Abstract
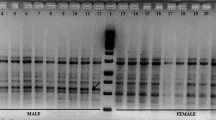
One hundred decamer primers of random-amplified polymorphic DNA were tested on dioecious Asparagus officinalis plants to identify sex-linked molecular markers. One primer (S368) produced two markers (S368-928 and S368-1178) in female plants. These two DNA markers were identified in 30 male and female plants, respectively, and a S368-928 marker was proved to be linked to the female sex locus. The female-linked S368-928 marker was sequenced and specific primers were synthesized to generate a 928 bp marker of sequence characterized amplified regions (SCAR) in female plants, SCAR928. SCAR928 could be used to correctly screen homozygous mm female plants of A. officinalis. However, results of Southern blot analysis suggest that the hybridization pattern of S368-928 was presented in both sex plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSA:
-
bulk segregant analysis
- MAS:
-
marker assisted selection
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- RAPD:
-
random-amplified polymorphic DNA
- SCAR:
-
sequence characterized amplified regions
- SSC:
-
sodium chloride-sodium citrate
References
Bennett, M.D. and Leitch, I.J., Plant DNA C-Values Database (release 2,0, January, 2003), 2003, http://www.rbgkew.org.uk/cval/homepage.html.
Flory, W.S., Genetic and Cytological Investigations on Asparagus officinalis L., Genet. Princeton, 1932, vol. 17, pp. 432–467.
Uno, Y., Li, Y., Kanechi, M., and Inagaki, N., Haploid Production from Polyembryonic Seeds of Asparagus officinalis L., Acta Hortic., 2002, vol. 589, pp. 2002–2007.
Löptien, H., Identification of the Sex Chromosome Pair in Asparagus (Asparagus officinalis L.), Z. Pflanzenzucht., 1979, vol. 82, pp. 162–173.
Paran, I. and Michelmore, R.W., Development of Reliable PCR Based Markers Linked to Downy Mildew Resistance Genes in Lettuce, Theor. Appl. Genet., 1993, vol. 85, pp. 985–993.
John, W. and Michael, M., Fingerprinting Genomes Using PCR with Arbitrary Primers, Nucleic Acids Res., 1990, vol. 18, pp. 7213–7218.
Williams, J.G., Kubelik, A.R., Livac, K.J., Rafalski, J.A., and Tingey, S.V., DNA Polymorphisms Amplified by Arbitrary Primers Are Useful as Genetic Markers, Nucleic Acids Res., 1990, vol. 18, pp. 6531–6535.
Lin, J.J. and Kuo, J., AFLP™: A Novel PCR-Based Assay for Plant and Bacterial DNA Fingerprinting, Focus, 1995, vol. 17, pp. 52–56.
Powell, W., Machray G.C., and Provan, J., Polymorphism Revealed by Simple Sequence Repeats, Trends Plant Sci., 1996, vol. 1, pp. 215–222.
Michelmore, R.W., Paran, I., and Kesseli, R.V., Identification of Markers Linked to Disease Resistance Genes by Bulk Segregant Analysis: A Rapid Method to Detect Markers in Specific Genomic Regions by Using Segregating Populations, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1991, vol. 88, pp. 9828–9832.
Zhang, Y.H., di Stilio, V., Rehman, F., Tucker, A., Mulcahy, D., and Kesseli, R., Y-Chromosome Specific Markers and the Evolution of Dioecy in the Genus Silene, Genome, 1998, vol. 41, pp. 141–147.
Mulcahy, D.L. and Weeden, N.F., DNA Probes for the Y-Chromosome of Silene latifolia, a Dioecious Angiosperm, Sex. Plant Reprod., 1992, pp. 86–88.
Yakubov, B., Barazani, O., and Golan-Goldhirsh, A., Combination of SCAR Primers and Touchdown-PCR for Sex Identification in Pistacia vera L., Sci. Hortic., 2005, vol. 103, pp. 473–478.
Ottĭ, T., Năndor, B., Erzsěbet, K., Hajnalka, H., Zsuzsanna, F.K., Ivăn, B., Istvăn, N., and Lăszlĭ, E.H., Novel Male-Specific Molecular Markers (MADC5, MADC6) in Hemp, Euphytica, 2002, vol. 127, pp. 209–218.
Polley, E., Seigner, E., and Ganal, M.W., Identification of Sex in Hop (Humulus lupulus) Using Molecular Markers, Genome, 1997, vol. 40, pp. 357–361.
Gill, G.P., Harvey, C.F., Gardner, R.C., and Fraser, L.G., Development of Sex-Linked PCR Markers for Gender Identification in Actinidia, Theor. Appl. Genet., 1998, vol. 97, pp. 439–445.
