Abstract
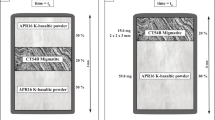
Alteration of mantle wedge rocks under the influence of fluids and melts is a poorly known subduction-zone process. It was experimentally modeled using various materials analogous to the crust (glaucophane schist and amphibolite) and mantle (olivine and olivine + orthopyroxene) under the P-T conditions (800°C and 29 kbar) corresponding to a hot subduction zone. Schist or amphibolite was loaded into the lower part of a capsule and underwent partial (10–90%) eclogitization during the experiment with the formation of omphacite, garnet, and quartz, sometimes coexisting with Ca-Na amphibole and orthopyroxene. The eclogitization was accompanied by the release of aqueous fluid, which dissolved minerals and products of partial melting of the schist. Ascending fluid flows transported major components into the overlying peridotite. This resulted in the formation of a garnet-phlogopite-orthopyroxene reaction zone at the base of the peridotite layer; this zone accumulated Si and K, which was practically absent in the starting materials. The gain of Si, Al, and CO2 and loss of Mg resulted in the growth of new minerals in the olivine material: garnet, orthopyroxene, and magnesite. Under natural conditions, such a change would have been described as dunite transformation to garnet-bearing harzburgite. The experiments showed that the mineral and chemical composition of the suprasubduction mantle strongly depends on the transfer of components from a downgoing lithospheric slab.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aranovich, L.Y. and Newton, R.C., H2O activity in concentrated NaCl solutions at high pressures and temperatures measured by the brucite-periclase equilibrium, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1996, vol. 125, pp. 200–212.
Bebout, G.E. and Barton, M.D., Tectonic and metasomatic mixing in a high-T, subduction zone mélange. Insights into the geochemical evolution of the slab-mantle interface, Chem. Geol., 2002, vol. 187, pp. 79–106.
Bell, D.R., Gregoire, M., Grove, T.L., et al., Silica and volatile-element metasomatism of Archean mantle: a xenolith-scale example from the Kaapvaal Craton, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 2005, vol. 150, pp. 251–267.
Bergman, S.C., Lamproites and other potassium-rich igneous rocks: a review of their occurrences, mineralogy and geochemistry, Alkaline Igneous Rocks, Fitton, J.G. and Upton, B.G.J., Eds., Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ., 1987, vol. 30. pp. 103–190.
Berman, R.G., Thermobarometry using multiequilibrium calculations: a new technique with petrologic applications, Can. Mineral., 1991, vol. 29, pp. 833–855.
Bodinier, J.-L. and Godard, M., Orogenic, ophiolitic, and abyssal peridotites, in Treatise on Geochemistry, R. W. Carlson, Ed., Oxford: Elsevier-Pergamon, 2003, vol. 2, pp. 103–170.
Brueckner, H. and Medaris, G., A general model for the intrusion and evolution of’ mantle’ garnet peridotites in high-pressure and ultra-high-pressure metamorphic terrains, J. Metamorph. Geol., 2000, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 123–133.
Cloos, M., Flow melanges: numerical modeling and geologic constraints on their origin in the Franciscan subduction complex, California, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 1982, vol. 93, pp. 330–345.
Comodi, P., Nazzareni, S., Fumagalli, P., and Capitani, G.C., The peculiar crystal-chemistry of phlogopite from metasomatized peridotites: evidence from laboratory and nature, Period. Mineral., 2011, vol. 80, pp. 181–197.
Connolly, J.A.D., Computation of phase equilibria by linear programming: a tool for geodynamic modeling and its application to subduction zone decarbonation, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2005, vol. 236, pp. 524–541.
Foley, S., Petrological characterization of the source components of potassic magmas, geochemical and experimental constraints, Lithos, vol. 28, pp. 187–204.
Ganne, J., De Andrade, V., Weinberg, R.F., et al., Modernstyle plate subduction preserved in the Palaeoproterozoic West African craton, Nature Geoscience, 2012, vol. 5, pp. 60–65.
