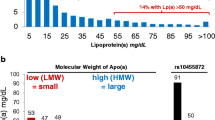
Abstract
An analysis of publications on the polymorphism of enzymes, receptors, and other systems of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism critical for the formation of vascular lipoprotein plaques and thrombi revealed the importance of certain genetic factors for the development of cardiovascular disorders. However, because of the polygenic nature of these disorders, the assessment of the corresponding hereditary risk factors requires multivariablecorrelation analysis. Population studies show that the polymorphism of individual genes manifests itself in the difference in incidence rates between ethnic groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalow, W., Goedde, H., and Agarwal, D., Eds., Ethnic Differences in Reactions to Drugs and Xenobiotics, Progr. Clin. Biol. Res., New York: Alan R. Liss, 1985, vol. 214.
Piruzyan, L.A., Pharmacological Metrology, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Biol., 1990, no. 2, p. 302.
Piruzyan, L.A., Sukhanov, V.A., and Saprin, A.N., Prognostic Risk Factor of the Development of Pathological Processes Based on Polymorphism of Xenobiotic Metabolism Metabolizing Xenobiotics, Fiziol. Chel., 2000, vol. 26, no. 2, p. 115 [Hum. Physiol. (Engl. Transl.), vol.26, no. 2, p. 224].
Licinio, J. and Wong, M., Eds., Pharmacogenomics: The Search for Individualized Therapies, Weinheim: Wiley, 2002.
Piruzyan, L.A., Sukhanov, V.A., Kalinina, E.V., and Saprin, A.N., Biomedical Aspects of Metabolic Portraiture, Dokl. Akad. Nauk, 2001, vol. 377, p. 129 [Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 377, p. 72].
Piruzyan, L.A., Sukhanov, V.A., Kalinina, E.V., et al., Enzyme System of Metabolism and Detoxication of Xenobiotics as a Basis for the Metabolic Portraying Used for Prognosis of Pathological Risks, Izv. Ross. Akad. Nauk, Ser. Biol., 2002, no. 2, p. 149.
Piruzyan, L.A. and Mikhailovskii, E.M., Metabolic “in-vivo Designing” of Tumors at the Level of an Organism and Population under Conditions of Individual Genetic Predisposition: Communication I, Fiziol. Chel., 2001, vol. 27, no. 3, p. 113 [Hum. Physiol. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 27, no. 3, p. 360].
Piruzyan, L.A. and Mikhailovskii, E.M., Metabolic Populational in-vivo Construction of Tumors under Conditions of Individual Genetic Predisposition: Communication II, Fiziol. Chel., 2002, vol. 28, no. 1, p. 101 [Hum. Physiol. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 28, no. 1, p. 88].
Piruzyan, L.A. and Mikhailovskii, E.M., Metabolic “in-vivo Designing” of Tumors at the Organism and Population Levels under Conditions of Individual Genetic Predisposition: Communication III, Fiziol. Chel., 2002, vol. 28, no. 5, p. 103 [Hum. Physiol. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 28, no. 5, p. 598].
Piruzyan, L.A. and Mikhailovskii, E.M., Metabolic “in-vivo Designing” of Tumors at the Organism and Population Level under Conditions of Individual Genetic Predisposition: Communication IV, Fiziol. Chel., 2003, vol. 29, no. 2, p. 118 [Hum. Physiol. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 29, no. 2, p. 238]
Budoff, M., Yang, T., Shavelle, R., et al., Ethnic Differences in Coronary Atherosclerosis, J. Am. College Cardiol., 2002, vol. 39, p. 408.
Woo, K., McCrohon, J., Chook, P., et al., Chinese Adult Are Less Susceptible Than Whites to Age-Related Endothelial Dysfunction, JACC, 1997, vol. 30, p. 113.
Doevendans, P., Jukema, W., Spiering, W., et al., Molecular Genetics and Gene Expression in Atherosclerosis, Int. J. Cardiol., 2001, vol. 80, p. 161.
Funke, H. and Assman, G., Strategies for the Assessment of Genetic Coronary Artery Disease Risk, Curr. Opin, Lipidol., 1999, vol. 10, p. 285.
