Abstract
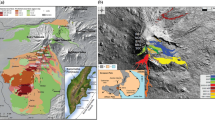
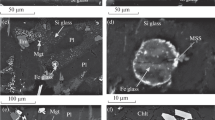
The results of a study of mineral-hosted melt inclusions were used to reconstruct the evolution of tholeiitic melts that produced the rocks of the shield edifice of Wangtian’e volcano, Northeast China, including the P–T parameters of their crystallization. Primary melt inclusions were studied in plagioclase of tholeiitic basalts. They contain “dry” Fe-rich silicate glass or a crystallized fine-grained mineral aggregate, feldspar rim, and globules of various compositions: water-bearing Fe-rich globules, water-bearing Si-rich globules and “dry” Si-rich globules. In the groundmass of tholeiitic basalts, “dry” Si-rich and Fe-rich glasses, as well as hydrated Fe-rich glass with an H2O content of up to 10–15 wt.% were identified. The fractional crystallization path of Wangtian’e tholeiitic melts was calculated by the COMAGMAT-5.2.2 software using glass compositions of homogenized melt inclusions in plagioclase from the basalts. It was shown that the calculated temperatures of the beginning of plagioclase crystallization are in good agreement with temperatures obtained in thermometric experiments with melt inclusions in plagioclase, and correspond to 1180–1200°C. Based on our studies, several stages of the melt differentiation during the formation of Wangtian’e volcanic rocks were identified. The first stage includes the Fenner-type crystal fractionation of the melt due to the appearance of plagioclase on the liquidus at the beginning of magma crystallization. The separation of the ferrobasaltic melt into Si-rich and Fe-rich silicate immiscible liquids (“dry” and hydrated) corresponds to the second stage of differentiation. The occurrence of silicate liquid immiscibility follows from the presence of Fe-rich and Si-rich glasses in the intergranular space of the basalts and in the melt inclusions in plagioclase of these rocks.










Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Andreeva, O.A., Yarmolyuk, V.V., Andreeva, I.A., et al., The composition and sources of magmas of Changbaishan Tianchi Volcano (China–North Korea), Dokl. Earth Sci., 2014, vol. 456, no. 1, pp. 572–578.
Andreeva, O.A., Andreeva, I.A., Yarmolyuk, V.V., et al., Evolution of melts of the Changbaishan Tianchi Volcano (China–North Korea) as a model of ore–magmatic system formation: data from melt inclusions studies, Dokl. Earth Sci., 2016, vol. 466, no. 1, pp. 82–87.
Andreeva, O.A., Yarmolyuk, V.V., Andreeva, I.A., and Borisovskiy, S.E., Magmatic evolution of Changbaishan Tianchi Volcano, China–North Korea: evidence from mineral-hosted melt and fluid inclusions, Petrology, 2018, vol. 26, no.5, pp. 535-566.
Ariskin, A.A., Bychkov, K.A., Nikolaev, G.S., and Barmina, G.S., The COMAGMAT-5: modeling the effect of Fe–Ni sulfide immiscibility in crystallizing magmas and cumulates, J. Petrol., 2018, vol. 59, no. 2, pp. 283–298.
Babansky, A.D., Ryabchikov, I.D., and Bogatikov, O.A., Evolyutsiya shchelochno-zemel’nykh magm (Evolution of Alkali-Earth Magmas), Moscow: Nauka, 1983.
Ballhaus, C., Fonseca, R.O.C., Munker, K., et al., Spheroidal textures in igneous rocks—textural consequences of H2O saturation in basaltic melts, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2015, vol. 167, pp. 241–252.
Le Bas, M.J., Le Maitre, R.W., Streckeisen, A., and Zanettin, B., A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali–silica diagram, J. Petrol., 1986, vol. 27, p. 745.
Brooks, C.K. and Nielsen, T.F.D., Early stages in the differentiation of the Skaergaard magma as revealed by a closely related suite of dike rocks, Lithos, 1978, vol. 11, pp. 1–14.
Carmichael, I.S.E., The petrology of Thingmuli, a Tertiary volcano in eastern Iceland, J. Petrol., 1964, vol. 5, pp. 435–460.
Chai, F., Yang, F., Liu, F., et al., The Aagong apatite-rich magnetite deposit in the Chinese Altay orogenic belt: a Kiruna-type iron deposit, Ore Geol. Rev., 2014, vol. 57, pp. 482–497.
