Abstract
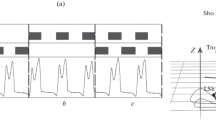
We examined the possibility of initiation of involuntary stepping movements by spinal electromagnetic stimulation (SEMS) during leg suspension. The subject’s legs were supported by a special apparatus in a gravity neutral position that to provide horizontal rotation in the hip, knee and ankle. SEMS (3 Hz and 1.56 Tesla) over the T11–T12 vertebrae induced involuntary locomotor_like movements in the legs. The latency period from the initiation of stimulation to the first EMG burst was 0.68 1.0 s. Increasing the frequency of SEMS from 3 Hz to 20 Hz resulted in shortening of the latency period. Thus, SEMS is able to initiate involuntary stepping in humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jankowska, E., Jukes, M.G., Lund, S., and Lundberg, A., The Effect of DOPA on the Spinal Cord, Acta Physiol. Scand., 1967, vol. 70, p. 399.
Vilensky, J.A., Moore, A.M., Eidelberg, E., and Walden, J.G., Recovery of Locomotion in Monkeys with Spinal Cord Lesions, J. Motor Behavior, 1992, vol. 24, p. 288.
Dimitrijevic, M., Gerasimenko, Yu., and Pinter, M. Evidence for a Spinal Central Pattern Generator in Humans, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 1998, vol. 860, p. 360.
Gerasimenko, Yu.P., Spinal Mechanisms of Regulation of Motor Activity in the Absence of Supraspinal Influences, Doctoral (Biol.) Dissertation, St. Petersburg: 2000.
Shapkova, E.Yu., Spinal Locomotor Capability Revealed by Electrical Stimulation of the Lumbar Enlargement in Paraplegic Patients, in Progress in Motor Control, Latash, M., Levin, M., Eds., Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics Publishers, 2004, p. 254.
Minassian, K., Persy, I., Rattay, F., Pinter, M.M., Kern, H., and Dimitrijevic, M.R., Human Lumbar Cord Circuitries Can Be Activated by Extrinsic Tonic Input to Generate Locomotor-Like Activity, Human Movement Sci., 2007, vol. 26, p. 275.
Dietz, V., and Harkema, S.J., Locomotor Activity in Spinal Cord-Injured Persons, J. Appl. Physiol., 2004, vol. 96, p. 1954.
Gurfinkel’, V.S., Levik, Yu.S., Kazennikov, O.V., and Selionov, V.A., Does the Prime Mover of Stepping Movements Exist in Humans?, Human Physiology, 1998, vol. 24, no. 3, p. 42.
Selionov, V.A., Ivanenko, Yu.P., Solopova, I.A., and Gurfinkel’, V.S., Tonic Central and Sensory Stimuli Facilitate Involuntary Air-Stepping in Humans, J. Neurophysiol., 2009, vol. 101, p. 2847.
Barker, A.T., Jalinous, R., and Freeston, I.L., Non-Invasive Magnetic Stimulation of Human Motor Cortex, Lancet, 1985, vol. 1, p. 1106.
Hallett M., Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: a Primer, Neuron, 2007, vol. 55, no. 2, p. 187.
Hallett M., Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and the Human Brain, Nature, 2000, vol. 406, p. 147.
Gerasimenko, Yu., Gorodnichev, R., Machueva, E., Pivovarova, E., Semenov, D., Savochin, A., Roy, R.R., and Edgerton, V.R., Novel and Direct Access to the Human Locomotor Spinal Circuitry, in Congress of the Neuroscience, Chicago, 2009.
Grillner, S., Wallen, P., Saitoh, K., Kozlov, A., and Robertson, B., Neural Bases of Goal-Directed Locomotion in Vertebrates-an Overview, Brain Res. Rev., 2008, vol. 57, no. 1, p. 2.
Gerasimenko, Yu.P., Roy, R.R., and Edgerton, V.R., Epidural Stimulation: Comparison of the Spinal Circuits That Generate and Control Locomotion in Rats, Cats and Humans, Exp. Neurology, 2008, vol. 209, p. 417.
Courtine, G., Harkema, S.J, Dy, C.J., Gerasimenko, Yu.P., and Dyhre-Poulsen, P., Modulation of Multisegmental Monosynaptic Responses in a Variety of Leg Muscles during Walking and Running in Humans, J. Physiology, 2007, vol. 585, p. 1125.
Ko, H.-Y., Park, J.H., Shin, Y.B., and Baek, S.Y., Gross Quantitative Measurements of Spinal Cord Segments in Human, Spinal Cord, 2004, vol. 42, p. 35.
Gerasimenko, Yu., Musienko, P., Bogacheva, I., Moshonkina, T,. Savochin, A., Lavrov, I., Roy, R.R., and Edgerton, V.R., Propriospinal Bypass of The Serotonergic System that Can Facilitate Stepping, J. Neurosci., 2009, vol. 29, p. 5681.
Iwahara, T., Atsuta, Y., Garcia-Rill, E., and Skinner, R.D., Spinal Cord Stimulation-Induced Locomotion In The Adult Cat, Brain Res. Bull., 1992, vol. 28, p. 99.
Lavrov, I.A., Dy, C.J., Fong, A.J., Gerasimenko, Yu., Courtine, G., Zhong, H., Roy, R.R., and Edgerton, V.R., Epidural Stimulation Induced Modulation of Spinal Locomotor Networks in Adult Spinal Rats, J. Neurosci., 2008, vol. 28, p. 6022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © R.M. Gorodnichev, E.N. Machueva, E.A. Pivovarova, D.V. Semenov, S.M. Ivanov, A.A. Savokhin, V.R. Edgerton, Yu.P. Gerasimenko, 2010, published in Fiziologiya Cheloveka, 2010, Vol. 36, No. 6, pp. 95–103.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gorodnichev, R.M., Machueva, E.N., Pivovarova, E.A. et al. A new method for the activation of the locomotor circuitry in humans. Hum Physiol 36, 700–707 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119710060113
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119710060113