Pedersen, T., Lipoprotein Changes and Reduction in the Incidence of Major Coronary Heart Disease Events in the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study, Circulation, 1998, vol. 97, p. 1453.
Maitland-van der Zee, A., Klungel, O., Strickler, B., et al., Genetic Polymorphisms: Importance for Response to HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors, Atherosclerosis, 2002, vol. 163, p. 213.
Marcil, M., Mutations in the ABC1 Gene in Familial HDL Deficiency with Defective Cholesterol Efflux, Lancet, 1999, vol. 354, p. 1341.
Hill, S. and McQueen, M., Reverse Cholesterol Transport, Clin. Biochem., 1997, vol. 30, p. 517.
Tall, A. and Wang, N., Tanger Disease as a Test of the Reverse Cholesterol Transport Hypotheses, J. Clin. Invest., 2000, vol. 106, p. 1205.
Jukema, J., The Asp9 Asn Mutation in the Lipoprotein Lipase Gene Is Associated with Increased Progression of Coronary Atherosclerosis, Circulation, 1996, vol. 94, p. 193.
Mailly, F., A Common Variant in the Gene for Lipoprotein Lipase Asp9-Asn: Functional Implications and Prevalence in Normal and Hyperlipidemic Subjects, Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 1995, vol. 15, p. 468.
Winkelmann, B., Hager, J., Kraus, W., et al., Genetics in Coronary Heart Disease: Current Knowledge and Research Principles, Am. Heart J., 2000, vol. 140,suppl., p. S11.
van den Ende, A., Lipoprotein (a), Adv. Clin. Chem., 1996, vol. 32, p. 73.
Pati, U. and Pati, N., Lipoprotein (a), Atherosclerosis, and Apolipoprotein (a) Gene Polymorphism, Mol. Genet. Metab., 2000, vol. 71, p. 87.
Kronenberg, F., Role of Lipoprotein (a) and Apolipoprotein (a) Phenotype in Atherogenesis, Circulation, 1999, vol. 100, p. 1154.
Talmud, P., Martin., S., Taskinen, M., et al., APOA5 Gene Variants, Lipoprotein Particle Distribution, and Progression of Coronary Heart Disease, J. Lipid Res., 2004, vol. 45, p. 750.
Dzau, V., Vascular Biology and Medicine in the 1990s: Scope, Concepts, Potentials, and Perspectives, Circulation, 1993, vol. 87, p. 705.
Kuivenhoven, J., The Role of a Common Variant of the Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein Gene in the Progression of Coronary Atherosclerosis, New Engl. J. Med., 1998, vol. 338, p. 86.
Owen J., Role of ABC1 Gene in Cholesterol Efflux and Atheroprotection, Lancet, 1999, vol. 354, p. 1402.
Evans, D. and Beil, F., The Association of the R219K Polymorphism in the ATP-binding Cassette Transporter 1 (ABCA1) Gene with Coronary Heart Disease and Hyperlipidemia, J. Mol. Med., 2003, vol. 81, p. 264.
Mertens, A., Verhamme, P., Bielicki, J., et al., Increased Low-Density Lipoprotein Oxidation and Impaired High-Density Lipoprotein Antioxidant Defense Are Associated with Increased Macrophage Homing and Atherosclerosis in Dyslipidemic Obese Mice, Circulation, 2003, vol. 107, p. 1640.
Doevendans, P. and van Bilsen, M., Transcription Factors and the Cardiac Gene Programme, Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol., 1996, vol. 28, p. 387.
Shiau, M., Wu, C., Huang, C., et al., TNF-α Polymorphisms and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Taiwanese Patients, Tissue Antigens, 2003, vol. 61, p. 393.
Tsuzura, S., Ikeda, Y., Suehiro, T., et al., Correlation of Plasma Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Levels to Vascular Complications and Human Serum Paraoxonase in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes, Metabolism, 2004, vol. 53, p. 297.
Yasushi, I., Hiroyuki, M., Hiroki, K., et al., Evidence for Association Between Paraoxonase Gene Polymorphisms and Atherosclerotic Diseases, Atherosclerosis, 2000, vol. 149, p. 435.
Zama, T., Murata, M., Matsubara, Y., et al., A 192Arg Variant of the Human Paraoxonase Gene Polymorphism Is Associated with an Increased Risk for Coronary Artery Disease in the Japanese, Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 1997, vol. 17, p. 3565.
