Abstract
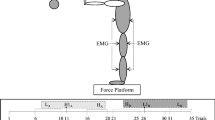
Balance function is dramatically deteriorated after exposure to microgravity. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the role and the contribution of different gravity sensory systems to the development of balance impairment after long-term spaceflights. Postural perturbations (pushes to the chest) of the threshold, medium, and sub-maximal intensities were produced in eight cosmonauts before, and on the day 3, 7, and 11 following spaceflight. Postural corrective responses were analyzed by anterior-posterior body sway fluctuation and electromyographic activity of leg muscles. The characteristics of the postural corrective responses changed significantly on the day 3 following spaceflight: the amplitude of posterior sway caused by perturbation of threshold intensity was increased reaching 135% of preflight value; the corrective responses lasted more than 6 s in 50% of all trials, while it did not last more than 4 s in 96% before spaceflight. The EMG responses were characterized by increased contribution of medium- and long-latency reactions. On the day 11 following spaceflight, most of the characteristics of postural corrective responses were close to preflight values. We assumed that the balance alterations after spaceflight are caused by changes in weightlessness of functions of two main gravity sensory systems, namely, weight-bearing and vestibular one. The deficit of weight-bearing afferentation triggers a decline of the extensors’ muscle tone, while changes of vestibular function cause a decline of accuracy of postural corrections.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kozlovskaya, I.B., Kreidich, Y.V., Oganov, V.S., et al., Pathophysiology of Motor Functions in Prolonged Manned Space Flights, Acta Astronaut., 1981, vol. 8, pp. 1059.
Kozlovskaya, I.B., Sayenko, I.V., Sayenko, D.G., et al., Role of Support Afferentation in Control of the Tonic Muscle Activity, Acta Astronaut., 2007, vol. 60, pp. 285.
Reschke, M.F., Bloomberg, J.J., Paloski, W.H., et al., Postural Reflexes, Balance Control, and Functional Mobility with Long-Duration Head-Down Bed Rest, Aviat. Space Environ. Med., 2009, vol. 80, pp. 45.
Jain, V., Wood, S.J., Feiveson, A.H., et al., Diagnostic Accuracy of Dynamic Posturography Testing after Short-Duration Spaceflight, Aviat. Space Environ. Med., 2010, vol. 81, pp. 625.
Kozlovskaya, I.B and Kirenskaya, A.V, Gravitational Mechanisms in Motor System. Studies in Real and Simulated Weightlessness, in New Concepts of Motor Control, Massion, J., Ed., Plenum Press, 1987.
Paloski, W.H., Oman, C.M., Bloomberg, J.J., et al., Risk of Sensorimotor Performance Failures Affecting Vehicle Control during Space Missions: A Review of the Evidence, J. Gravit. Physiology, 2008, vol. 15, p. 1.
Gurfinkel, V.S., Kots, Ya.M., and Shik, M.L., Regulyatsiya pozy cheloveka (Human Posture Regulation), Moscow: Nauka, 1965.
Gurfinkel, V.S, Levik, Y.S, Popov, K.E, et al., Body Scheme in the Control of Postural Activity, in Stance and Motion, Gurfinkel, V.S., Ioffe, M.E., Massion, J., and Roll, J.P., Eds., New York: Plenum Press, 1988, p. 185.
Nashner, L.M., Shupert, C.L., Horak, F.B., et al., Organization of Posture Controls: An Analysis of Sensory and Mechanical Constraints, Prog. Brain Res., 1989, vol. 80, p. 411.
Kozlovskaya, I.B., Barmin, V.A., Stepantsov, V.I., et al., Results of Studies of Motor Functions in Long-Term Space Flights, Physiologist, 1990, vol. 33, p. 1.
Fitts, R.H., Riley, D.R., and Widrick, J.J., Physiology of a Microgravity Environment Invited Review: Microgravity and Skeletal Muscle, J. Appl. Physiol., 2000, vol. 89, p. 823.