Ruas, F., Fairbanks, D.J., Evans, R.P., Stutz, H.C., Andersen, W.R., and Ruas, P.M., Male-Specific DNA in the Dioecious Species Atriplex garrettii (Chenopodiaceae), Am. J. Bot., 1998, vol. 85, pp. 162–167.
Urasaki, N., Tokumoto, M., Tarora, K., Ban, Y., Kayano, T., Tanaka, H., Oku, H., Chinen, I., and Terauchi, R., A Male and Hermaphrodite Specific RAPD Marker for Papaya (Carica papaya L.), Theor. Appl. Genet., 2002, vol. 104, pp. 281–285.
Gunter, L.E., Roberts, G.T., Lee, K., Larimer, F.W., and Tuskan, G.A., The Development of Two Flanking SCAR Markers Linked to a Sex Determination Locus in Salix viminalis L., J. Hered., 2003, vol. 94, pp. 185–189.
Helena, K., A Genetic Method to Resolve Gender Complements Investigations on Sex Ratios in Rumex acetosa, Mol. Ecol., 2002, vol. 11, pp. 2151–2156.
Khadka, D.K., Nejidat, A., Tal, M., and Golan-Goldhirsh, A., DNA Markers for Sex: Molecular Evidence for Gender Dimorphism in Dioecious Mercurialis annua L., Mol. Breed., 2002, vol. 9, pp. 251–257.
Xu Wen-Jie, Wang Bing-Wu, and Cui Ke-Ming, RAPD and SCAR Markers Linked to Sex Determination in Eucommia ulmoides Oliv, Euphytica, 2004, vol. 136, pp. 233–238.
Doyle, J.J. and Doyle, J.L., A Rapid Isolation Procedure for Small Quantities of Fresh Leaf Tissue, Phytochem. Bull., 1987, vol. 19, pp. 11–15.
Richard, C.M., Olga, K., Sabine, L.H., Jiri, S., Roman, H., Boris, V., and Sarah, R.G., Genetic and Functional Analysis of DD44, a Sex-Linked Gene from the Dioecious Plant Silene latifolia, Provides Clues to Early Events in Sex Chromosome Evolution, Genetics, 2003, vol. 163, pp. 321–334.
Maestri, E., Restivo, F.M., Marziani-Longo, G.P., Falavigna, A., and Tassi, F., Isozyme Gene Markers in the Dioecious Species Asparagus officinalis L., Theor. Appl. Genet., 1991, vol. 81, pp. 613–618.
Lorraine, A., Sheppard, A.M., Brunner, K.V., Krutovskii, W.H., Rottmann, J.S.S., Sheila, S.V., and Steven, H.S., A DEFICIENS Homolog from the Dioecious Tree Black Cottonwood Is Expressed in Female and Male Floral Meristems of the Two-Whorled, Unisexual Flowers, Plant Physiol., 2000, vol. 124, pp. 627–639.
Yamasaki, S., Fujii, N., and Takahashi, H., The Ethylene Regulated Expression of CS-ETR2 and CS-ERS Genes in Cucumber Plants and Their Possible Involvement with Sex Expression in Flowers, Plant Cell Physiol., 2000, vol. 41, pp. 608–616.
Chailakhyan, M.Kh. and Khryanin, V.N., The Role of Roots in Sex Expression in Hemp Plants, Planta, 1978, vol. 138, pp. 185–187.
Khryanin, V.N., Role of Phytohormones in Sex Differentiation in Plants, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2002, vol. 49, pp. 545–551.
Jiang, C. and Sink, K.C., RAPD and SCAR Markers Linked to the Sex Expression Locus M in Asparagus, Euphytica, 1997, vol. 94, pp. 329–333.
Reamon-Büttner, S.M., Schondelmaier, J., and Jung, C., AFLP Markers Tightly Linked to the Sex Locus in Asparagus officinalis L., Mol. Breed., 1998, vol. 4, pp. 91–98.
Reamon-Büttner, S.M. and Jung, C., AFLP-Derived STS Markers for the Identification of Sex in Asparagus officinalis L., Theor. Appl. Genet., 2000, vol. 100, pp. 432–438.
Grant, S., Houben, A., Viskot, B., Siroky, J., Pan, W., Macas, J., and Saedler, H., Genetics of Sex Determination in Flowering Plants, Dev. Gen., 1994, vol. 15, pp. 214–230.
Clark, M.S., Parker, J.S., and Ainsworth, C.A., Repeated DNA and Heterochromatin Structure in Rumex acetosa, Heredity, 1993, vol. 70, pp. 527–536.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This text was submitted by the authors in English.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, W.J., Li, R.L., Li, S.F. et al. Identification of two markers linked to the sex locus in dioecious Asparagus officinalis plants. Russ J Plant Physiol 54, 816–821 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443707060143
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443707060143