Abstract
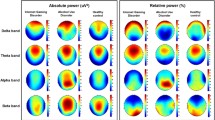
A study was conducted to identify EEG patterns in various forms of nonchemical addiction (gaming and Internet addictions). When the game dependence is observed, the EEG is shifted towards high-amplitude waves, which indicates activation of the diencephalic synchronizing structures of the brain and corresponds to a neurotic state of the anxiety type. In the case of Internet addiction, the prevalence of the spectral characteristics of the β rhythm was detected, indicating an increase in the influence of the stem desynchronizing brain formations and a neurotic state of the stressed type. A characteristic feature of the EEG in both gaming and Internet addictions is the predominance of the functional activity of the right hemisphere.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Dagher, A. and Robbins, T.W., Personality, addiction, dopamine: insights from Parkinson’s disease, Neuron, 2009, vol. 61, no. 4, p. 502.
O’Sullivan, S.S., Evans, A.H., and Lees, A.J., Dopamine dysregulation syndrome: an overview of its epidemiology, mechanisms and management, CNS Drugs, 2009, vol. 23, no. 2, p. 157.
Potenza, M.N., The neurobiology of pathological gambling and drug addiction: an overview and new findings, Philos. Trans. R. Soc., B, 2008, vol. 363, no. 1507, p. 3181.
Hou, H., Jia, S., Hu, S., et al., Reduced striatal dopamine transporters in people with internet addiction disorder, J. Biomed. Biotechnol., 2012, vol. 2012, no. 3, p. 854524.
Malygin, V.L. and Merkur’eva, Yu.A., The neuropsychological profile of adolescents with Internet-addicted behavior, Konsul’t. Psikhol. Psikhoter., 2015, no. 4, p. 130.
Smirnov, A.V., Psikhologiya addiktivnogo povedeniya (Psychology of Addictive Behavior), Yekaterinburg: Ural. Gos. Pedagog. Univ., 2014.
Balodis, I.M., Kober, H., Worhunsky, P.D., et al., Diminished frontostriatal activity during processing of monetary rewards and losses inpathological gambling, Biol. Psychiatry, 2012, vol. 71, no. 8, p. 749.
Yip, S.W., Lacadie, C.M., Xu, J., et al., Reduced genual corpus callosal white matter integrity in pathological gambling and itsrelationship to alcohol abuse or dependence, World J. Biol. Psychiatry, 2013, vol. 14, no. 2, p. 129.
Munno, D., Saroldi, M., Bechon, E., et al., Addictive behaviors and personality traits in adolescents, Spectrums, 2016, vol. 21, no. 2, p. 207.
Ben-Yehuda, L., Greenberg, L., and Weinstein, A., Internet addiction by using the smartphone-relationships between internet addiction, frequency of smartphone use and the state of mind of male and female students, J. Reward Defic. Syndr. Addict. Sci., 2016, vol. 2, no. 1, p. 22.
Nechaeva, S.A., The concept of non-chemical dependencies: sociological aspect of the problem, Materialy Mezhdunarodnoi nauchno-prakticheskoi konferentsii “Proryvnye nauchnye issledovaniya kak dvigatel’ nauki,” Sterlitamak, 29 noyabrya 2017 g. (Proc. Int. Sci.-Pract. Conf. “Advanced Scientific Studies as the Basis for Science,” Sterlitamak, November 29, 2017), Ufa: Agent. Mezhdunar. Issled., 2017, p. 38.
Akhmetova, E.A., Disharmonious family as a factor in the formation of addiction to new synthetic “designer” drugs, Med. Vestn. Bashkort., 2017, vol. 12, no. 1 (67), p. 15.
Perezhogin, L.O., Clinic of addiction to the Internet and mobile devices, Materialy Mezhdunarodnoi konferentsii “Tsifrovoe obshchestvo kak kul’turno-istoricheskii kontekst razvitiya cheloveka,” Kolomna, 11–13 fevralya 2016 g. (Proc. Int. Conf. “Digital Society as the Cultural-Historical Context of Human Development,” Kolomna, February 11–13, 2016), Ershova, R.V., Ed., Kolomna: Gos. Sots.-Gumanit. Univ., 2016, p. 329.
Chukhrova, M.G., Modern concepts on behavioral additions, Sib. Pedagog. Zh., 2014, no. 5, p. 105.
Mandel’, B.R., Psikhologiya zavisimostei (addiktologiya). Uchebnoe posobie (Psychology of Addictions (Addictology): Manual), Moscow: INFRA-M, 2015.
Dressvyannikov, V.L., Chukhrova, M.G., and Pronin, S.V., Internet–zavisimost’ (Internet Addition), Novosibirsk: Nemo-Press, 2015.
Khil’kevich, S.O., Nekhimicheskie zavisimosti: diagnostika, lechenie, profilaktika: uchebno-metodicheskoe posobie dlya studentov meditsinskikh vuzov (Diagnostics, Treatment, and Prevention of Non-Chemical Additions: Practical Manual for Students of Medical Higher Education Institutions), Gomel: Gomel’sk. Gos. Med. Univ., 2017.
Perezhogin, L.O., Comorbid mental disorders of children and adolescents in dependence formed from a personal computer, the Internet and mobile devices, Materialy XV Nauchno-prakticheskoi konferentsii s mezhdunarodnym uchastiem “Prikladnaya psikhologiya na sluzhbe razvivayushcheisya lichnosti,” Kolomna, 9–10 fevralya 2017 g. (Proc. XV Sci.-Pract. Conf. with Int. Participation “Role of Applied Psychology in Personality Development,” Kolomna, February 9–10, 2017), Ershova, R.V., Ed., Kolomna: Gos. Sots.-Gumanit. Univ., 2017, p. 183.