Gerya, T.V., Stöckhert, B., and Perchuk, A.L., Exhumation of high-pressure metamorphic rocks in subduction channel: a numerical simulation, Tectonics, 2002, vol. 21, no. 6, art. no. 1056.
Girnis, A.V., Bulatov, V.K., Brey, G.P., and Höfer, H.E., Experiments on hydrous carbonated sediment interaction with peridotite under supersolidus conditions at 6–10 GPa, Eur. Mineral. Conference, 2012, vol. 1, EMC2012–730.
Gorman, P.J., Kerrick, D.M., and Connolly, J.A.D., Modeling open system metamorphic decarbonation of subducting slabs, Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems, 2006, vol. 7, Q04007.
Grove, T.L., Chatterjee, N., Parman, S.W., and Medard, E., The influence of H2O on mantle wedge melting, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2006, vol. 249, nos. 1–2, pp. 74–89.
Grove, T.L., Till, C.B., and Krawczynski, M.J., The role of H2O in subduction zone magmatism, Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci., 2012, vol. 40, pp. 413–39.
Hermann, J., Experimental constraints on phase relations in subducted continental crust, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 2002, vol. 143, no. 2, pp. 219–235.
Holland, T.J.B., The reaction albite = jadeite + quartz determined experimentally in the range 600–1200°C, Am. Mineral., 1980, vol. 65, pp. 129–134.
Ishimaru, S., Arai, S., Ishida, Y., Shirasaka, M., and Okrugin, V.M., Melting and multi-stage metasomatism in the mantle wedge beneath a frontal arc inferred from highly depleted peridotite xenoliths from the Avacha Volcano, Southern Kamchatka, J. Petrol., 2007, vol. 48, no. 2, pp. 395–433.
Kerrick, D.M. and Connolly, J.A.D., Metamorphic devolatilization of subducted oceanic metabasalts: implications for seismicity, arc magmatism and volatile recycling, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2001, vol. 189, pp. 19–29.
Leake, B.E., Arps, C.E.S., Birch, W.D., et al., Nomenclature of amphiboles: report of the subcommittee on amphiboles of the international mineralogical association, commission on new minerals and mineral names, Can. Mineral., 1997, vol. 35, pp. 219–246.
Mibe, K., Kawamoto, T., Matsukage, K.N., et al., Slab melting versus slab dehydration in subduction-zone magmatism, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 2011, vol. 108, no. 20, pp. 8177–8182.
Morimoto, N., Fabries, J., Ferguson, A.K., et al., Nomenclature of pyroxenes, Am. Mineral., 1988, vol. 73, pp. 1123–1133.
Mysen, B.O. and Boettcher, A.L., Melting of a hydrous mantle 1. Phase relations of natural peridotite at high-pressures and temperatures with controlled activities of water, carbon-dioxide, and hydrogen, J. Petrol., 1975, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 520–548.
Padrón-Navarta, J.A., Tommasi, A., Garrido, C., et al., Fluid transfer into the wedge controlled by high-pressure hydrofracturing in the cold top-slab mantle, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2010, vol. 297, nos. 1–2, pp. 271–286.
Peacock, S.M., Thermal and petrological structure of subduction zones (overview), in Subduction, Top to Bottom, Bebout, G. E. et al., Eds., Geophys. Monograph Series, 1996, vol. 96, pp. 119–134.
Perchuk, A.L. and Korepanova, O.S., The problem of CO2 recycling in subduction zones, Mosk. Univ. Geol. Bull., 2011, vol. 66, no. 4, pp. 250–260.
Perchuk, A. and Morgunova, A., Variable P-T paths and HP-UHP metamorphism in a Precambrian terrane, Gridino, Russia: petrological evidence and geodynamic implications, Gondwana Res., 2013, DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.09.009.
Perchuk, A.L. and Yapaskurt, V.O., Experimental simulation of orthopyroxene enrichment and carbonation in the suprasubduction mantle under the influence of H2O, CO2, and SiO2, Geochem. Int., 2013, vol. 51, no. 4, pp. 291–302.
Perchuk, A.L., Korepanova, O.S., and Yapaskurt, V.O., Fluid-magmatic interaction between glaucophane schist and olivine: experimental modeling under the conditions of a thermal gradient, Dokl. Earth Sci., 2011, vol. 437, no. 1, pp. 393–395.
