Abstract
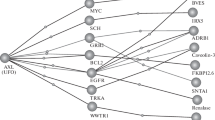
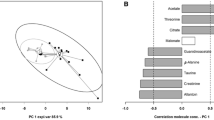
Mass spectrometry–based proteomics was employed to analyze urine from eight healthy volunteers during a 21-day bed rest (BR) study. The analysis included trypsinolysis in solution prior to liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), and spectrum processing using the bioinformatic tools. Relying on 221 IPI indices with scores from 24 to 1700, 169 different proteins were identified. Molecular functions, biological processes, and cell components as the loci of certain protein functioning were determined with the help of UniProt-GOA. Associative interactions networks were constructed using BiNGO. There were 14 proteins identified that were functional in the cardiovascular system mostly. They were annotated, and the dynamics of their occurrence throughout the experiment was considered. Grounding on the biological functions of these proteins and an assumption of eligible activation of different biological processes during BR was made.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
He, J.C., Chuang, P.Y., Ma’ayan, A., and Iyengar, R., Systems biology of kidney diseases, Kidney Int., 2012, vol. 81, no. 1, pp. 22–39.
Lathers, C.M. and Charles, J.B., Comparison of cardiovascular function during the early hours of bed rest and space flight, J. Clin. Pharmacol., 1994, vol. 34, no. 5, pp. 489–499.
Larina, I.M., Popova, I.A., Mikhailov, V.M., et al., The hormonal mechanisms supporting muscle work during prolonged head-down tile hypokinesia, Fiziol. Chelov., 1999, vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 117–124.
Lobachik, V.I., Abrosimov, V.V., Zhidkov, D.K., and Endeka, S.V., Hemodynamic effects of microgravity and their ground-based simulations, Acta Astronaut., 1991, vol. 23, pp. 35–40.
Larina, I.M., Sukhanov, Yu.V., and Lakota, N.G., Mechanisms of early reactions of a water and electrolytic human metabolism in various land models of microgravity effects, Aviakosm. Ekol. Med., 1999, vol. 33, no. 4, pp. 17–23.
Larina, O.N., The protein composition of human and animal blood plasma in space flight simulation and effects of weightlessness, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. (Biol.) Dissertation, Moscow, 1992.
Vorob’ev, D.V., Larina, I.M., and Goncharova, A.G., Reactions of the pituitary-adrenal system in men and women in conditions of prolonged antiorthostatic hypokinesia, XI Konferentsiya po kosmicheskoi biologii i aviakosmicheskoi meditsine, Moskva, 22–26 iyunya 2998 g., Tezisy dokladov (Proc. XI Conf. on Space Biology and Aerospace Medicine, Moscow, June 22–26, 1998, Abstracts of Papers), Moscow, 1998, vol. 1, p. 174.
Fliser, D., Wittke, S., and Mischak, H., Capillary electrophoresis coupled to mass spectrometry for clinical diagnostic purposes, Electrophoresis, 2005, vol. 26, no. 14, pp. 2708–2716.
Pastushkova, L.Kh., Kireev, K.S., Kononikhin, A.S., et al., Constant proteins of urine of the healthy person in experiment with 520-day isolation, Aviakosm. Ekol. Med., 2014, vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 48–54.
Penescu, M., Purcarea, V.L., Sisu, I., and Sisu, E., Mass spectrometry and renal calculi, J. Med. Life, 2010, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 128–136.
Rampoldi, L., Scolari, F., Amoroso, A., et al., The rediscovery of uromodulin (Tamm–Horsfall protein): from tubulointerstitial nephropathy to chronic kidney disease, Kidney Int., 2011, vol. 80, no. 4, pp. 338–347.
Patel, P.C., Ayers, C.R., Murphy, S.A., et al., Association of cystatin C with left ventricular structure and function: the Dallas Heart Study, Circ.: Heart Failure, 2009, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 98–104.
Makhneva, N.V. and Beletskaya, L.V., Cell expression of adhesion molecules of cadherin complex and their role in the diagnostics of autoimmune bullous dermatosis, Fundam. Issled., 2012, no. 1, pp. 59–63.
Severin, E.S., Biokhimiya: uchvnik dlya vuzov (Biochemistry: Manual for Higher Education Institutions), Severin, E.S., Ed., Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2013, 5th ed.
Hashemy, S.I., The human thioredoxin system: modifications and clinical applications, Iran J. Basic Med. Sci., 2011, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 191–204.
Miyamoto, S., Kawano, H., Sakamoto, T., et al., Increased plasma levels of thioredoxin in patients with coronary spastic angina, Antioxid. Redox Signal., 2004, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 75–80.
Landmesser, U. and Drexler, H., Endothelial function and hypertension, Cur. Opin. Cardiol., 2007, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 316–320.
Chen, H.L., Qu, L.N., Li, Q.D., et al., Simulated microgravity-induced oxidative stress in different areas of rat brain, Sheng Li Xue Bao, 2009, vol. 61, no. 2, pp. 108–114.
Baqai, F.P., Gridley, D.S., Slater, J.M., et al., Effects of spaceflight on innate immune function and antioxidant gene expression, J. Appl. Physiol., 2009, vol. 106, no. 6, pp. 1935–1342.
Markin, A.A. and Zhuravleva, O.A., Biochemical blood test. Postflight medicine and physiological researches, in Orbital’naya stantsiya “Mir” (Mir Orbital Station), Moscow: Inst. Med.-Biol. Probl., Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2001, vol. 1, pp. 606–612.
Zhuravleva, O.A., Morukov, B.V., Markin, A.A., Vostrikova, L.V., and Zabolotskaya, I.V., Lipid peroxidation rate and the antioxidant protection system during the readaptation period after long-term space flights on board the International Space Station, Hum. Physiol., 2011, vol. 37, no. 3, pp. 347–350.
Pastushkova, L.Kh., Valeeva, O.A., Kononikhin, A.S., et al., Changes in urine protein composition in human organism during long term space flights, Acta Astronaut., 2012, vol. 81, pp. 430–434.
Mikhailov, V.M., Hypokinesia as a risk factor in extreme conditions, Aviakosm. Ekol. Med., 2001, vol. 35, no. 2, pp. 26–31.
Grigor’ev, A.I. and Baevskii, R.M., Kontseptsiya zdorov’ya i kosmicheskaya meditsina (Concept of Health and Space Medicine), Moscow: Slovo, 2007.
Butler, G.C., Xing, H.C., Northey, D.R., and Hughson, R.L., Reduced orthostatic tolerance following 4 h head-down tilt, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol., 1991, vol. 62, no. 1, pp. 26–33.
Baevskii, R.M., Concept of physiological norms and criteria of health, Ross. Fiziol. Zh. im. I.M. Sechenova, 2003, no. 4, pp. 473–487.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © L.Kh. Pastushkova, M.-A. Custaud, A.S. Kononikhin, A.G. Brzhozovsky, L.E. Dmitrieva, I.V. Dobrokhotov, E.S. Tiis, I.M. Larina, 2015, published in Aviakosmicheskaya i Ekologicheskaya Meditsina, 2015, Vol. 49, No. 5, pp. 11–16.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pastushkova, L.K., Custaud, M.A., Kononikhin, A.S. et al. Modification of the Urine Proteome in Healthy Human during 21-day Bed Rest. Hum Physiol 43, 813–817 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119717070155
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119717070155