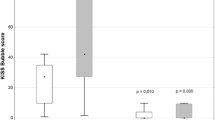
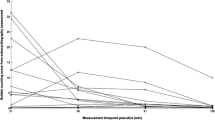
Abstract
The risks of decompression sickness and its complications in professional divers and amateur divers with various methods of diving in real and simulated conditions are considered. The pathogenesis of disorders of the plasma and vascular hemostasis system under the influence of environmental factors on the body during various types of dives is discussed. Generalization of the research results showed that the mechanisms of activation of thrombosis under this influence are complex and are caused by microbubble-mediated platelet activation as well as by development of endothelial dysfunction, oxidative, and psychophysiological stress. The study of hemostasis parameters in professional and amateur divers can be one of the main methods of assessing the risk of its development. The considered means of preventing thrombosis during diving and decompression, according to the results of the studies included in the review, are quite effective.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Levett, D.Z. and Millar, I.L., Bubble trouble: a review of diving physiology and disease, Postgrad. Med. J., 2008, vol. 84, no. 997, p. 571.
Spira, A., Diving and marine medicine review part II: diving diseases, J. Travel Med., 1999, vol. 6, no. 3, p. 180.
Beale, P., Kitchen, L., Graf, W.R., and Fenton, M.E., Abdominal decompression illness following repetitive diving: a case report and review of the literature, Undersea Hyperbaric Med., 2019, vol. 46, no. 2, p. 211.
Vann, R.D., Butler, F.K., Mitchell, S.J., and Mo-on, R.E., Decompression illness, Lancet, 2011, vol. 377, no. 9760, p. 153.
Pollock, N.W. and Buteau, D., Updates in decompression illness, Emerg. Med. Clin. North Am., 2017, vol. 35, no. 2, p. 301.
Kohshi, K., Denoble, P.J., Tamaki, H., et al., Decompression illness in repetitive breath-hold diving: why ischemic lesions involve the brain? Front. Physiol., 2021, vol. 12, p. 711850.
Kohshi, K., Tamaki, H., Lemaître, F., et al., Diving-related disorders in commercial breath-hold divers (Ama) of Japan, Diving Hyperbaric Med., 2021, vol. 51, no. 2, p. 199.
Vann, R.D., Denoble, P.J., Howle, L.E., et al., Resolution and severity in decompression illness, Aviat. Space Environ. Med., 2009, vol. 80, no. 5, p. 466.
Alcock, J. and Brainard, A.H., Gene-environment mismatch in decompression sickness and air embolism, Med. Hypotheses, 2010, vol. 75, no. 2, p. 199.
Beuster, W. and van Laak, U., Severe decompression sickness in divers, Wien. Med. Wochenschr., 1999, vol. 151, nos. 5−6, p. 111.
Eichhorn, L. and Leyk, D., Diving medicine in clinical practice, Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int., 2015, vol. 112, no. 9, p. 147.
Leffler, C.T., Effect of ambient temperature on the risk of decompression sickness in surface decompression divers, Aviat. Space Environ. Med., 2001, vol. 72, no. 5, p. 477.
Bosco, G., Yang, Z.J., Savini, F., et al., Environmental stress on diving-induced platelet activation, Undersea Hyperbaric Med., 2001, vol. 28, no. 4, p. 207.
Madden, L.A. and Laden, G., Gas bubbles may not be the underlying cause of decompression illness—the at-depth endothelial dysfunction hypothesis, Med. Hypotheses, 2009, vol. 72, no. 4, p. 389.
Lambrechts, K., Pontier, J.M., Balestra, C., et al., Effect of a single, open-sea, air scuba dive on human micro- and macrovascular function, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol., 2013, vol. 113, no. 10, p. 2637.
Toyota, S., Nagata, S., Yoshino, S., et al., Mesenteric venous thrombosis as a rare complication of decompression sickness, Surg. Case Rep., 2020, vol. 6, no. 1, p. 24.