Charlier, B., Namur, O., Toplis, M.J., et al., Large-scale silicate liquid immiscibility during differentiation of tholeiitic basalt to granite and the origin of the Daly gap, Geology, 2011, vol. 39, pp. 907–910.
Charlier, B. and Grove, T.L., Experiments on liquid immiscibility along tholeiitic liquid lines of descent, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 2012, vol. 164, pp. 27–44.
Dixon, S. and Rutherford, M.J., Plagiogranites as late-stage immiscible liquids in ophiolite and mid-ocean ridge suites: an experimental study, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1979, vol. 45, pp. 45–60.
Duchesne, J.C., Fe-Ti deposits in Rogaland anorthosites (South Norway): geochemical characteristics and problems of interpretation, Mineral. Deposita, 1999, vol. 34, pp. 182–198.
Eggler, D.H. and Osborn, E.F., Experimental studies of the system MgO–FeO–Fe2O3-NaAlSi3O8-CaAl2Si2O8–SiO2—a model for subalkaline magmas, Am. J. Sci., 1982, vol. 282, pp. 1012–1041.
Fan, Q.C., Liu, R.X., Zhang, G.H., et al., The genesis and evolution of bimodal volcanic rocks in Wangtian’e Colcano, Changbaishan (in Chinese), Acta Petrol. Sinica, 1998, vol. 14, pp. 305–317.
Fan, Q., Liu, R., Li, D., and Li, Q., Significance of K-Ar age of bimodal volcanic rocks at Wangtian’e Colcano, Changbaishan area, Chinese Sci. Bull., 1999, vol. 44, no. 7, pp. 660–663.
Fan, Q., Sui, J.L., Wang, T.H., et al., History of volcanic activity, magma evolution and eruptive mechanisms of the Changbai volcanic province, Geol. J. China Univ., 2007, no. 13, pp. 175–190.
Fischer, L.A., Wang, M., Charlier, B., et al., Immiscible iron-and silica-rich liquids in the upper zone of the Bushveld complex, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2016, vol. 443, pp. 108–117.
Ghiorso, M.S. and Carmichael, I.S.E., Modeling magmatic systems: petrologic applications, Rev. Mineral. Geochem., 1987, vol. 17, pp. 467–499.
Ghiorso, M.S. and Evans, B.W., Thermodynamics of rhombohedral oxide solid solutions and a revision of the Fe–Ti two-oxide geothermometer and oxygen-barometer, Amer. J. Sci., 2008, vol. 308, pp. 957–1039.
Higgins, M.D., A new model for the structure of the Sept Iles intrusive suite, Canada, Lithos, 2005, vol. 83, pp. 199–213.
Holness, M.B., Stripp, G., Humphreys, M.C.S., et al., Silicate liquid immiscibility within the crystal mush: late-stage magmatic microstructures in the Skaergaard intrusion, East Greenland, J. Petrol., 2011, vol. 52, pp. 175–222.
Hou, T. and Veksler, I.V., Experimental confirmation of high-temperature silicate liquid immiscibility in multicomponent ferrobasaltic systems, Am. Mineral., 2015, vol. 100, pp. 1304–1307.
Hou, T., Charlier, B., Holtz, F., et al., Immiscible hydrous Fe–Ca–P melt and the origin of iron oxide-apatite ore deposits, Nat. Commun., 2018, vol. 9, no. 1415, pp. 1–8.
Hunter, R.H. and Sparks, R.S.J., The differentiation of the Skaergaard intrusion, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1987, vol. 95, pp. 451–461.
Irvine, T.N. and Baragar, W.R.A., A guide to chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks, Can. J. Earth Sci., 1971, vol. 8, pp. 523–548.
Irvine, T.N., Andersen, J.C., and Brooks, C.K., Included blocks (and blocks within blocks) in the Skaergaard intrusion: geological relations and the origins of rhythmic modally graded layers, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 1998, vol. 110, pp. 1398–1447.
Jakobsen, J.K., Veksler, I.V., Tegner, C., and Brooks, C.K., Crystallization of the Skaergaard intrusion from an emulsion of immiscible iron- and silica-rich liquids: evidence from melt inclusions in plagioclase, J. Petrol., 2011, vol. 52, pp. 345–373.