Odawara, M., Tachi, Y., and Yamashita, K., Paraoxonase Polymorphism (Gln192Arg) Is Associated with Coronary Artery Disease in Japanese, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 1997, vol. 82, p. 2257.
Sanghera, D., Saha, N., Aston, C., and Kamboh, M., Genetic Polymorphism of Paraoxonase and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease, Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 1997, vol. 17, p. 1067.
Ruiz, J., Blanche, H., James, R., et al., Gln-Arg192 Polymorphism of Paraoxonase and Coronary Heart Disease in Type 2 Diabetes, Lancet, 1995, vol. 346, p. 869.
Serrato, M. and Marian, A., A Variant of Human Paraoxonase/Arylesterase Gene Is a Risk Factor for Coronary Artery Disease, J. Clin. Invest., 1995, vol. 96, p. 3005.
Suehiro, T., Nakauchi, Y., Yamamoto, M., et al., Paraoxonase Gene Polymorphism in Japanese Subjects with Coronary Heart Disease, Int. J. Cardiol., 1996, vol. 57, p. 69.
Herrman, S., Blanc, H., Poirier, O., et al., The Gln/Arg Polymorphism of Human Paraoxonase (Pon 192) Is Not Related to Myocardial Infarction, Atherosclerosis, 1996, vol. 126, p. 299.
Antikainen, M., Murtomaki, S., Syvanne, M., et al., The Gln-Arg191 Polymorphism of the Human Paraoxonase Gene Is Not Associated with the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Finns, J. Clin. Invest., 1996, vol. 98, p. 883.
Rice J., Ossei-Gerning, N., Stickland, M., and Grant, P., The Paraoxonase Gln-Arg192 Polymorphism in Subjects with Ischaemic Heart Disease, Coron. Artery Dis., 1997, vol. 8, p. 677.
Ombres, D., Pannitteri, G., Montali, A., et al., The Gln-Arg192 Polymorphism Is Not Associated with Coronary Artery Disease in Italian Patients, Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 1998, vol. 18, p. 1611.
Ko, J., Ko, J.L., Wang, S., et al., The Gln-Arg192 Polymorphism of the Human Paraoxonase Gene Is Not Associated with the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease among Chinese in Taiwan, Atherosclerosis, 1998, vol. 141, p. 259.
Czalai, C., Keszei, M., Duba, J., et al., Polymorphism in the Promoter Region of the Apolipoprotein A5 Gene Is Associated with an Increased Susceptibility for Coronary Artery Disease, Atherosclerosis, 2004, vol. 173, p. 109.
Lee, K., Ayyobi, A., Frohlich, J., and Hill, J., APOA5 Gene Polymorphism Modulates Levels of Triglyceride, HDL Cholesterol, and FERHDL but Is Not a Risk Factor for Coronary Artery Disease, Atherosclerosis, 2004, vol. 176, p. 165.
Shoulders, C., Jones, E., and Naoumova, R., Genetics of Familial Combined Hyperlipidemia and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2004, vol. 13, p. R149.
Sans, S., Kasteloot, H., Kromhout, D., The burden of Cardiovascular Diseases Mortality in Europe, Eur. Heart. J., 1997, vol. 18, p. 1231.
Baronil, M., Berni, A., Romeo, S., et al., Genetic Study of Common Variants at the ApoE, ApoA1, ApoC3, ApoB, LPL, and Hepatic Lipase, (LIPC) Genes and Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), BMC Med. Genet., 2003, vol. 4, p. 8.
Bertolini, S., Pisciotta, L., Di Scala, L., et al., Genetic Polymorphisms Affecting the Phenotypic Expression of Familial Hypercholesterolemia, Atherosclerosis, 2004, vol. 174, p. 57.
Izar, M., Fonseca, F., Ihara, S., et al., Risk Factors, Biochemical Markers, and Genetic Polymorphism in Early Coronary Artery Disease, Arq. Bras. Cadiol., 2003, vol. 80, p. 375.
Schmidt, H. and Kostner, M., Familial Hypercholesterolemia in Austria Reflects the Multi-ethnic Origin of Our Country, Atherosclerosis, 2000, vol. 148, p. 431.