Krystal, H., Disorders of emotional development in addictive behavior, in The Psychology and Treatment of Addictive Behavior, New York: Int. Univ. Press, 1995, chap. 4, p. 65.
Drepa, M.I., Psychological portrait of the students with the Internet-addiction, Vestn. Tomsk. Gos. Pedagog. Univ., 2009, no. 4, p. 75.
Mel’nikov, M.E. and Shubin, O.S., Modern electroencephalographic studies of chemical additions, Usp. Fiziol. Nauk, 2013, vol. 44, no. 3, p. 16.
de Bruin, E.A., Bijl, S., Stam, C.J., et al., Abnormal EEG synchronization in heavily drinking students, Clin. Neurophysiol., 2004, vol. 115, no. 9, p. 2048.
Egorov, A.Yu., Non-chemical (behavioral) addictions, Addiktologiya, 2005, no. 1, p. 65.
Egorov, A.Yu., Non-chemical addictions: fake diagnoses or disorders? Nevrol. Vestn., 2019, vol. 51, no. 1, p. 38.
Zav’yalov, V.Yu., Skok, A.B., Shtark, M.B., and Shubina, O.S., Dynamics of psychophysiological aspects of addictive behavior during alpha-stimulating training, Byull. Sib. Otd., Ross. Akad. Med. Nauk, 1999, vol. 1, no. 1, p. 39.
Choi, J.-S., Shin, Y.-C., Jung, W.H., et al., Altered brain activity during reward anticipation in pathological gambling and obsessive-compulsive disorder, PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7, no. 9, p. e45938.
Lee, H.W., Choi, J., Shin, Y., Lee, J., et al., Impulsivity in internet addiction: a comparison with pathological gambling, Cyberpsychol., Behav. Soc. Networking, 2012, vol. 15, no. 7, p. 373.
Lee, J., Hwang, J.Y., Park, S.M., et al., Differential resting-state EEG patterns associated with comorbid depression in internet addiction, Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 2014, vol. 50, p. 21.
Wang, G.Y. and Bulanova, I.G., Electrophysiological activity is associated with vulnerability of Internet addiction in non-clinical population, Addict. Behav., 2018, vol. 84, p. 33.
Pavlov, Yu.G., The effective treatment of addiction by the EEG-biocontrol, Nats. Psikhol. Zh., 2013, no. 2 (10), p. 80.
Young, K.S., Internet addiction: the emergence of a new clinical disorder, CyberPsychol. Behav., 1998, vol. 1, no. 3, p. 237.
Bryun, E.A., Buzik, O.Zh., Koporov, S.G., et al., Profilaktika, lechenie i reabilitatsiya igrovoi zavisimosti: Metodicheskie rekomendatsii (Prevention, Treatment, and Rehabilitation of Gambling Addiction: Methodological Recommendations), Moscow: Media-Studiya, 2016.
Nerobkova, L.N., Avakyan, G.G., Voronina, T.A., and Avakyan, G.N., Klinicheskaya elektroentsefalografiya. Farmakoelektroentsefalografiya (Clinical Electroencephalography. Pharmacoelectroencephalography), Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2018.
Aleksandrov, M.V., Ivanov, L.B., Lytaev, S.A., et al., Elektroentsefalografiya (Electroencephalography), Aleksandrov, M.V., Ed., St. Petersburg: Strategii Budushchego, 2019, 2nd ed.
Zvezdochkina, N.V., Issledovanie elektricheskoi aktivnosti golovnogo mozga cheloveka (Analysis of Electric Activity of Human Brain), Kazan: Kazan. Gos. Univ., 2014.
Kuznetsova, T.G. and Gorbacheva, M.V., Frequency asymmetry of the main EEG rhythms in preschool children upon reaching the goal, Asimmetriya, 2013, vol. 7, no. 3, p. 11.
Zenkov, L.R., Klinicheskaya elektroentsefalograiya (s elementami epileptologii): rukovodstvo dlya vrachei (Clinical Electroencephalography (with Elements of Epileptology): Guide for Physicians), Moscow: MEDpress-Inform, 2017.
Fokina, Yu.O., Kulichenko, A.M., and Pavlenko, V.B., The role of the dopaminergic brain system in the effects of feedback sessions according to the electroencephalogram data, Byull. Sib. Med., 2010, no. 2, p. 140.
Kropotov, Ju.D., Quantitative EEG, Event-Related Potentials and Neurotherapy, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2012, 6th ed.
Belasheva, Kh.V., Internet addiction as a predictor of the personality disorders by various types of interhemispheric asymmetries, Znanie. Ponimanie. Umenie, 2015, no. 1, p. 224.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to Arsen Nabievich Dzhabrailov, the director of the PSI-FACTOR Psychological Center at the Dagestan State University, for the assistance in conducting the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare no apparent or potential conflicts of interest related to the publication of this article.
Statement of compliance with standards of research involving humans as subjects. All studies were conducted in accordance with the principles of biomedical ethics, formed in the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and its subsequent updates and approved by the local bioethical committee of the Dagestan State University (Makhachkala). Each study participant submitted voluntary written informed consent, signed by him after explaining to him the potential risks and benefits, as well as the nature of the forthcoming study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabadanova, A.I., Taygibova, Z.A. Characteristic EEG Patterns in Individuals with Nonchemical Addiction. Hum Physiol 46, 636–644 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119720050114
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119720050114