Gertler, S.L., Stein, J., Simon, T., and Miyai, K., Mesenteric venous thrombosis as sole complication of decompression sickness, Dig. Dis. Sci., 1984, vol. 29, no. 1, p. 91.
Kassar, E.V., Bass, J.R., Douglas, E., and Speake, M.R., Portal and mesenteric vein thrombosis associated with decompression sickness in a 48-year-old deep sea self-contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA) diver, Am. J. Case Rep., 2022, vol. 23, p. e935473.
Boussuges, A., Succo, E., Juhan-Vague, I., and Sainty, J.M., Activation of coagulation in decompression illness, Aviat. Space Environ. Med., 1998, vol. 69, no. 2, p. 129.
Gempp, E., Morin, J., Louge, P., and Blatteau, J.E., Reliability of plasma D-dimers for predicting severe neurological decompression sickness in scuba divers, Aviat. Space Environ. Med., 2012, vol. 83, no. 8, p. 771.
Bolboli, L., Khodadadi, D., and Azimi, F., Can diving depth affect blood hemostasis system responses? Sport Physiol., 2019, vol. 11, no. 41, p. 123.
Pontier, J.M., Jimenez, C., and Blatteau, J.E., Blood platelet count and bubble formation after a dive to 30 msw for 30 min, Aviat. Space Environ. Med., 2008, vol. 79, no. 12, p. 1096.
Lambrechts, K., Balestra, C., Theron, M., et al., Venous gas emboli are involved in post-dive macro, but not microvascular dysfunction, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol., 2017, vol. 117, no. 2, p. 335.
Pontier, J.M., Gempp, E., and Ignatescu, M., Blood platelet-derived microparticles release and bubble formation after an open-sea air dive, Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab., 2012, vol. 37, no. 5, p. 888.
Moon, R.E., Hyperbaric oxygen treatment for decompression sickness, Undersea Hyperbaric Med., 2014, vol. 41, no. 2, p. 151.
Barratt, D.M., Harch, P.G., and Van Meter, K., Decompression illness in divers: a review of the literature, Neurologist, 2002, vol. 8, no. 3, p. 186.
Malmgren, R., Thorsen, T., Nordvik, A., and Holmsen, H., Microbubble-induced phospholipase C activation does not correlate with platelet aggregation, Thromb. Haemostasis, 1993, vol. 69, no. 4, p. 394.
Eckmann, D.M. and Armstead, S.C., Influence of endothelial glycocalyx degradation and surfactants on air embolism adhesion, Anesthesiology, 2006, vol. 105, no. 6, p. 1220.
Barak, O.F., Janjic, N., Drvis, I., et al., Vascular dysfunction following breath-hold diving, Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 2020, vol. 98, no. 2, p. 124.
Eichhorn, L., Dolscheid-Pommerich, R., Erdfel-der, F., et al., Sustained apnea induces endothelial activation, Clin. Cardiol., 2017, vol. 40, no. 9, p. 704.
Leite, A.R., Borges-Canha, M., Cardoso, R., et al., Novel biomarkers for evaluation of endothelial dysfunction, Angiology, 2020, vol. 71, no. 5, p. 397.
El-Gamal, H., Parray, A.S., Mir, F.A., et al., Circulating microparticles as biomarkers of stroke: a focus on the value of endothelial- and platelet-derived microparticles, J. Cell. Physiol., 2019, vol. 234, no. 10, p. 16739.
Culic, V.C., van Craenenbroeck, E., Muzinic, N.R., et al., Effects of scuba diving on vascular repair mechanisms, Undersea Hyperbaric Med., 2014, vol. 41, no. 2, p. 97.
Olszański, R., Sićko, Z., Baj, Z., et al., Effect of saturated air and nitrox diving on selected parameters of haemostasis, Bull. Inst. Marit. Trop. Med. Gdynia, 1997, vol. 48, nos. 1—4, p. 75.
