Abstract
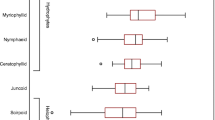
Long-term dynamics of water level in Lake Nero (1930–2011) has been analyzed. Pronounced trends, determined by the climate and anthropogenic components have been identified. Up to the 1970s, at a drop in lake water level, the ecosystem still showed the main features of a shallow water body overgrown with macrophytes. Water level rise caused a more intense development of phytoplankton, an increase in biogenic element concentrations, a decrease in water transparency and the contribution of cyanobacteria of S1 codon; pondweed disappeared almost completely. Step-by-step regression analysis of phytoplankton development indices and hydrological characteristics showed that water transparency in Lake Nero depends by 80% directly on water exchange and inversely on the concentration of chlorophyll a in seston. The main hypothesis of the study was confirmed: the key trigger in phytoplankton–macrophytes competition is water level rise.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andronikova, I.N., Strukturno-funktsional’naya organizatsiya zooplanktona ozernykh ekosistem (Structural and Functional Organization of Zooplankton in Lacustrine Ecosystems), St. Petersburg: Nauka, 1996.
Babanazarova, O.V., Phytoplankton structure and the dynamics of biogenic element concentrations in Lake Nero, Biol. Vnutr. Vod, 2003, no. 1, pp. 33–39.
Babanazarova, O.V., Karmaier, R., Sidelev, S.I., Aleksandrina, E.M., and Sakharova, E.G., Phytoplankton structure and microcystine concentration in the highly eutrophic Nero Lake, Water Resour., 2011, no. 2, pp. 229–237.
Babanazarova, O.V., Papchenkov, V.G., Sidelev, S.I., Litvinov, A.S., Zubishina, A.A., Ovseenko, A.S., Mart’yanov, O.V., Rakhmangulov, R.N., Rusinova, N.V., Zadvornova, L.V., and Vinogradova, T.G., Analysis of the state of Lake Nero ecosystem in long-term dynamics: water level–phytoplankton–macrophytes, in Formirovanie i realizatsiya ekologicheskoi politiki na regional’nom urovne (Formation and Implementation of Environmental Policy at Regional Level), Yaroslavl: Izd. Akademii Pastukhova, 2013, pp. 11–15.
Bikbulatov, E.S., Bikbulatova, E.M., Litvinov, A.S., and Poddubnyi, S.A., Gidrologiya i gidrokhimiya ozera Nero (Hydrology and Hydrochemistry of Lake Nero), Rybinsk: Rybinskii Dom Pechati, 2003.
Bolokhontsev, E.N., Phytoplankton of some lakes in Rostov sheading, Yaroslavl guberniya, and two lakes in Vladimir guberniya, Tr. Saratovskogo obshch. estestvoispytatelei i lyubitelei prirody, Saratov, 1903, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 253–269.
Bullion, V.V., Contribution of macrophytes and phytobenthos to the primary production of lake ecosystems, VIII S”ezd gidrobiologicheskogo obshchestva RAN (VIII Congress of Hydrobiological Society, Russian Academy of Sciences), Kaliningrad: Kalin. Gos. Tekh. Univ., 2001, vol. 1, pp. 158–159.
Bullion, V.V., Pervichnaya produktsiya planktona vnutrennikh vodoemov (Primary Production of Plankton in Inland Water Bodies), Leningrad: Nauka, 1983.
Gapeeva, M.V., Dovbnya, I.V., Zakonnov, V.V., and Shirokova, M.A., Empirical relationships between metal concentrations in plants and bottom sediments of the eutrophic Lake Nero, Ekologiya, 1995, no. 3, pp. 217–221.
Greze, B.S., Studies of Lake Nero in hydrobiological and fishery respects, Part 1. Hydrology, Sb. tr. Rostov. nauch. obshch. po izucheniyu mestnogo kraya (Trans. Rostov Scientific Community for Studying Local Territory), Rostov-Yaroslavskii: Rostovskii kraeved, 1929, no. 1, pp. 9–36.
Grigor’ev, S.V., O nekotorykh opredeleniyakh i pokazatelyakh v ozerovedenii, in Materialy po gidrologii Karelii (Materials on Karelian Hydrology), Petrozavodsk: Karel’skii fil. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1958, no. 18, pp. 29–45.
Damskaya, S.A., Overgrowths of Lake Nero and their fauna, Tr. Yaroslavskogo Estestvenno-Istorich. Obshch., 1921, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 90–103
Dovbnya, I.V., Production of hydrophilic plants of Lake Nero, in Biologiya vnutrennikh vod: informats. byul. (Inland Water Biology: Information Bulletin), Leningrad: Nauka, 1995, no. 98, pp. 13–16.
Il’inskii, A.L., Phytoplankton of lakes in Yaroslavl oblast, in Ozera Yaroslavskoi oblasti i perspektivy ikh khozyaistvennogo ispol’zovaniya (Lakes in Yaroslavl oblast and the perspectives of their economic development), Yaroslavl: Izd. Yar. Gos. Ped. Univ., 1970, pp. 273–303.
Lazareva, V.I. and Smirnova, S.M., Crustaceans and Rotifers, in Sostoyanie ekosistemy ozera Nero v nachale XXI veka (The State of Lake Nero Ecosystem in the Early XXI Century), Moscow: Nauka, 2008, p. 175–211.