Ferencak, G., Pasalic, D., Grskovic, B., et al., Lipoprotein Lipase Gene Polymorphisms in Croatian Patients with Coronary Artery Disease, Clin. Chem. Lab. Med., 2003, vol. 41, p. 541.
Machicao, F., Staiger, H., Fritsche, A., et al., Association of the −514C → T Polymorphism in the Hepatic Lipase Gene Promoter with Elevated Fasting Insulin Concentrations, but not Insulin Resistance, in Nondiabetic Germans, Horm. Metab. Res., 2004, vol. 36, p. 303.
Ashavaid, T., Shalia, K., Kondkar, A., et al., Gene Polymorphism and Coronary Risk Factors in Indian Population, Clin. Chem. Lab. Med., 2002, vol. 40, p. 975.
Puri, R., Tewari, S., Sinha, N., et al., Polymorphisms in the ApoB B-100 Gene: Association with Plasma Lipid Concentration and CAD, Indian Heart J., 2003, vol. 55, p. 60.
Misra, A., Luthra, K., and Vikram, N., Dyslipidemia in Asian Indians, J. Assoc. Physicians India, 2004, vol. 52, p. 137.
Hamdy, S., Hiratsuka, M., Narahara, K., et al., Allele and Genotype Frequencies of Polymorphic DCP1, CETP, ADRB2, and HTR2A in the Egyptian Population, Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 2002, vol. 58, p. 29.
Kuivenhoven., J., Wouter, J., Zwinderman, A., et al., The Role of a Common Variant of the Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein Gene in the Progression of Coronary Atherosclerosis, New Engl. J. Med., 1998, vol. 33, p. 86.
Corella, D., Saiz, C., and Guillen, M., Association of Taq1B Polymorphism in the Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein Gene with Plasma Lipid Levels in a Healthy Spanish Population, Atherosclerosis, 2000, vol. 152, p. 367.
Song, G., Han, G., Chae, J., et al., The Effects of the Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein Gene and Environmental Factors on the Plasma High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels in the Korean Population, Mol. Cells, 1997, vol. 7, p. 615.
Gudnason, V., Kakko, S., Nicaud, V., et al., CETP Gene Effect on CETP Activity and Plasma HDLP in European Populations, Eur. J. Clin. Invest., 1999, vol. 29, p. 116.
Garin, M., James, R., Dussoix, P., et al., Paraoxonase Polymorphism Met-Leu54 Is Associated with Modified Serum Concentrations of the Enzyme, J. Clin. Invest., 1997, vol. 99., p. 62.
Sandhera, D., Aston, C., Saha, N., and Kamboh, M., DNA Polymorphism in Two Paraoxonase Genes Are Associated with the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease, Am. J. Hum. Genet., 1998, vol. 62, p. 36.
Pickup, J., Mattock, M., Chusney, G., and Burt, D., NIDDM As a Disease of the Innate Immune System: Association of Acute Phase Reactants and Interleukin-6 with Metabolic Syndrome X, Diabetologia, 1997, vol. 40, p. 1286.
Pickup, J., Chusney, G., Thomas, S., and Burt, D., Plasma IL-6, α-TNF, and Blood Cytokine Production in Type 2 Diabetes, Life Sci., 2000, vol. 67, p. 291.
Hotamisligil, G., Arner, P., Caro, J., et al., Increased Adipose Tissue Expression of TNF-α in Human Obesity and Insulin Resistance, J. Clin. Invest., 1995, vol. 95, p. 2409.
Wilson, A., di Giovine, F., Blakemore, A., et al., Single Base Polymorphism in the TNF-α Gene, Hum. Mol. Genet., 1992, vol. 1, p. 353.
Wilson, A., Symons, J., McDowell, T., et al., Effects of a Polymorphism in the Human TNF-α Promoter on Transcriptional Activation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1997, vol. 94, p. 3195.
Kroeger, K., Steer, J., Joyce, D., and Abraham, L., Effect of Stimulus and Cell Type on the Expression of the 308-TNF Promoter Polymorphism, Cytokine, 2000, vol. 12, p. 110.
