Abstract
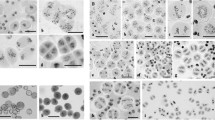
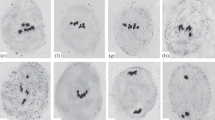
A formerly developed method of microspreading of mushroom basidial nuclei was applied to study meiotic prophase I in bisporic white button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) strains. Meiotic recombination and assemblage of axial structures (axial elements and synaptonemal complexes) of chromosomes in meiotic prophase I are interrelated. It is known that the frequency of meiotic recombination is reduced in the bisporic A. bisporus variety. We showed that formation of axial structures of meiotic chromosomes in bisporic strains of this mushroom was disrupted. The anomalous phenotypes in spread prophase nuclei are diverse. In leptotene and early zygotene, many nuclei contain abnormal, often short, and, as a rule, few chromosomal axial elements. The abnormalities in the formation of synaptonemal complexes at the zygotene-diplotene stage are of the same kind and even more pronounced. We discovered an important feature of meiosis in A. bisporus associated with fruit-body morphogenesis. Meiosis starting in basidia (meiocytes) of young closed fruit bodies is accompanied by disruption of chromatin condensation in prophase I and, probably, is arrested. After partial veil breakage, the course of meiosis normalizes. Preparations with clearly observable chromosomal axial structures can be obtained only at this stage of fruit-body development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogdanov, Yu.F., Variation and Evolution of Meiosis, Rus. J. Genet., 2003, vol. 39, no. 4, pp. 363–381.
Henderson, K.A. and Keeney, S., Tying Synaptonemal Complex Initiation to the Formation and Programmed Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2004, vol. 101, pp. 4519–4524.
Celerin, M., Merino, S.T., Stone, J.E., et al., Multiple Roles of Spo11 in Meiotic Chromosome Behavior, EMBO J., 2000, vol. 19, pp. 2739–2750.
Bhuiyan, H. and Schmekel, K., Meiotic Chromosome Synapsis in Yeast Can Occur without Spo11-Induced DNA Double-Strand Breaks, Genetics, 2004, vol. 168, pp. 775–783.
Haber, J.E., The Many Interfaces of Mre11, Cell (Cambridge, Mass.), 1998, vol. 95, pp. 583–586.
Gerecke, E.E. and Zolan, M.E., An mre11 Mutant of Coprinus cinereus Has Defects in Meiotic Chromosome Pairing, Condensation and Synapsis, Genetics, 2000, vol. 154, pp. 1125–1139.
Heyting, C., Synaptonemal Complexes: Structure and Function, Curr. Biol. Cell Biol., 1996, vol. 8, pp. 389–396.
Schwarzacher, T., Meiosis, Recombination and Chromosomes: A Review of Gene Isolation and Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization Data in Plants, J. Exp. Bot., 2003, vol. 54, pp. 11–23.
Grishchuk, A.L. and Kohli, J., Five RecA-Like Proteins of Schizosaccharomyces pombe Are Involved in Meiotic Recombination, Genetics, 2003, vol. 165, pp. 1031–1048.
Jiao, K., Salem, L., and Malone, R., Support for a Meiotic Recombination Initiation Complex: Interactions among Rec102p, Rec104p, and Spo11p, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2003, vol. 23, pp. 5928–5938.
Namekawa, S., Ichijima, Y., Hamada, F., et al., DNA Ligase IV from a Basidiomycete, Coprinus cinereus, and Its Expression during Meiosis, Microbiology, 2003, vol. 149, pp. 2119–2128.
Anuradna, S. and Muniyappa, K., Meiosis-Specific Yeast Hop1 Protein Promotes Synapsis of Double-Stranded DNA Helices Via the Formation of Guanine Quartets, Nucleic Acids Res., 2004, vol. 32, pp. 2378–2385.
Royse, D.J. and May, B., Use of Isozyme Variation to Identify Genotypic Classes of Agaricus brunnescens, Mycologia, 1982, vol. 74, pp. 93–102.
Castle, A.J., Horgen, P.A., and Anderson, J.B., Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms in the Mushrooms Agaricus brunnescens and Agaricus bitorquis, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1987, vol. 53, pp. 816–822.
Summerbell, R.C., Castle, A.J., Horgen, P.A., and Anderson, J.B., Inheritance of Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms in Agaricus brunnescens, Genetics, 1989, vol. 123, pp. 293–300.