Jiang, N. and Chu, X., A magnetite-apatite deposit in the Fanshan alkaline ultramafic complex, northern china, Econ. Geol., 2004, vol. 99, pp. 397–408.
Kadik, A.A., Maksimov, A.P., and Ivanov, B.V., Fiziko-khimicheskie usloviya kristallizatsii i genezis andezitov (Physicochemical Conditions of Crystallization and Genesis of Andesites), Moscow: Nauka, 1986.
Kadik, A.A., Lukanin, O.A., and Lapin, I.V., Fiziko-khimicheskie usloviya evolyutsii bazal’tovykh magm v pripoverkhnostnykh ochagakh (Physicochemical Conditions of Evolution of Basaltic Magmas in Subsurface Chambers), Moscow: Nauka, 1990.
Kamenetsky, V.S., Charlier, B., Zhitova, L., et al., Magma chamber-scale liquid immiscibility in the Siberian traps represented by melt pools in native iron, Geology, 2013, vol. 41, no. 10, pp. 1091–1094.
Kolker, A., Mineralogy and geochemistry of Fe–Ti oxide and apatite (nelsonite) deposits and evaluation of the liquid immiscibility hypothesis, Econ. Geol., 1982, vol. 77, pp. 1146–1158.
Kuno, H., Fractionation trends of basalt magmas in lava flows, J. Petrol., 1965, vol. 6, pp. 302–321.
Kupletskii, B.M., Palagonite basalts of Timan, Tr. Inst. Geol. Nauk AN SSSR, 1940, vol. 25, ser. 8, pp. 7–22.
Lapin, I.V., Lukanin, O.A., and Kadik, A.A., Influence of redox mode on crystallization and differentiation of Iceland basalts under subsurface conditions, Geokhimiya, 1985, no. 6, pp. 747–760.
Liu, J., Chen, Sh.-Sh., Guo, Zh., et al., Geological background and geodynamic mechanism of Mt. Changbai volcanoes on the China–Korea border, Lithos, 2015, vol. 236–237, pp. 46–73.
Lukanin, O.A., Reasons of bimodal distribution of volcanic series rocks, Geokhimiya, 1985, no. 3, pp. 348–359.
McBirney, A.R. and Nakamura, Y., Immiscibility in late-stage magmas of the Skaergaard intrusion, Carnegie Inst.Washington Yearbook, 1974, vol. 73, pp. 348–352.
McBirney, A.R. and Naslund, H.R., The differentiation of the Skaergaard intrusion. A discussion of Hunter and Sparks (Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., vol. 95, pp. 451–461), Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1990, vol. 104, pp. 235–240.
Morse, S.A., Kiglapait geochemistry IV: The major elements, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1981, vol. 45, pp. 461–479.
Mysen, B., Water-melt interaction in hydrous magmatic systems at high temperature and pressure, Progress in Earth Planet. Sci., 2014, vol. 1, p. 4.
Naslund, H.R., The effect of oxygen fugacity on liquid immiscibility in iron-bearing silicate melts, Am. J. Sci., 1983, vol. 283, pp. 1034–1059.
Naslund, H.R., Petrology of the upper border series of the Skaergaard intrusion, J. Petrol., 1984, vol. 25, pp. 185–212.
Osborn, E.F., Role of oxygen pressure in the crystallization and differentiation of basaltic magma, Am. J. Sci., 1959, vol. 257, pp. 609–647.
Peretyazhko, I.S. and Savina, E.A., Silicate–iron liquid immiscibility in rhyolitic magma, Dokl. Earth Sci., 2014, vol. 457, no. 2, pp. 1028–1033.
Philpotts, A.R., Textural evidence for liquid immiscibility in tholeiites, Mineral. Mag., 1978, vol. 42, pp. 113–127.
Philpotts, A.R., Liquid immiscibility in silicate melt inclusions in plagioclase phenocrysts, Soc. Fr. Mineral. Cristallogr. Bull., 1981, vol. 104, pp. 1–8.
Philpotts, A.R., Compositions of immiscible liquids in volcanic rocks, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1982, vol. 80, pp. 201–218.
Presnall, D.C., The join forsterite–diopside–iron oxide and its bearing on the crystallization of basaltic and ultramafic magmas, Am. J. Sci., 1966, vol. 264, pp. 753–809.
Roedder, E., Low-temperature liquid immiscibility in the system K2O–FeO–Al2O3–SiO2, Am. Mineral., 1951, vol. 36, pp. 282–286.