Louis, E., Franchimont, D., Piron, A., et al., TNF Gene Polymorphism Influences TNF-α Production in LPS-stimulated Whole Blood Cell Culture in Healthy Humans, Clin. Exp. Immunol., 1998, vol. 113, p. 401.
D’Alfonso, S. and Richiardi, P., A Polymorphic Variation in a Putative Regulation Box of the TNFA Promoter Region, Immunogentetics, 1994, vol. 39, p. 150.
Grove, J., Daly, A., Bassendine, B., and Day, C., Association of TNFA Promoter Polymorphism with Susceptibility to Alcoholic Stearohepatitis, Hepatology, 1997, vol. 26, p. 143.
Lee, S., Pu, Y., Thomas, G., et al., TNFA Gene G-308A Polymorphism in the Metabolic Syndrome, Metabolism, 2000, vol. 49, p. 1021.
Hoffstedt, J., Eriksson, P., Hellstrom, L., et al., Excessive Fat Accumulation Is Associated with the TNFA-308G/A Promoter Polymorphism in Women but not in Men, Diabetologia, 2000, vol. 43, p. 117.
Herrmann, S., Ricard, S., Nicaud V., et al., Polymorphism of the TNF-α Gene, Coronary Heart Disease, and Obesity, Eur. J. Clin. Invest., 1998, vol. 28, p. 59.
Brand, E., Schorr, U., Kunz I., et al., TNF-α-308G/A Polymorphism in Obese Caucasians, Int. J. Obese Relat. Metab. Disord., 2001, vol. 25, p. 581.
Dalziel, B., Gosby, A., Richman, R., et al., Association of the TNFA-308G/A Promoter Polymorphism with Insulin Resistance in Obesity, Obes. Res., 2002, vol. 10, p. 401.
Shue, W., Lee, W., Lin, L., et al., TNFA-238 and-308 Polymorphisms Do Not Associate with Insulin Resistance in Hypertensive Subjects, Metabolism, 2001, vol. 50, p. 1447.
Walston, J., Seibert, M., Yen, C., et al., TNFA-238 and 308 Polymorphisms Do Not Associate with Traits Related to Obesity and Insulin Resistance, Diabetes, 1999, vol. 48, p. 2096.
Koch, M., Rett, K., Volk, A., et al., TNFA-238G/A and-308G/A Promoter Polymorphisms Are Not Associated with Insulin Sensitivity and Insulin Secretion in Young Healthy Relatives of Type 2 Diabetic Patients, Diabetologia, 2000, vol. 43, p. 181.
Fernandes-Real, J., Guttierez, C., Richar, W., et al., The TNF-α Gene Nco1 Polymorphism Influences the Relationship among Insulin Resistance, Percent Body Fat, and Increased Serum Leptin Levels, Diabetes, 1997, vol. 46, p. 1468.
Grant, P., The Genetics of Atherothrombotic Disorders, J. Thromb. Haemost., 2003, vol. 1, p. 1381.
Chandler, A., Coronary Thrombosis in Myocardial Infarction, Am. J. Cardiol., 1974, vol. 34, p. 823.
Davis, M. and Thomas, A., Thrombosis and Acute Coronary Artery Lesions in Sudden Cardiac Ischemic Death, New. Engl. J. Med., 1984, vol. 310, p. 1137.
DeWood, M., Spores, J., Notske, M., et al., Prevalence of Total Coronary Occlusion during the Early Hours of Transmural Myocardial Infarction, New Engl. J. Med., 1980, vol. 303, p. 897.
Allen, J., Young, D., Blumenthal, R., et al., Prevalence of Hypercholesterolemia among Siblings of Persons with Premature Coronary Heart Disease, Arch. Intern. Med., 1996, vol. 156, p. 1654.
Newman, P., Derbes, R., and Aster, R., The Human Platelet Alloantigens, PLA1 and PLA2, Are Associated with a Leu33Pro Polymorphism in Membrane GP IIIA and Are Distinguishable by DNA Typing, J. Clin. Invest., 1989, vol. 83, p. 1778.
Nurden, A., Polymorphisms of Human Platelet Membrane Glycoproteins: Structure and Clinical Significance, Thromb. Haemost., 1995, vol. 74, p. 345.
