Abstract
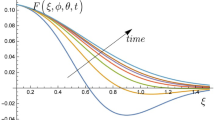
The evolution of the concentrations of particles of two types that annihilate at collision is considered. The kinetic model describing the dynamics of the mixture is represented by a system of two first-order nonlinear partial differential equations. It is shown that the solutions of this model are related to the solutions of the inhomogeneous transport equations by the Bäcklund transform. Analytic solutions of the problem about penetration of particles of the first type from the left half-plane into the right half-plane occupied by the particles of the second type (the two-dimensional penetration problem or molecular beam problem) and of the problem of outflow of the particles of the first type from a circular source into a domain occupied by the particles of the second type are obtained. Possible generalizations of the model are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Krapivsky, S. Redner, and E. Ben-Naim, Kinetic View of Statistical Physics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2010).
D. Avraham, M. Burschka, and C. Doering, “Statics and dynamics of a diffusion-limited reaction: Anomalous kinetics, noneqnilibrium self-ordering, and a dynamic transition,” J. Stat. Phys. 60, 695–728 (1990).
J. D. Murray, Lectures on Non-linear-Differential Equation Models in Biology (Clarendon, Oxford, 1977).
V. Aristov and O. Il’in, “A description of fast invasion processes based on the kinetic model,” Komp. Issled. Modelir. 6, 829–838 (2014).
V. Aristov and O. Ilyin, “Kinetic models for historical processes of fast invasion and aggression,” Phys. Rev. E 91, 042806 (2015).
J. Weiss, M. Tabor, and G. Carnevale, “The Painleve property for partial differential equations,” J. Math. Phys. 24, 522–526 (1983).
J. Weiss, “on classes of integrable systems and the Painleve property,” J. Math. Phys. 25, 13–24 (1984).
J. Weiss, “The Painleve Property for partial differential equations. II: Bäcklund transformation, Lax pairs, and the Schwarzian derivative,” J. Math. Phys. 24, 1405–1413 (1983).
V. Aristov and E. Shakhov, “Nonlinear scattering of a pulse molecular beam in a rarefied gas,” Zh. Vychisl. Mat. Mat. Fiz. 27, 1845–1852 (1987).
V. Vladimirov, Equations of Mathematical Physics (Nauka, Moscow, 1981) [in Russian].
A. Sveshnikov, A. Bogolyubov, and V. Kravtsov, Lectures on Mathematical Physics (Mosk. Gos. Univ. Moscow, 1993) [in Russian].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O.V. Ilyin, 2016, published in Zhurnal Vychislitel’noi Matematiki i Matematicheskoi Fiziki, 2016, Vol. 56, No. 12, pp. 2110–2114.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ilyin, O.V. Solutions of the generalized kinetic model of annihilation for a mixture of particles of two types. Comput. Math. and Math. Phys. 56, 2079–2083 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965542516120101
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965542516120101