Abstract
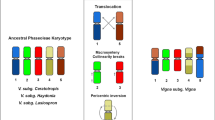
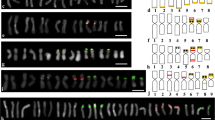
Chromosome C-banding and two-color fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) were used to compare the chromosomes, to identify the chromosomal localization of the 45S and 5S rRNA genes, and to analyze the sequences of internal transcribed spacers 1 and 2 (ITS1 and ITS2) of the 45S rRNA genes in the genomes of grasses Zingeria biebersteiniana (2n = 4), Z. pisidica, Z. trichopoda (2n = 8), Colpodium versicolor (2n = 4), and Catabrosella variegata (syn. Colpodium variegatum) (2 n = 10). Differences in C-banding pattern were observed for two Z. biebersteiniana accessions from different localities. Similar C-banding patterns of chromosomes 1 and 2 were demonstrated for the Z. pisidica and Z. biebersteininana karyotypes. Chromosome C banding and localization of the 45S and 5S rRNA genes on the chromosomes of the two Zingeria species confirmed the assumption that Z. pisidica is an allotetraploid with one of the subgenomes similar to the Z. biebersteiniana genome. ITS comparisons showed that the unique two-chromosome grasses (x = 2)—Z. biebersteiniana (2n = 4), Z. trichopoda (2n = 8), Z. pisidica (2n = 8), and C. versicolor (2n = 4), which were earlier assigned to different tribes of subtribes of the family Poaceae—represent two closely related genera, the genetic distance (p-distance) between their ITSs being only 1.2–4.4%. The Zingeria species and C. versicolor formed a common clade with Catabrosella araratica (2n = 42, x = 7) on a molecular phylogenetic tree. Thus, the karyotypes of Zingeria and Colpodium, which have the lowest known basic chromosome number (x = 2), proved to be monophyletic, rather than originating from different phylogenetic lineages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levitskii, G.A., Cytological Bases of Evolution, Priroda, 1939, no. 5, pp. 33–44.
Avdulov, N.P., Karyo-Systematic Study of the Family Gramineae, Tr. Prikladnoi Botanike Genet. Selektsii, 1931, no. 44, pp. 1–352.
Paterson, A.H., Bowers, J.E., and Chapman, B.A., Ancient Polyploidization Predating Divergence of the Cereals, and Its Consequences for Comparative Genomics, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2004, vol. 101, pp. 9903–9908.
Paterson, A.H., Bowers, J.E., Feltus, F.A., et al., Comparative Genomics of Grasses Promises a Bountiful Harvest, Plant Physiol., 2009, vol. 149, pp. 125–131.
Tang, H., Bowers, J.E., Wang, X., et al., Synteny and Colinearity in Plant Genomes, Science, 2008, vol. 320, pp. 486–488.
Tsvelev, N.N. and Zhukova, P.G., On the Minimal Main Chromosome Cycle in Poaceae, Bot. Zh., 1974, vol. 59, pp. 265–269.
Sokolovskaya, A.P. and Probatova, N.S., On the Minimal Main Chromosome Cycle (2n = 4) in Colpodium versicolor (Stev.) Woronow (Poaseae), Bot. Zh., 1977, vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 241–245.
Semenov, V.I. and Semenova, E.V., Differential Staining of Chromosomes in Zingeria biebersteiniana (Claus) P. Smirn. during Mitosis and Meiosis, Izv. Sib. Otd. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Biol., 1975, vol. 3, no. 15, pp. 80–84.
Sorokin, S.N. and Punina, E.O., Karyo-Systematics of Zingeria biebersteiniana (Poaceae), Bot. Zh., 1992, vol. 77, no. 7, pp. 75–79.
Cremonini, R., Castiglione, M.R., Grif, V.G., et al., Chromosome Banding and DNA Methylation Patterns, Chromatin Organization and Nuclear DNA Content in Zingeria biebersteiniana, Biologia Plantarum, 2003, vol. 4, pp. 543–550.
Bennett, M.D., Smith, J.B., and Seal, A.G., The Karyotype of the Grass Zingeria biebersteiniana (2n = 4) by Light and Electron Microscopy, Can. J. Genet. Cytol., 1986, vol. 28, pp. 554–562.
Bennett, S.T., Leitch, I.J., and Bennett, M.D., Chromosome Identification and Mapping in the Grass Zingeria biebersteiniana (2n = 4) Using Fluorochromes, Chromosome Res., 1995, vol. 3, pp. 101–108.
Kotseruba, V., Gernand, D., Meister, A., and Houben, A., Uniparental Loss of Ribosomal DNA in the Allotetraploid Grass Zingeria trichopoda (2n = 8), Genome, 2003, vol. 46, pp. 156–163.
Kotseruba, V., Pistrick, K., Gernand, D., et al., Characterization of the Low-Chromosome Number Grass Colpodium versicolor (Stev.) Schmalh. (2n = 4) by Molecular Cytogenetics, Caryologia, 2005, vol. 58, pp. 241–245.
Rodionov, A.V., Punina, E.O., Dobroradova, M.A., et al., Chromosome Numbers of Some Grasses (Poaceae): Aveneae, Poeae, Phalarideae, Phleeae, Bromeae, Triticeae, Bot. Zh., 2006, vol. 91, no. 4, pp. 615–627.
Tsvelev, N.N. and Bolkhovskikh, Z.V., Genus Zingeria P. Smirn. and Related Genera of Gramineae (Karyo-Systematic Study), Bot. Zh., 1965, vol. 50, no. 9, pp. 1317–1320.