Kerrigan, R.W., Royer, J.C., Baller, L.M., et al., Meiotic Behavior and Linkage Relationships in Secondary Homotallic Fungus Agaricus bisporus, Genetics, 1993, vol. 133, pp. 225–236.
D’yakov, Yu.T., Fungal Reproduction Systems and Their Evolution, Mikol. Fitopatol., 1999, vol. 33, pp. 137–149.
Evans, H.J., Nuclear Behavior in the Cultivated Mushroom, Chromosoma, 1959, vol. 10, pp. 115–135.
Raper, C.A., Raper, J.R., and Miller, R.E., Genetic Analysis of the Life-Cycle of Agaricus bisporus, Mycologia, 1972, vol. 64, pp. 1088–1117.
Elliott, T.J., Breedeng Strategies in Agaricus bisporus, Mush. Sci., 1979, vol. 10, pp. 73–81.
Callac, P., Billette, C., Imbernon, M., and Kerrigan, R., Morphological, Genetic and Interfertility Analyses Reveal a Novel, Tetrasporic Variety of Agaricus bisporus from the Sonoran Desert of California, Mycologia, 1993, vol. 89, no. 5, pp. 835–851.
Imbernon, M.P., Callac, P., Gasqui, P., et al., BSN, the Primary Determinant of Basidial Spore Number and Reproductive Mode in Agaricus bisporus, Maps to Chromosome I, Mycologia, 1996, vol. 88, pp. 749–761.
Callac, P., Desmerger, C., Kerrigan, R.W., and Imbernon, M., Conservation of Genetic Linkage with Map Expansion in Distantly Related Crosses of Agaricus bisporus, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 1997, vol. 146, pp. 235–240.
Mazheika, I.S. and Kolomiets, O.L., A Method for Preparation of Synaptonemal Complexes of Meiotic Chromosomes from Basidial Protplasts of the White Button Mushroom Agaricus bisporus (Lange) Imbach, Rus. J. Genet., 2003, vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 283–287.
Seitz, L.C., Tang, K., Cummings, W.J., and Zolan, M.E., The rad9 Gene of Coprinus cinereus Encodes a Proline-Rich Protein Required for Meiotic Chromosome Condensation and Synapsis, Genetics, 1996, vol. 142, pp. 1105–1117.
Kües, U., Life History and Developmental Processes in the Basidiomycete Coprinus cinereus, Microbiol. Mol. Biol., 2000, vol. 64, pp. 316–353.
Callac, P., Hocquart, S., Imbernon, M., et al., Bsn-t Alleles from French Field Strains of Agaricus bisporus, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1998, vol. 64, pp. 2105–2110.
Takami, K., Matsuda, S., Sono, A., and Sakaguchi, K., A Meiotic DNA Polymerase from a Mushroom Agaricus bisporus, Biochem. J., 1994, vol. 299, pp. 335–340.
Bostok, K. and Samner, E., Khromosoma eukarioticheskoi kletki (Chromosome of the Eukaryotic Cell), Moscow: Mir, 1981.
Royer, J.C., Hintz, W.E., Kerrigan, R.W., and Horgen, P.A., Electrophoretic Karyotype Analysis of the Button Mushroom, Agaricus bisporus, Genome, 1992, vol. 35, pp. 694–698.
Thielke, C., Meiotic Divisions in the Basidium, Basidium and Basidiocarp, Wells, K. and Wells, E.K., Eds., New York: Springer-Verlag, 1982, pp. 75–91.
Lu, B.C., Gallo, N., and Kües, U., White-Cap Mutants and Meiotic Apoptosis in the Basidiomycete Coprinus cinereus, Fungal Genet. Biol., 2003, vol. 39, pp. 82–93.
Fletcher, H.L., A Search for Synaptonemal Complexes in Ustilago maydis, J. Cell Sci., 1981, vol. 50, pp. 171–180.
Saksena, K.N., Marino, R., Haller, M.N., and Lemke, P.A., Study on Development of Agaricus bisporus by Fluorescent Microscopy and Scanning Electron Microscopy, J. Bacteriol., 1976, vol. 126, pp. 417–428.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.S. Mazheika, O.L. Kolomiets, Yu.T. Dyakov, Yu.F. Bogdanov, 2006, published in Genetika, 2006, Vol. 42, No. 3, pp. 361–368.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mazheika, I.S., Kolomiets, O.L., Dyakov, Y.T. et al. Abnormal meiosis in bisporic strains of white button mushroom Agaricus bisporus (Lange) imbach. Russ J Genet 42, 279–285 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795406030070
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795406030070