniaceae) from the Caucasus, Bot. Zh., 1987, vol. 72, no. 11, pp. 1504–1514.
Punina, E.O., Karyological Study of Some Representatives of the Genus Paeonia L. (Paeoniaceae) from the Caucasus Using Giemsa Chromosome Banding, Bot. Zh., 1989, vol. 74, no. 3, pp. 332–339.
Punina, E.O., A New Peony Species for the Flora of the Caucasus and Russia, Paeonia officinalis (Paeoniaceae) and Its Karyosystematic Study, Bot. Zh., 2005, vol. 90, no. 3, pp. 332–339.
Punina, E.O., Machs, E.M., Mordak, E.V., et al., The Genus Paeonia in Russia and on Adjacent Territories: Revision Using Methods of Karyosystematics and Molecular Systematics, Fundamental’nye i prikladnye problemy v botanike XXI veka (Fundamental and Applied Aspects in Botany of the 21th Century) (Proc. All-Russia Conf.), Petrozavodsk, 2008, pp. 68–71.
Punina, E.O. and Mordak, E.V., Conspectus of Species of the Genus Paeonia from the Caucasus, Bot. Zh., 2009, vol. 94, no. 11, pp. 1681–1696.
Punina, E.O., Mordak, E.V., Timukhin, I.N., and Litvinskaya, S.A., Conspectus of Notospecies of the Genus Paeonia from the Caucasus and Crimea, Nov. Sist. Vyssh. Rast., 2010, vol. 42, pp. 120–131.
Kotseruba, V., Gernand, D., Meister, A., and Houben, A., Uniparental Loss of Ribosomal DNA in the Allotetraploid Grass Zingeria trichopoda (2n=8), Genome, 2003, vol. 46, pp. 156–163.
Kovarik, A., Dadejova, M., Lim, Y.K., et al., Evolution of rDNA in Nicotiana Allopolyploids: A Potential Link between rDNA Homogenization and Epigenetics, Ann. Bot., 2008, vol. 101, pp. 815–823.
Malinska, H., Tate, J.A., Matyasek, R., et al., Similar Patterns of rDNA Evolution in Synthetic and Recently Formed Natural Populations of Tragopogon (Asteraceae) Allotetraploids, BMC Evol. Biol., 2010, vol. 10, pp. 291–308.
Rodionov, A.V., Tyupa, N.B., Kim, E.S., et al., Genomic Configuration of the Autotetraploid Oat Species Avena macrostachya Inferred from Comparative Analysis of ITS1 and ITS2 Sequences: On the Oat Karyotype Evolution during the Early Events of the Avena Species Divergence, Russ. J. Genet., 2005, vol. 41, no. 5, pp. 518–528.
Rodionov, A.V., Nosov, N.N., Kim, E.S., et al., The Origin of Polyploid Genomes of Bluegrasses (Poa L.) and Gene Flow between Northern Pacific and Sub-Antarctic Islands, Russ. J. Genet., 2010, vol. 46, no. 12, pp. 1407–1416.
Tyupa, N.B., Kim, E.S., Loskutov, I.G., and Rodionov, A.V., Origin of Polyploids in the Genus Avena L.: A Molecular-Phylogenetic Study, Tr. Prikl. Bot. Genet. Sel., 2009, vol. 165, pp. 13–20.
Sang, T., Crawford, D.J., and Stuessy, T.F., Documentation of Reticulate Evolution in Peonies (Paeonia) Using Internal Transcribed Spacer Sequences of Nuclear Ribosomal DNA: Implications for Biogeography and Concerted Evolution, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1995, vol. 92, pp. 6813–6817.
Stern, F.C., A Study of Genus Paeonia, London: Royal Horticultural Soc., 1946.
Hong, D.-Yu. and Zhou, Sh.-L., Paeonia (Paeoniaceae) in the Caucasus, Bot. J. Linn. Soc., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 135–150.
Halda, J.J. and Waddick, J.W., The Genus Paeonia, Portland: Timber Press, 2004.
Doyle, J.J. and Doyle, J.L., A Rapid DNA Isolation Procedure for Small Quantities of Fresh Leaf Tissue, Phytochem. Bull., 1987, vol. 19, p. 11.