Roedder, E., Silicate liquid immiscibility in magmas and in the system K2O–FeO–Al2O3–SiO2: an example of serendipity, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1978, vol. 43, pp. 1597–1617.
Roedder, E. and Weiblen, P.W., Lunar petrology of silicate melt inclusions, Apollo 11 rocks, Apollo 11 Lunar Sci. Conf. Proc: Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1970, pp. 801–837.
Ryabov, V.V., Likvatsiya v prirodnykh steklakh na primere trappov (Liquid Immiscibility in Natural Glasses by the Example of Traps), Novosibirsk: Nauka SO, 1989.
Sakhno, V.G., Noveishii i sovremennyi vulkanizm yuga Dal’nego Vostoka (pozdnepleistotsen-golotsenovyi etap) (Youngest and Modern Volcanism of Southern Far East: Late Pleistocene–Holocene Stage), Vladivostok: Dal’nauka, 2008.
Sazonova, Z.A., Petrography of basalts of Cheshskya Bay, Tr. Petrograf. Inst. AN SSSR, 1938, vol. 12, pp. 107–154.
Sensarma, S. and Palme, H., Silicate liquid immiscibility in the ~2.5 Ga Fe-rich andesite at the top of the Dongargarh large igneous province (India), Lithos, 2013, vol. 170–171, pp. 239–251.
Sisson, T.W., Ratajeski, K., Hankins, W.B., and Glazner, A.F., Voluminous granitic magmas from common basaltic sources, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 2005, vol. 148, pp. 635–61.
Snyder, D., Carmichael, I.S.E., and Wiebe, R.A., Experimental study of liquid evolution in a fe-rich, layered mafic intrusion: constraints of the Fe–Ti oxide precipitation on the T–fO2 and t-P paths of tholeiitic magmas, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1993, vol. 113, pp. 73–86.
Sobolev, A.V., Melt inclusions in minerals as a source of principle petrological information, Petrology, 1996, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 209–220.
Toplis, M.J. and Carroll, M.R., An experimental study of the influence of oxygen fugacity on Fe–Ti oxide stability, phase relations, and mineral–melt equilibria in ferro-basaltic systems, J. Petrol., 1995, vol. 36, pp. 1137–1170.
Wager, L. and Brown, G., Layered Igneous Rocks, Edinburgh–London: Oliver and Boyd, 1968.
Veksler, I.V., Dorfman, A.M., Borisov, A.A., et al., Liquid immiscibility and the evolution of basaltic magma, J. Petrol., 2007, vol. 48, pp. 2187–2210.
Veksler, I.V., Dorfman, A.M., Borisov, A.A., et al., Liquid immiscibility and evolution of basaltic magma: reply to S.A. Morse, A.R. McBirney and A.R. Philpotts, J. Petrol., 2008, vol. 49, pp. 2177–2186.
Velasco, F., Tornos, F., and Hanchar, J.M., Immiscible iron- and silica-rich melts and magnetite geochemistry at the El Laco volcano (northern Chile): evidence for a magmatic origin for the magnetite deposits, Ore Geol. Rev., 2016, vol. 79, pp. 346–366.
Visser, W. and Koster van Groos, A.F., Liquid immiscibility in K2O–FeO–Al2O3–SiO2, Nature, 1976, pp. 426–427.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank Z.A. Kotelnikova and A.Yu. Bychkov for constructive criticism that led us to improve the manuscript.
Funding
This study was carried out at the Laboratory of Rare-Metal Magmatism of the Institute of Geology of Ore Deposits, Petrography, Mineralogy, and Geochemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences, under government-financed research program 0136-2018-0026 “Mantle–Crust Interaction in Areas of Anorogenic Magmatism and Its Role in Generating Rare-Metal Magmas: A Case Study of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt” (headed by Acad. V.V. Yarmolyuk). Microprobe and ion-probe studies of melt inclusions were supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project no. 20-05-00306, and Grant MK-2419.2019.5 from the President of the Russian Federation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by E. Kurdyukov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andreeva, O.A., Andreeva, I.A., Yarmolyuk, V.V. et al. Silicate Liquid Immiscibility as a Result of Fenner-Type Crystal Fractionation of Wangtian’e Tholeiitic Melts, Northeast China. Petrology 28, 357–373 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0869591120040025
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0869591120040025