Abstract
Data of hydrogeochemical studies of the Ivano-Arakhleiskie Lakes have been collected for different climatic phases of territory moistening. Three groups of water bodies are identified, including ultrafresh, fresh, and slightly saline. The lake waters are shown to differ by mineralization, chemistry, and pH. The least mineralized waters are found to be of HCO3-Ca type, which, at an increase in water salinity and pH, changes to HCO3-Mg and further to HCO3-Na, and finally, to SO4-Na. The changes are found to be larger in small slightly saline lakes and smaller in large ultrafresh lakes. The major processes that control the hydrogeochemical diversity of lakes are identified, including the interaction between water and aluminosilicate rock, sulfate reduction, oxidation of sulfides, and evaporation concentration.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Alekin, O.A., Osnovy gidrokhimii (Fundamentals of Hydrochemistry), Leningrad: Gidrometeoizdat, 1970.
Borzenko, S.V., Main features of water chemistry formation in the mineral lakes of Chitino-Ingodinskaya depression (Eastern Transbaikalia), Izv. Akad. Nauk, Ser. Geogr., 2014, no. 4, pp. 95–101.
Borzenko, S.V., Principal parameters controlling water composition in saline and brackish lakes in Eastern Transbaikalia, Geochem. Int., 2020, vol. 65, no. 12, pp. 1356–1373.
Borzenko, S.V. and Zamana, L.V., Reduced forms of sulfur in the brine of saline–soda Lake Doroninskoe, Eastern Transbaikal Region, Geochem. Int., 2011, vol. 49, no. 3, pp. 253–2261.
Gas’kova, O.L. and Sklyarova, O.A., Effect of natural organic acids on Mg/Ca ratio in bottom sediments of lakes with a high water TDS, Geol. Geofiz., 2013, vol. 54, no. 6, pp. 829–840.
Gas’kova, O.L., Strakhovenko, V.D., and Ovdina, E.A., The composition of brines and the mineral zonality of bottom sediments in soda lakes of Kulundinskaya Steppe (West Siberia), Geol. Geofiz., 2017, vol. 58, no. 10, pp. 1514–1527.
GN 2.1.5.1315-03 Predel’no dopustimye kontsentratsii (PDK) khimicheskikh veshchestv v vode vodnykh ob’’ektov khozyaistvenno-pit’evogo i kul’turno-bytovogo vodopol’zovaniya (Maximal Allowable Concentrations (MAC) of Chemicals in Water of Water Bodies Used for Domestic–Drinking Water Supply and Recreation), Moscow: Minzdrav Rossii, 2003. Amended July 3, 2017.
GN 2.1.5.2280-07 Predel’no dopustimye kontsentratsii (PDK) khimicheskikh veshchestv v vode vodnykh ob"ektov khozyaistvenno-pit’evogo i kul’turno-bytovogo vodopol’zovaniya (Maximal Allowable Concentrations (MAC) of Chemicals in Water of Water Bodies Used for Domestic–Drinking Water Supply and Recreation), Moscow: Federal’nyi tsentr gigieny i epidemiologii Rospotrebnadzora, 2008. Supplements and amendments no. 1 to GN 2.1.5.1315-03.
GOST (State Standard) 27384-2002: Water. Standards for Errors in Measurements of Composition Characteristics and Properties, Moscow: Standartinform, 2010, p. 6.
Dinu, M.I., Geochemical specifics of the distribution of elements between their forms in lakes in the European Part of Russia and Western Siberia, Geochem. Int., 2018, no. 10, pp. 1036–1045.
Zamana, L.V. and Borzenko, S.V., Hydrochemical regime of salt lakes of Southeastern Transbaikalia, Geogr. Prir. Res., 2010, no. 4, pp. 100–107.
Ivano-Arakhleiskii zakaznik: prirodno-resursnyi potentsial territorii (Ivano-Arakhleiskii Wildlife Reserve: The Natural-Resource Potential of the Territory), Gorlachev, V.P, Ed., Chita: Poisk, 2002.
Ivanov, M.V., Evolyutsiya global’nogo biogeokhimicheskogo tsikla (Evolution of Global Biogeochemical Cycle), Moscow: Nauka, 1989.
Ivanov, P.V., Classification of world lakes by their size and mean depth, Byul. LGU, 1948, no. 20, pp. 29–36.
Ivanova, M.E., Morkovkin, G.G., and Tailashev, D.A., Studying the processes of Ca2+ and Mg2+ export from top soil leached black-earth horizons in meadow steppe of Altai Krai under the effect of long-term use as cropland, Agroekologiya, 2007, no. 1, vol. 27, pp. 13–15.
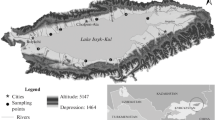
Itigilova, M.Ts., Pronin, N.M., Yurgenson, G.A., Ptitsyn, A.B., Kalugin, I.A., Dar’in, A.V., Reshetova, S.A., Obyazov, V.A., Pomazkova, N.V., Tsybekmitova, G.Ts., Mikheev, I.E., Faleichik, L.M., Zamana, L.V., Subbotina, V.N., Koryakina, E.A., Kuklin, A.P., Matafonov, P.V., Tashlykova, N.A., Bazarova, B.B., and Sokolov, A.V., Ivano-Arakhleiskie ozera na rubezhe vekov (sostoyanie i dinamika) (Ivano-Arakhleiskie Lakes at the Turn of Centuries: The State and Dynamics), Novosibirsk: Sib. Otd. Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2013.