Kitaev, S.P., Osnovy limnologii dlya gidrobiologov i ikhtiologov (Fundamentals of Limnology for Hydrobiologists and Ichthyologists), Petrozavodsk: Kar. Nauch. Tsentr Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2007.
Kulemin, A.A., Studying Lake Nero in hydrobiological and fishery respects, Part 3, Feeding and growth of bream, Sb. tr. Rostov. nauch. obshch. po izucheniyu mestnogo kraya (Trans. Rostov Scientific Community for Studying Local Territory), Rostov-Yaroslavskii: Rostovskii kraeved, 1930, no. 2, pp. 181–200.
Lakin, G.F., Biometriya (Biometry), Moscow: Vyssh. shk, 1990.
Lyashenko, O.A., Phytoplankton of Lake Nero, Sovremennoe sostoyanie ekosistemy ozera Nero (Current State of Lake Nero Ecosystem), Rybinsk: Inst. Biol. Vnutr. Vod Ross. Akad. Nauk, 1991, no. 65 (68), pp. 10–32.
Metodicheskie rekomendatsii po sboru i obrabotke materialov pri gidrobiologicheskikh issledovaniyakh na presnovodnykh vodoemakh. Zooplankton i ego produktsiya (Methodological Recommendations for the Collection and Processing of Data in Hydrobiological Studies in Freshwater Bodies. Zooplankton and Its Production), Leningrad: Gos. Nauch.-Issled. Inst. Ozer. Rech. Ryb. Khoz., Zool. Inst. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1984.
Mel’nikov, V., The Difficult Fate of Lake Nero: Polemical Remarks, Nash Sovremennik, 1979, no. 12, pp. 101–140.
Monakov, A.V. and Ekzertsev, V.A., Communities of riparian and aquatic plants in Lake Nero and their fauna, in Ozera Yaroslavskoi oblasti i perspektivy ikh khozyaistvennogo ispol’zovaniya (Lakes of Yaroslavl Oblast and the Perspectives of Their Economic Use), Yaroslavl: Izd. Yar. Gos. Ped. Univ., 1970, pp. 304–319.
Riv’er, I.K. and Stolbunova, V.N., Zooplankton of Lake Nero, Sovremennoe sostoyanie ekosistemy ozera Nero (Current State of Lake Nero Ecosystem), Rybinsk: Inst. Biol. Vnutr. Vod Ross. Akad. Nauk, 1991, no. 65 (68), pp. 74–108.
Sostoyanie ekosistemy ozera Nero v nachale XXI veka (The State of Lake Nero Ecosystem in the Early XXI Century), Moscow: Nauka, 2008.
Titov, A.A., Rostovskii uezd Yaroslavskoi gubernii. Istoriko-arkheologicheskoe i statisticheskoe opisanie s risunkami i kartoi uezda (Rostov Sheading of Yaroslavl Guberniya. Historic–Archeological and Statistical Description with Figures and a Map of the Sheading), Moscow, 1885.
Chizhikov, N.V., Geomorphology and soils in the basin of Lake Nero and the Ust’e-Kotorosl River, Tr. lab. sapropelevykh otlozhenii (Trans. Laboratory of Sapropel Deposits), 1956, no. 6, pp. 130–144.
Babanazarova, O.V. and Lyashenko, O.A., Inferring long-term changes in the physical-chemical environment of the shallow, enriched Lake Nero from statistical and functional analyses of its phytoplankton, J. Plankton Res., 2007, no. 9, p. 747–756.
Babanazarova, O.V., Sidelev, S.I., and Fastner, J., Northern expansion of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanoprokaryota) observed in shallow highly eutrophic Lake Nero (Russia), Int. J. Algae, 2015, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 131–141.
Babanazarova, O.V., Sidelev, S.I., and Shisheleva, S.V., The structure of winter phytoplankton in Lake Nero, Russia, a hypertrophic lake dominated by Planktothrixlike Cyanobacteria, Aquat. Biosyst., 2013, vol. 9, no. 18, pp. 1–11.
Bulgakov, N.G. and Levich, A.P., The nitrogen: phosphorus ratio as a factor regulating phytoplankton community structure, Arch. Hydrobiol., 1999, vol. 146, no. 1, pp. 3–22.
Reynolds, C.S., The Ecology of Freshwater Phytoplankton, Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press, 1984.
Reynolds, C.S., Huszar, V., Kruk, C., Naselli-Flores, L., and Melo, S., Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton, J. Plankton Res., 2002, vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 417–428.
Scheffer, M. and Carpenter, S.R., Catastrophic regime shifts in ecosystems: linking theory to observation, Trends Ecol. Evol., 2003, vol. 18, pp. 648–656.
Scheffer, M., Rinaldi, S., Gragnani, A., Mur, L.R., and Nes, E.H., On the dominance of filamentous cyanobacteria in shallow, turbid lakes, Ecology, 1997, vol. 78, no. 1, pp. 272–282.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O.V. Babanazarova, S.I. Sidelev, S.M. Zhdanova, A.S. Litvinov, A.S. Ovseenko, K.P. Korovkina, 2018, published in Vodnye Resursy, 2018, Vol. 45, No. 6, pp. 629–639.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babanazarova, O.V., Sidelev, S.I., Zhdanova, S.M. et al. Water Level in a Shallow Highly Eutrophic Lake: Development Factor by Macrophyte or Phytoplankton Type: Case Study of Lake Nero, Yaroslavl Oblast. Water Resour 45, 897–907 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807818060027
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807818060027