Tsvelev, N.N., Zlaki SSSR (Grasses of the Soviet Union), Leningrad: Nauka, 1976.
Clayton, W.D. and Renvoize, S.A., Genera Graminum, Grasses of the World, London: HMSO, 1986.
Saunders, V.A. and Houben, A., The Pericentromeric Heterochromatin of the Grass Zingeria biebersteiniana (2n = 4) Is Composed of Zbcen1-Type Tandem Repeats That Are Intermingled with Accumulated Dispersedly Organized Sequences, Genome, 2001, vol. 44, no. 6, pp. 955–961.
Muravenko, O.V., Samatadze, T.E., and Zelenin, A.V., Computer and Visual Analysis of G-Like Banding Patterns of Matricaria chamomilla Chromosomes, Biol. Membrany, 1998, vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 670–678.
Samatadze, T.E., Muravenko, O.V., Popov, K.V., and Zelenin, A.V., Genome Comparison of the Matricaria chamomilla L. Varieties by the Chromosome C- and OR-Banding Patterns, Caryologia, 2001, vol. 54, pp. 299–306.
Muravenko, O.V., Samatadze, T.E., Popov, K.V., et al., Comparative Genome Analysis of Two Flax Species by C-Banding Patterns, Russ. J. Genet., 2001, vol. 37, no. 3, pp. 253–256.
Semenova, O.Yu., Samatadze, T.E., Zelenin, A.V., and Muravenko, O.V., The Comparative Genome Study of the Flax Species of Sections Adenolinum and Stellerolinum by Means of Fluorescent Hybridization in situ (FISH), Biol. Membrany, 2006, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 453–460.
Gerlach, W.L. and Bedbrook, J.R., Cloning and Characterisation of Ribosomal RNA Genes from Wheat and Barley, Nucleic Acids Res., 1979, vol. 7, pp. 1869–1885.
Gerlach, W.L. and Dyer, T.A., Sequence Organization of the Repeating Units in the Nucleus of Wheat Which Contains 5S rRNA Genes, Nucleic Acids Res., 1980, vol. 8, pp. 4851–4865.
Cox, A.V., Bennett, S.T., Parokonny, A.S., et al., Comparison of Plant Telomere Locations Using a PCR-Generated Synthetic Probe, Ann. Botany, 1993, vol. 72, pp. 239–247.
Popov, K.V., Muravenko, O.V., Samatadze, T.E., et al., Specificity of Heterochromatic Regions Analysis in Small Chromosomes of Plants, Dokl. Akad. Nauk, 2001, vol. 381, no. 4, pp. 562–565.
Doyle, J.J. and Doyle, J.L., A Rapid DNA Isolation Procedure for Small Quantities of Fresh Leaf Tissue, Phytochem. Bull., 1987, vol. 19, pp. 11–15.
Rodionov, A.V., Tyupa, N.B., Kim, E.S., et al., Genomic Configuration of the Autotetraploid Oat Species Avena macrostachya Inferred from Comparative Analysis of ITS1 and ITS2 Sequences: On the Oat Karyotype Evolution during the Early Events of the Avena Species Divergence, Russ. J. Genet., 2005, vol. 41, no. 5, pp. 518–528.
Gardes, M. and Brunes, T.D., ITS Primers with Enhanced Specificity for Basidiomycetes—Application to the Identification of Mycorrhizae and Rusts, Mol. Ecol., 1993, vol. 2, pp. 130–138.
Ridgway, K.P., Duck, J.M., and Young, J.P.W., Identification of Roots from Grass Swards Using PCR-RFLP and FFLP of the Plastid TrnL (UAA) Intron, BMC Ecol., 2003, vol. 3, p. 8.
White, T.J, Bruns, T, Lee, S, and Taylor, J, Amplification and Direct Sequences of Fungal Ribosomal RNA Genes for Phylogenetics, PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications, Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., and White, T.J., Eds., San Diego, 1990, pp. 315–322.
Nosov, N.N. and Rodionov, A.V., Molecular Phylogenetic Study of Relationship between Representatives of Genus Poa (Poaseae), Bot. Zh., 2008, vol. 93, no. 12, pp. 1919–1936.
Kumar, S., Tamura, K., and Nei, M., MEGA3: Integrated Software for Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis and Sequence Alignment, Briefings Bioinf., 2004, vol. 5, pp. 150–163.
Nei, M. and Kumar, S., Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics, Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press, 2000.
Felsenstein, J., Confidence Limits on Phylogenesis: An Approach Using the Bootstrap, Evolution, 1985, vol. 39, pp. 783–791.
Pogosyan, A.I., Narinyan, S.G., and Voskanyan, V.E., Towards Karyological and Geographical Study of Aragats Montains Flora, Biol. Zh. Arm., 1972, vol. 25, no. 9, pp. 15–22.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.S. Kim, N.L. Bolsheva, T.E. Samatadze, N.N. Nosov, I.V. Nosova, A.V. Zelenin, E.O. Punina, O.V. Muravenko, A.V. Rodionov, 2009, published in Genetika, 2009, Vol. 45, No. 11, pp. 1506–1515.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, E.S., Bolsheva, N.L., Samatadze, T.E. et al. The unique genome of two-chromosome grasses Zingeria and Colpodium, its origin, and evolution. Russ J Genet 45, 1329–1337 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795409110076
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795409110076