Bao, X.-C., Shen, Q., Fang, Y.-Q., and Wu, J.-Q., Human physiological responses to a single deep helium-oxygen diving, Front. Physiol., 2021, vol. 12, p. 735986.
Durgin, B.G. and Straub, A.C., Redox control of vascular smooth muscle cell function and plasticity, Lab. Invest., 2018, vol. 98, no. 10, p. 1254.
Laurindo, F.R.M., Redox cellular signaling pathways in endothelial dysfunction and vascular disease, Endothelium and Cardiovascular Diseases, Da Luz, P.L., Libby, P., Chagas, A.C.P., and Laurindo, F.R.M. Eds., Cambridge, MA: Academic, 2018, chapter 10, p. 127.
Madamanchi, N.R., Vendrov, A., and Runge, M.S., Oxidative stress and vascular disease, Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 2005, vol. 25, no. 1, p. 29.
Cadroy, Y., Dupouy, D., Boneu, B., and Plaisancié, H., Polymorphonuclear leukocytes modulate tissue factor production by mononuclear cells: role of reactive oxygen species, J. Immunol., 2000, vol. 164, no. 7, p. 3822.
Görlach, A., Brandes, R.P., Bassus, S., et al., Oxidative stress and expression of p22phox are involved in the up-regulation of tissue factor in vascular smooth muscle cells in response to activated platelets, FASEB J., 2000, vol. 14, no. 11, p. 1518.
Herkert, O., Diebold, I., Brandes, R.P., et al., NADPH oxidase mediates tissue factor-dependent surface procoagulant activity by thrombin in human vascular smooth muscle cells, Circulation, 2002, vol. 105, no. 17, p. 2030.
Swiatkowska, M., Szemraj, J., Al-Nedawi, K.N., and Pawłowska, Z., Reactive oxygen species upregulate expression of PAI-1 in endothelial cells, Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett., 2002, vol. 7, no. 4, p. 1065.
Berenji Ardestani, S., Matchkov, V.V., Eftedal, I., and Pedersen, M.A., Single simulated heliox dive modifies endothelial function in the vascular wall of ApoE knockout male rats more than females, Front. Physiol., 2019, vol. 10, p. 1342.
Brubakk, A.O., Duplancic, D., Valic, Z., et al., A single air dive reduces arterial endothelial function in man, J. Physiol., 2005, vol. 566, part 3, p. 901.
Obad, A., Marinovic, J., Ljubkovic, M., et al., Successive deep dives impair endothelial function and enhance oxidative stress in man, Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging, 2010, vol. 30, no. 6, p. 432.
Roka-Moiia, Y., Ammann, K.R., Miller-Gutierrez, S., et al., Shear-mediated platelet activation in the free flow: II. Evolving mechanobiological mechanisms reveal an identifiable signature of activation and a bi-directional platelet dyscrasia with thrombotic and bleeding features, J. Biomech., 2021, vol. 123, p. 110415.
Casa, L.D.C. and Ku, D.N., Thrombus formation at high shear rates, Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng., 2017, vol. 19, p. 415.
Sandrini, L., Ieraci, A., Amadio, P., et al., Impact of acute and chronic stress on thrombosis in healthy individuals and cardiovascular disease patients, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2020, vol. 21, no. 21, p. 7818.
Thorsen, T., Lie, R.T., and Holmsen, H., Induction of platelet aggregation in vitro by microbubbles of nitrogen, Undersea Biomed. Res., 1989, vol. 16, no. 6, p. 453.
Pendergast, D.R., Moon, R.E., Krasney, J.J., et al., Human physiology in an aquatic environment, Compr. Physiol., 2015, vol. 5, no. 4, p. 1705.
Anegg, U., Dietmaier, G., Maier, A., et al., Stress-induced hormonal and mood responses in scuba divers: a field study, Life Sci., 2002, vol. 70, no. 23, p. 2721.