Weiss, E., Goldschmidt-Clermont, P., Grigoryev, D., et al., A monoclonal antibody (SZ21) Specific for Platelet GPIIIa Distinguishes PLA1 from PLA2, Tissue Antigens, 1995, vol. 46, p. 374.
Weiss, E., Bray, P., Tayback, M., et al., A Polymorphism of a Platelet Glycoprotein Receptor As an Inherited Risk Factor for Coronary Thrombosis, New Engl. J. Med., 1996, vol. 334, p. 1090.
Goldschmidt-Clermont, P., Roos, C., and Cooke, G., Platelet PLA2 Polymorphism and Thromboembolic Events: From Inherited Risk to Pharmacogenetics, J. Thrombosis Thrombolysis, 1999, vol. 8, p. 89.
Grove, E., Orntoft, T., Lassen, J., et al., The Platelet Polymorphism PIA2 Is a Genetic Risk Factor for Myocardial Infarction, J. Intern. Med., 2004, vol. 255, p. 637.
Cooke, G., Bray, P., Hamlington, J., et al., PLA2 Polymorphism and Efficacy of Aspirin, Lancet, 1998, vol. 351, p. 1253.
Zotikov, E.A., Platelet Antigens and Antibodies Specific to Them, Byull. Eksp. Biol. Med., 2000, vol. 129, p. 244.
Jones, D., Bunce, M., Fuggle, S., et al., Human Platelet Alloantigens, Eur. J. Immunogenet., 2003, vol. 30, p. 415.
Kim, H., Jin, Y., Blakemore, K., et al., Gene Frequencies of the Major Human Platelet Antigens in African American, White, and Korean Populations, Tranfusion, 1995, vol. 10, p. 863.
Chiba, B., Kuwano, F., Carvalho, V., et al., Platelet Alloantigen Frequencies in Amazon Indians and Brazilian Blood Donors, Transfus. Med., 2000, vol. 10, p. 207.
Drzevek, D., Brojer, N., and Zupanska, L., The Frequency of Human Platelet Antigen (HPA) Genotypes in the Polish Population, Transfus. Med., 1998, vol. 8, p. 339.
Castro, V., Origa, A., Annichino, J., et al., Frequencies of Platelet-specific Alloantigen Systems 1–5 in Three Distinct Ethnic Groups in Brazil, Eur. J. Immunogenet., 1999, vol. 26, p. 355.
Covas, D., Delgado, M., Zeitune, M., et al., Gene Frequencies of the HPA-1 and HPA-2 Platelet Antigen Alleles among the Amerindians, Vox Sanguinis, 1997, vol. 73, p. 182.
Seo, P., Kim, F., and Ueno, H., Gene Frequencies of Eight Human Platelet-specific Antigens in Koreans, Transfus. Med., 1998, vol. 8, p. 129.
Halle, L., Bach, H., Martageix, C., et al., Eleven Human Platelet Systems Studied in the Vietnamese and Ma’ohis Polynesian Populations, Tissue Antigens, 2004, vol. 63, p. 34.
Bennett, J., Palmer, L., and Musk, A., Gene Frequencies of Human Platelet Antigens 1–5 in Indigenous Australians in Western Australia, Transfus. Med., 2002, vol. 12, p. 199.
Chen, F., Jian, Z., Xie, Q., et al., Polymorphism of Human Platelet Alloantigen in Chinese Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction and Acute Ischemic Stroke, Chin. Med. J., 2000, vol. 113, p. 702.
Zhang, K., Wang, Z., Wang, B., and Li, Y., Analysis of Human Platelet Antigen Genotypic Frequencies in Chinese Populations, Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi, 2001, vol. 9, p. 256.
Reiner, A. and Teramura, G., A Modified PCR-RFLP Genotyping Method Demonstrates the Presence of the HPA-4b Platelet Alloantigen in a North American Indian Population, Immunohematology, 1997, vol. 13, p. 37.
Shih, M., Liu, T., Lin, I., et al., Gene Frequencies of the HPA-1 to HPA-12, Oe and Gov Platelet Antigen Alleles in Taiwanese, Indonesian, Filipino, and Thai Populations, Int. J. Mol., Med., 2003, vol. 12, p. 609.
