Abstract
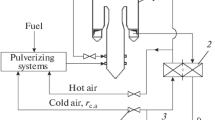
A new approach to thermal calculation of dust-preparation systems, at which the dust system is considered and calculated as part of the boiler plant operating in a single technological cycle with the boiler and having a common dust-gas-air duct with it. This approach provides for the possibility of conducting a joint thermal calculation of the boiler and dust systems. The thermal balance of the dust system is considered with determining the parameters of the drying agent according to the actual composition of the flue gas and air flows directed to the dust system, calculated from the general material balance of the gas-air duct of the boiler plant with the boiler, and the calculation of the enthalpy of gases and air in accordance with the standards of thermal calculation of boilers for the full elemental composition of burned fuels and their mixtures. Basic formulas for calculating the components of the heat balance of a dust system and methods for determining the output parameters of the drying agent are given. The proposed method of thermal calculation makes it possible to take into account the actual heat supplied with the drying agent when burning not only one type of fuel but also a mixture of solid fuels as well as solid fuels together with gaseous and/or liquid fuels. According to the developed algorithm for thermal calculation, along with the thermal calculation of the dust system, the general material balances of the gas-air path of the boiler plant and the dust-gas-air path of the boiler furnace and burner are compiled, the parameters of the drying agent along its path are calculated, taking into account the actual places of entry of the flows of the recirculating drying agent, air suction, and air to the seal of the mills. The algorithm for thermal calculation of dust systems is implemented in a computer program that has been tested in the calculations of several boiler installations, including thermal calculations joint with the boiler.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Calculation and Design of Dust Preparation Units for Boiler Aggregates (Regulatory Materials) (Tsentr. Kotlo-Turbinnyi Inst., Leningrad, 1971) [in Russian].
Thermal Calculation of Boilers (Standard Method) (Tsentr. Kotlo-Turbinnyi Inst., St. Petersburg, 1998) [in Russian].
V. A. Volkovinskii, K. F. Roddatis, and E. N. Tolchinskii, Dust Preparation Systems with Fan Mills (Energoatomizdat, Moscow, 1990) [in Russian].
A. A. Aleksandrov and B. A. Grigor’ev, Tables of Thermophysical Properties of Water and Water Vapor: A Reference Book (Mosk. Energ. Inst., Moscow, 1999) [in Russian].
V. M. Supranov, M. A. Izyumov, E. N. Vakhrameev, and A. D. Smirnov, “Using the modern software in calculation of boiler units,” in Proc. 3rd Int. Conf. on Information Technologies in Engineering Education (INFORINO-2016), Moscow, Apr. 12–13, 2016 (Mosk. Energ. Inst., Moscow, 2016), pp. 443–446.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maidanik, M.N., Tugov, A.N. & Supranov, V.M. Thermal Calculation of Dust-Preparation Systems in Boiler Plants: A New Approach. Therm. Eng. 68, 434–440 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040601521060057
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040601521060057