Belozerova, I.N., Nemirovskaya, T.L., Shenkman, B.S., et al., Structural and Metabolic Characteristics of Human Soleus Fibers after Long Duration Spaceflight, J. Gravit. Physiol., 2002, vol. 9, p. 125.
Tomilovskaya, E.S., Berger, M., Gerstenbrand, F., et al., Alterations of Characteristics of Horizontal Gaze Fixation Reaction in Long-Term Space Flights, J. Gravit. Physiol., 2007, vol. 14, p. 79.
Nashner, L.M. and Peters, J.F., Dynamic Posturography in the Diagnosis and Management of Dizziness and Balance Disorders, Neurol. Clin., 1990, vol. 8, p. 331.
Dietz, V., Human Neuronal Control of Automatic Functional Movements: Interaction Between Central Programs and Afferent Input, Physiol. Rev., 1992, vol. 72, p. 33.
Allum, J.H. and Shepard, N.T., An Overview of the Clinical Use of Dynamic Posturography in the Differential Diagnosis of Balance Disorders, J. Vestib. Res., 1999, vol. 9, p. 223.
Jacobs, J.V. and Horak, F.B., Cortical Control of Postural Responses, J. Neural Transm., 2007, vol. 114, p. 1339.
Gevlich, G.N., Grigor’eva, L.S., Boiko, M.I., and Kozlovskaya, I.B., Estimation of the Tone of Skeletal Muscles by the Method of Lateral Stiffness Registration, Kosm. Biol. Aviakosm. Med., 1983, vol. 5, p. 86.
Saenko, D.G., Saenko, I.V., Shestakov, M.P., Ivanov, A.M., and Kozlovskaya, I.B., The Effect of 120 Day Anti-Orthostatic Hypokinesia on the Status of the Posture Regulation Systems, Aviakosm. Ekol. Med., 2000, vol. 34, no. 5, p. 6.
Ogneva, I.V., Transversal Stiffness of Fibers and Desmin Content in Leg Muscles of Rats Under Gravitational Unloading of Various Durations, J. Appl. Physiol., 2010, vol. 109, p. 1702.
Casadio, M., Morasso, P.G., and Sanguineti, V., Direct Measurement of Ankle Stiffness during Quiet Standing: Implications for Control Modelling and Clinical Application, Gait Posture, 2005, vol. 21, p. 410.
Masani, K., Vette, A.H., Kawashima, N., et al., Neuromusculoskeletal Torque-Generation Process Has a Large Destabilizing Effect on the Control Mechanism of Quiet Standing, J. Neurophysiol., 2008, vol. 100, p. 1465.
Vette, A.H., Masani, K., Nakazawa, K., et al., Neural-Mechanical Feedback Control Scheme Generates Physiological Ankle Torque Fluctuation during Quiet Stance, IEEE Trans Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng., 2010, vol. 18, p. 86.
Dietz, V., Horstmann, G.A., Trippel, M., et al., Human Postural Reflexes and Gravity—an Under Water Simulation, Neurosci. Lett., 1989, vol. 106, p. 350.
Roll, R., Kavounoudias, A., and Roll, J.P., Cutaneous Afferents from Human Plantar Sole Contribute to Body Posture Awareness, Neuroreport, 2002, vol. 13, p. 1957.
Miller, T.F., Saenko, I.V., Popov, D.V., et al., Effect of Mechanical Stimulation of the Support Zones of Soles on the Muscle Stiffness in 7-Day Dry Immersion, J. Gravit. Physiol., 2004, vol. 11, p. 135.
Dietz, V. and Colombo, G., Effects of Body Immersion on Postural Adjustments to Voluntary Arm Movements in Humans: Role of Load Receptor Input, J. Physiol., 1996, vol. 497, no. 3, p. 849.
Kavounoudias, A., Roll, R., and Roll, J.P., Foot Sole and Ankle Muscle Inputs Contribute Jointly to Human Erect Posture Regulation, J. Physiol., 2001, vol. 532, p. 869.