Lai, Y., Chen, F., Xie, Q., et al., Gene Frequency of HPA among Human Population of Han Nationality, Human Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao, 1997, vol. 22, p. 491.
Rozman, P., Drabbels, J., Schipper, R., et al., Genotyping for Human Platelet-specific Antigens HPA-1–5 in the Slovenian Population, Eur. J. Immunogenet., 1999, vol. 26, p. 265.
Mojaat, N., Halle, L., Proulle, V., et al., Gene Frequencies of Human Platelet Antigens in the Tunisian Population, Tissue Antigens, 1999, vol. 54, p. 201.
Ferrer, G., Muniz-Diaz, E., Alujia, M., et al., Analysis of Human Platelet Antigen Systems in a Moroccan Berber Population, Transfus. Med., 2002, vol. 12, p. 49.
Liu, T., Shih, M., Lin, C., et al., Gene Frequencies af the HPA-1 to HPA-8w Platelet Antigen Alleles in Taiwanese, Indonesian and Thai, Ann. Hematol., 2002, vol. 81, p. 244.
Lyou, J., Chen, Y, Hu, H., et al., PCR with Sequence-specific Primer-based Simultaneous Genotyping of Human Platelet Antigen-1 to-13w, Trasfusion, 2002, vol. 42, p. 1089.
Cozen, A., Moriwaki, H., Kremen, M., et al., Macrophage-targeted Overexpression of Urokinase Causes Accelerated Atherosclerosis, Coronary Artery Occlusions, and Premature Death, Circulation, 2004, vol. 109, p. 2129.
Festa, A., D’Agostino, R., Rich, S., et al., Promoter (4G/5G) Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Genotype and Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Levels in Blacks, Hispanics, and Non-Hispanic Whites, Circulation, 2003, vol. 107, p. 2422.
Tregouet, D., Barbaux, S., Poirier, O., et al., SELPLG Gene Polymorphisms in Relation to Plasma SELPLG Levels and CAD, Ann. Hum. Genet., 2003, vol. 67 (pt. 6), p. 504.
Ye, S., Eriksson, P., Hamsten, A., et al., Progression of Coronary Atherosclerosis Is Associated with a Common Genetic Variant of the Human Stromelysin-1 Promoter Which Results in Reduced Gene Expression, J. Biol. Chem., 1996, vol. 271, p. 13055.
Nikkari, S., O’Brien, K., Ferguson, M., et al., Intestinal Collagenase (MMP-1) Expression in Human Carotid Atherosclerosis, Circulation, 1995, vol. 92, p. 1393.
Galis, Z., Sukhova, G., Kranzhofer, R., et al., Macrophage Foam Cells from Experimental Atheroma Constitutively Produce Matrix-degrading Proteinases, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1995, vol. 92, p. 402.
Han, X., Fiehler, R., and Broze, G., Isolation of a Protein Z-dependent Plasma Protease Inhibitor, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1998, vol. 95, p. 9250.
Han, X., Huang, Z., Fiehler, R., and Broze, G., The Protein Z-dependent Protease Inhibitor Is a Serpin, Biochemistry, 1999, vol. 38, p. 11073.
Han, X., Fiehler, R., and Broze, G., Characterization of the Protein Z-dependent Protease Inhibitor, Blood, 2000, vol. 96, p. 3049.
Heeb, M., Paganini-Hill, A., Griffin, J., and Fisher, M., Low Protein Z Levels and Risk of Ischemic Stroke: Differences by Diabetic Status and Gender, Blood Cells. Mol. Diseases, 2002, vol. 29, p. 139.
Casas, J., Hingorani, A., Bautista, L., and Sharma, P., Meta-Analysis of Genetic Studies in Ischemic Stroke: Thirty-Two Genes Involving Approximately 18000 Cases and 58000 Controls, Arch. Neurol., 2004, vol. 61, p. 1652.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.A. Sukhanov, L.A. Piruzyan, 2006, published in Fiziologiya Cheloveka, 2006, Vol. 32, No. 3, pp. 98–110.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sukhanov, V.A., Piruzyan, L.A. Physiological and ethnogenetic risk factors for cardiovascular thrombosis. Hum Physiol 32, 334–345 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119706030145
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119706030145