Powell, R. and Holland, T.J.B., An internally consistent dataset with uncertainties and correlations: 3. Applications to geobarometry, worked examples and a computer program, J. Metamorph. Geol., 1988, vol. 6, pp. 173–204.
Rapp, R.P., Shimizu, N., and Norman, M.D., Reaction between slab-derived melts and peridotite in the mantle wedge: experimental constraints at 3.8 GPa, Chem. Geol., 1999, vol. 160, pp. 335–356.
Reverdatto, V.V., Selyatitskiy, A.Yu., and Carswell, D.A., Geochemical distinctions between “mantle” and “crustal” peridotites/pyroxenites in metamorphic complexes of high-superhigh pressures, Russ. Geol. Geophys., 2008, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 73–90.
Russell, J.K., Porritt, L.A., Lavalle, Y., and Dingwell, D.B., Kimberlite ascent by assimilation-fuelled buoyancy, Nature, 2012, vol. 481, pp. 352–356.
Scambelluri, M., Van Roermund, H.L.M., and Pettke, T., Mantle wedge peridotites: fossil reservoirs of deep subduction zone processes. Inferences from high and ultrahigh-pressure rocks from Bardane (Western Norway) and Ulten (Italian Alps), Lithos, 2010, vol. 120, pp. 186–201.
Schiano, P., Clocchiatti, R., Shimizu, N., et al., Hydrous, silica-rich melts in the sub-arc mantle and their relationship with erupted arc lavas, Nature, 1995, vol. 377, no. 6550, pp. 595–600.
Schmidt, M.W. and Poli, S., Experimentally based water budgets for dehydrating slabs and consequences for arc magma generation, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1998, vol. 163, pp. 361–379.
Spandler, C., Hermann, J., Faure, K., et al., The importance of talc and chlorite ‘hybrid’ rocks for volatile recycling through subduction zones; evidence from the high-pressure subduction mélange of New Caledonia, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 2008, vol. 155, pp. 181–198.
Syracuse, E.M, Van Keken, P.E, and Abers, G.A., The global range of subduction zone thermal models, Phys. Earth Planet. Int., 2010, vol. 183, no. 1, pp. 73–90.
Till, C.B., Grove, T.L., and Withers, A.C., The beginnings of hydrous mantle wedge melting, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 2012, vol. 163, pp. 669–688.
Van Roermund, H.L.M., Drury, M.R., Barnhoorn, A., and de Ronde, A.A., Super-silicic garnet microstructures from an orogenic garnet peridotite, evidence for an ultra-deep (>6 GPa) origin, J. Metamorph. Geol., 2002, vol. 18, pp. 135–147.
Vrijmoed, J.C., Podladchikov, Y.Y., Andersen, T.B., and Hartz, E.H., An alternative model for ultra-high pressure in the Svartberget Fe-Ti garnet-peridotite, Western Gneiss Region, Norway, Eur. J. Mineral., 2009, vol. 21, no. 6, pp. 1119–1133.
Winter, J.D., Principles of Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology, 2nd Ed. Pearson: Prentice Hall, 2010.
Wolf, M.B. and Wyllie, P.J., Dehydration-melting of amphibolite at 10 kbar: effects of temperature and time, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1994, vol. 115, pp. 369–383.
Zheng, Y.F., Xia, Q.X., Chen, R.X., and Gao, X.Y., Partial melting, fluid supercriticality and element mobility in ultra-high-pressure metamorphic rocks during continental collision, Earth Sci. Rev., 2011, vol. 107, pp. 342–374.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.L. Perchuk, M.Yu. Shur, V.O. Yapaskurt, S.T. Podgornova, 2013, published in Petrologiya, 2013, Vol. 21, No. 6, pp. 632–653.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perchuk, A.L., Shur, M.Y., Yapaskurt, V.O. et al. Experimental modeling of mantle metasomatism coupled with eclogitization of crustal material in a subduction zone. Petrology 21, 579–598 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0869591113060064
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0869591113060064