Ridgway, K.P., Duck, J.M., and Young, J.P.W., Identification of Roots from Grass Swards Using PCR-RFLP and FFLP of the Plastid trnL (UAA) Intron, BMC Ecol., 2003, vol. 19, pp. 3–8.
White, T.J., Bruns, T., Lee, S., and Taylor, J., Amplification and Direct Sequencing of Fungal Ribosomal RNA Genes for Phylogenetics, PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications, Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., and White, T.J., Eds., San Diego, 1990, pp. 315–322.
Kumar, S., Tamura, K., and Nei, M., MEGA3: Integrated Software for Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis and Sequence Alignment, Brief. Bioinform., 2004, vol. 5, pp. 150–163.
Uspenskaya, M.S., Piony, tsvety v sadu (Peony, Flowers in the Garden), Moscow: Fiton Plus, 2003.
Ketzchoveli, N.N., Two New Peonies for the Flora of Georgia, in Zametki po sistematike i geografii rasteniy, (Notes on Plant Systematics and Geography), Tbilisi, 1959, issue 21, pp. 15–18.
Kemularia-Nathadse, L.M., Caucasian Representatives of the Genus Paeonia L. (Paeoniaceae), Tr. Tbilisi Bot. Inst., 1961, vol. 21, pp. 3–51.
Schipczinsky, N.V., The Genus Peony-Paeonia L., Flora SSSR (Flora of the Soviet Union), Komarov, V.L., Ed., 1937, vol. 7, pp. 25–29.
Hong, D.-Y. and Pan, K.-Y., A Taxonomic Revision of the Paeonia anomala Complex (Paeoniaceae), Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard., 2004, vol. 91, pp. 87–98.
Troitzky, N.A., Observations on Some Plant Hybrids, Bot. Zh., 1932, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 211–226.
Kakheladze, N.A., Origin of Paeonia chamaeleon Troitzky and Its Experimental Analysis, in Voprosy introduktsii rastenii i zelenogo stroitel’stva (Problems of Plant Introduction and Green), Tbilisi, 1965, vol. 2, pp. 75–84.
Kemularia-Nathadse, L.M., Nomenclature and Taxonomy of Paeonia chamaeleon Troitzky and Its Related Species, in Zametki po sistematike i geografii rasteniy, (Notes on Plant Systematics and Geography), Tbilisi, 1980, issue 36, pp. 22–24.
Melikyan, A.P. and Astvatsatryan, N.Z., Spermoderm Comparative Anatomy of the Representatives of the Genus Paeonia L. in Relation to Their Phylogeny, Biol. Zh. Arm., 1971, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 54–60.
Uspenskaya, M.S., Peonies (Genus Paeonia L.) of the Flora the Soviet Union, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. (Biol.) Dissertation, Moscow, 1981, p. 21.
Litvinskaya, S.A. and Karpov, I.B., On the Growth of Two Rare Species (Orchis provincialis Balb. ex DC and Paeonia wittmanniana Hartw.) in Lazarevskiy Rayon of the Black Sea Coast of Russia, Geograficheskie issledo-vaniya Krasnodarskogo kraya (Geographical Investigations of Krasnodar Krai) (Collect. Sci. Pap. Kubanskii State Univ.), 2005, pp. 78–84.
Fukuda, I., Freeman, J.D., and Ito, M., Trillium channellii, sp. nov. (Trilliaceae), in Japan, and T. camschatcense Ker Gawler, Correct Name for the Asiatic Diploid Trillium, Novon, 1996, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 164–171.
Bolkhovskikh, Z.V., Grif, V.G., Zakhar’eva, O.I., and Matveeva, T.S., Khromosomnye chisla tsvetkovykh rastenii (Chromosome Numbers of the Flowering Plants), Leningrad: Nauka, 1969.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.O. Punina, E.M. Machs, E.E. Krapivskaya, E.S. Kim, E.V. Mordak, Y.A. Myakoshina, A.V. Rodionov, 2012, published in Genetika, 2012, Vol. 48, No. 7, pp. 812–826.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Punina, E.O., Machs, E.M., Krapivskaya, E.E. et al. Interspecific hybridization in the genus Paeonia (Paeoniaceae): Polymorphic sites in transcribed spacers of the 45S rRNA genes as indicators of natural and artificial peony hybrids. Russ J Genet 48, 684–697 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795412070113
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795412070113