Sayenko, D.G., Artamonov, A.A., Ivanov, O.G., et al., Effect of 6 Days of Support Withdrawal on Characteristics of Balance Function, J. Gravit. Physiol., 2005, vol. 12, p. 33.
van Deursen, R.W. and Simoneau, G.G., Foot and Ankle Sensory Neuropathy, Proprioception, and Postural Stability, J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther., 1999, no. 29, p. 718.
Meyer, P.F., Oddsson, L.I., and De Luca, C.J., The Role of Plantar Cutaneous Sensation in Unperturbed Stance, Exp. Brain Res., 2004, vol. 156, p. 505.
Maki, B.E., Perry, S.D., Norrie, R.G., et al., Effect of Facilitation of Sensation from Plantar Foot-Surface Boundaries on Postural Stabilization in Young and Older Adults, J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci., 1999, vol. 54, p. 281.
Meyer, P.F., Oddsson, L.I., and De Luca, C.J., Reduced Plantar Sensitivity Alters Postural Responses to Lateral Perturbations of Balance, Exp. Brain Res., 2004, vol. 157, p. 526.
Perry, S.D., McIlroy, W.E., and Maki, B.E., The Role of Plantar Cutaneous Mechanoreceptors in the Control of Compensatory Stepping Reactions Evoked by Unpredictable, Multi-Directional Perturbation, Brain Res., 2000, no. 877, p. 401.
Litvinova, K.S., Vikhlyantsev, I.M., Kozlovskaya, I.B., et al., Effects of Artificial Support Stimulation on Fiber and Molecular Characteristics of Soleus Muscle in Men Exposed to 7-Day Dry Immersion, J. Gravit. Physiol., 2004, vol. 11, p. 131.
Popov, D.V., Khusnutdinova, D.R., Shenkman, B.S., et al., Dynamics of Physical Performance During Long-Duration Space Flight (First Results of “Countermeasure” Experiment), J. Gravit. Physiol., 2004, vol. 11, p. 231.
Wolfson, L., Whipple, R., Judge, J., et al., Training Balance and Strength in the Elderly to Improve Function, J. Am. Geriatr. Soc., 1993, vol. 41, p. 341.
Melzer, I., Benjuya, N., Kaplanski, J., et al., Association between Ankle Muscle Strength and Limit of Stability in Older Adults, Age Ageing, 2009, vol. 38, p. 119.
Kozlovskaya, I.B., Countermeasures for Long-Term Space Flights, Lessons Learned from the Russian Space Program, J. Gravit. Physiol., 2002, vol. 9, p. 313.
Kozlovskaya, I.B. and Grigoriev, A.I., Russian System of Countermeasures on Board of the International Space Station (ISS): the First Results, Acta Astronaut., 2004, vol. 55, p. 233.
Kozlovskaya, I.B., Sayenko, I.V., Vinogradova, O.L., et al., New Approaches to Countermeasures of the Negative Effects of Microgravity in Long-Term Space Flights, Acta Astronaut., 2006, vol. 59, p. 13.
Paloski, W.H., Vestibulospinal Adaptation to Microgravity, Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg., 1998, no. 118, p. 39.
Kornilova, L.N., Vestibular Function and Sensory Interaction in Altered Gravity, Adv. Space Biol. Med., 1997, vol. 6, p. 275.
Reschke, M.F., Bloomberg, J.J., Harm, D.L., et al., Posture, Locomotion, Spatial Orientation, and Motion Sickness as a Function of Space Flight, Brain Res. Rev., 1998, vol. 28, p. 102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.G. Sayenko, A.A. Artamonov, I.B. Kozlovskaya, 2011, published in Fiziologiya Cheloveka, 2011, Vol. 37, No. 5, pp. 91–99.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sayenko, D.G., Artamonov, A.A. & Kozlovskaya, I.B. Characteristics of postural corrective responses before and after long-term spaceflights. Hum Physiol 37, 594–601 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119711050197
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119711050197