Leonova, G.A., Bogush, A.A., Bobrov, V.A., Bychinskii, V.A., Trofimova, L.V., and Malikov, Yu.I., Ecological-geochemical estimation of salt lakes in Altai Krai, Geogr. Prir. Resur., 2007, no. 1, pp. 51–59.
Moiseenko, T.I., Dinu, M.I., Gashkina, N.A., and Kremleva, T.A., Occurrence forms of metals in natural waters depending on water chemistry, Water Resour., 2013, vol. 40, no. 4, pp. 407–416. https://doi.org/10.7868/S0321059613040093
Novikov, Yu.V., Lastochkina, K.O., and Boldina, Z.N., Metody issledovaniya kachestva vody vodoemov (Methods of Studying Water Quality in Water Bodies), Shitskova, A.P, Ed., Moscow: Meditsina, 1990.
Obyazov, V.A., Variations of air temperature and moistening in Transbaikalian territory and near-border China regions, Materialy konf. “Prirodookhrannoe sotrudnichestvo Chitinskoi oblasti (RF) i Avtonomnogo raiona Vnutrennyaya Mongoliya (Kitai) v transgranichnykh ekologicheskikh raionakh” (Proc. Conf. “Nature-Protection Cooperation of Chita Oblast (RF) and Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (China) in Transboundary Ecological Regions”), Chita, 2007, pp. 247–250.
Posokhov, E.V., Obshchaya gidrogeokhimiya (General Hydrogeochemistry), Leningrad: Nedra, 1975.
Ptitsyn, A.B., Chu, G., Dar’in, A.V., Zamana, L.V., Kalugin, I.A., and Reshetova, S.A., Sedimentation rate in Lake Arakhlei (Central Transbaikalia) by radiogeochemical and palynological data, Geol. Geofiz., 2014, vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 473–480.
P’yanov, A.I., Pavlov, D.S., Bragin, N.V., Strizhova, T.A., and Mikheev, I.E., Results of studies of the spatial distribution of fishes in lakes Arakhlei and Kenon (Chita oblast), Vopr. Ikhtiol., 1995, vol. 35, no. 5, pp. 678–686.
Sonnenfeld, P., Rassoly i evapority (Brines and Evaporites), Moscow: Mir, 1988.
Fedorov, I.A. and Taskina, L.V., Humic acids and their migration forms in lake water in Eastern Transbaikalia, Khim. Interesah Ustoich. Razvit., 2020, vol. 28, no. 5, pp. 515–526.
Tsybekmitova, G.Ts., Faleichik, L.M., and Mikheev,I.E., Anthropogenic load onto the drainage basin of the Ivano-Arakhleiskie Lakes (East Transbaikalia), Voda: Khim. Ekol., 2013, vol. 2, no. 56, pp. 3–11.
Shvartsev, S.L., Hydrochemistry of hypergene zone, Geokhimiya, 2000, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 260–276.
Shvartsev, S.L., Kolpakova, M.N., Isupov, V.P., Vladimirov, A.G., and Ariunbileg, S., Geochemistry and chemical evolution of saline lakes of Western Mongolia, Geochem. Int., 2014, no. 5, pp. 388–403. https://doi.org/10.7868/S0016752514030078
Bethke, C. and Yeakel, S., The Geochemist’s Workbench Release 11—GWB Essentials Guide, Champaign, IL: Aqueous Solutions LLC, 2016.
Borzenko, S.V., Kolpakova, M.N., Shvartsev, S.L., and Isupov, V.P., Biogeochemical conversion of sulfur species in saline lakes of steppe Altai, J. Oceanol. Limnol., 2018, vol. 36, no. 3, pp. 676–686.
Borzenko, S.V. and Shvartsev, S.L., Chemical composition of salt lakes in East Transbaikalia (Russia), Applied Geochem., 2019, vol. 103, pp. 72–84.
Eugster, H.P. and Hardie, L.A., Saline Lakes, Lakes: Chemistry, Geology, Physics, Lerman, A., Ed., N. Y.: Springer, 1978, pp. 237–293.
Fei Zhang, Zhangdong Jin, Jimin Yu., Yunkai Zhou, and Ling Zhou, Hydrogeochemical processes between surface and groundwaters on the northeastern Chinese Loess Plateau: Implications for water chemistry and environmental evolutions in semi-arid regions, J. Geochem. Explor., 2015, no. 159, pp. 115–128.
Gibbs, R.J., Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry, Science (Washington, D.C.), 1970, no. 170, pp. 1088–1090.
Moiseenko, T.I., Gashkina, N.A., Dinu, M.I., Kremleva, T.A., and Khoroshavin, V.Y., Aquatic geochemistry of small lakes: effects of environment changes, J. Geochem. Explor., 2013, no. 13, p. 1031.
Funding
The studies were carried out under Governmental Order (subject FUFR-2021-0006 “Geoecology of Aquatic Ecosystems under the Conditions of the Modern Climate and Technogenesis, the Major Approaches to the Rational Use of Water and Its Biological Resources”).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by G. Krichevets
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borzenko, S.V., Fedorov, I.A. & Komogortseva, I.A. Hydrochemistry of the Ivano-Arakhleiskie Lakes in Different Climate Phases. Water Resour 48, 576–587 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807821040035
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807821040035