Zarezadeh, R. and Azarbayjani, M.A., The effect of air scuba dives up to a depth of 30 metres on serum cortisol in male divers, Diving Hyperbaric Med., 2014, vol. 44, no. 3, p. 158.
Olszański, R., Radziwon, P., Piszcz, J., et al., Activation of platelets and fibrinolysis induced by saturated air dives, Aviat. Space Environ. Med., 2010, vol. 81, no. 6, p. 585.
Domoto, H., Nakabayashi, K., Hashimoto, A., et al., Decrease in platelet count during saturation diving, Aviat. Space Environ. Med., 2001, vol. 72, no. 4, p. 380.
Lambrechts, K., Pontier, J.M., Mazur, A., et al., Effect of decompression-induced bubble formation on highly trained divers microvascular function, Physiol. Rep., 2013, vol. 1, no. 6, p. e00142.
Olszański, R., Radziwon, P., Baj, Z., et al., Changes in the extrinsic and intrinsic coagulation pathways in humans after decompression following saturation diving, Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis, 2001, vol. 12, no. 4, p. 269.
Radziwon, P., Olszański, R., Tomaszewski, R., et al., Decreased levels of PAI-1 and alpha 2-antiplasmin contribute to enhanced fibrinolytic activity in divers, Thromb. Res., 2007, vol. 121, no. 2, p. 235.
Baj, Z., Olszański, R., Majewska, E., and Konarski, M., The effect of air and nitrox divings on platelet activation tested by flow cytometry, Aviat. Space Environ. Med., 2000, vol. 71, no. 9, p. 925.
Olszański, R., Radziwon, P., Galar, M., et al., Diving up to 60 m depth followed by decompression has no effect on pro-enzyme and total thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor antigen concentration, Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis, 2003, vol. 14, no. 7, p. 659.
Olszański, R., Radziwon, P., Siermontowski, P., et al., Trimix instead of air, decreases the effect of short-term hyperbaric exposures on platelet and fibrinolysis activation, Adv. Med. Sci., 2010, vol. 55, no. 2, p. 313.
Bosco, G., Yang, Z.J., Di Tano, G., et al., Effect of in-water oxygen prebreathing at different depths on decompression-induced bubble formation and platelet activation, J. Appl. Physiol., 2010, vol. 108, no. 5, p. 1077.
Pontier, J.M. and Lambrechts, K., Effect of oxygen-breathing during a decompression-stop on bubble-induced platelet activation after an open-sea air dive: oxygen-stop decompression, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol., 2014, vol. 114, no. 6, p. 1175.
Madden, D., Thom, S.R., Milovanova, T.N., et al., Exercise before scuba diving ameliorates decompression-induced neutrophil activation, Med. Sci. Sports Exerc., 2014, vol. 46, no. 10, p. 1928.
Philp, R.B., Bennett, P.B., Andersen, J.C., et al., Effects of aspirin and dipyridamole on platelet function, hematology, and blood chemistry of saturation divers, Undersea Biomed. Res., 1979, vol. 6, no. 2, p. 127.
Philp, R.B., Freeman, D., Francey, I., and Bishop, B., Hematology and blood chemistry in saturation diving: I. Antiplatelet drugs, aspirin, and VK744, Undersea Biomed. Res., 1975, vol. 2, no. 4, p. 233.
Bakken, A.M., Farstad, M., and Holmsen, H., Fatty acids in human platelets and plasma: fish oils decrease sensitivity toward N2 microbubbles, J. Appl. Physiol., 1991, vol. 70 , no. 6, p. 2669.
Funding
The study was carried out within the Russian Academy of Sciences, Theme 65.1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
ETHICS APPROVAL AND CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
Not applicable.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuzichkin, D.S., Markin, A.A. & Zhuravleva, O.A. Risk of Thrombosis and Mechanisms of Activation of Hemostasis in Divers after Diving. Hum Physiol 49, 709–716 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119723700457
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119723700457