Abstract
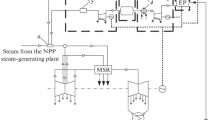
The effectiveness of combining nuclear power plants equipped with water-cooled water-moderated power-generating reactors (VVER) with other sources of energy within unified power-generating complexes is analyzed. The use of such power-generating complexes makes it possible to achieve the necessary load pickup capability and flexibility in performing the mandatory selective primary and emergency control of load, as well as participation in passing the night minimums of electric load curves while retaining high values of the capacity utilization factor of the entire power-generating complex at higher levels of the steam-turbine part efficiency. Versions involving combined use of nuclear power plants with hydrogen toppings and gas turbine units for generating electricity are considered. In view of the fact that hydrogen is an unsafe energy carrier, the use of which introduces additional elements of risk, a procedure for evaluating these risks under different conditions of implementing the fuel-and-hydrogen cycle at nuclear power plants is proposed. Risk accounting technique with the use of statistical data is considered, including the characteristics of hydrogen and gas pipelines, and the process pipelines equipment tightness loss occurrence rate. The expected intensities of fires and explosions at nuclear power plants fitted with hydrogen toppings and gas turbine units are calculated. In estimating the damage inflicted by events (fires and explosions) occurred in nuclear power plant turbine buildings, the US statistical data were used. Conservative scenarios of fires and explosions of hydrogen-air mixtures in nuclear power plant turbine buildings are presented. Results from calculations of the introduced annual risk to the attained net annual profit ratio in commensurable versions are given. This ratio can be used in selecting projects characterized by the most technically attainable and socially acceptable safety.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. V. Portyankin and V. A. Khrustalev, “Estimating the efficiency from using hydrogen toppings at nuclear power stations,” Therm. Eng. 58(9), 786 (2011).
R. Z. Aminov, A. N. Egorov, and V. E. Yurin, “Providing hydrogen cycle-based redundant power supply to NPP auxiliaries under the plant blackout conditions,” At. Energ. 114(4), 234–236 (2013).
R. Z. Aminov and A. N. Egorov, “Evaluating the thermodynamic efficiency of hydrogen cycles at wet-steam nuclear power stations,” Therm. Eng. 60(4), 255 (2013), DOI: 10.1134/S0040363613040012.
Appendices to SNIP (Construction Codes) 2.04.08-87 [Electronic resource], URL: http://www.stroyservice.ru/doki/snip/pril/2-04-08-87z_p.htm.
A Guide to Estimating the Fire Risk for Industrial Enterprises (Moscow, 2006) [Electronic resource], URL: http://www.complexdoc.ru/ntdpdf/541573/rukovodstvo_po_otsenke_pozharnogo_riska_dlya_promyshlennykh_predpriyatii.pdf.
R. Z. Aminov, V. A. Khrustalev, and A. V. Portyankin, “Explosion-and-fire hazard at NPPs with hydrogen toppings. Analysis of the problem and ways of solving it,” Trudy Akademenergo, No. 3, 41–51 (2013).
B. E. Gel’fand, O. E. Popov, and B. B. Chaivanov, Hydrogen: Combustion and Explosion Parameters (Fizmatgiz, Moscow, 2008) [in Russian].
V. M. Beschastnov, Industrial Explosions. Assessment and Prevention (Khimiya, Moscow, 1991) [in Russian].
K. P. Korobchinskii, Yu. A. Skob, M. L. Ugryumov, and V. V. Shentsov, “Numerical assessment of the consequences from hydrogen explosion in the atmosphere,” Nats.-Kosm. Tekhn. Tekhnol., No. 1 (48) (2008) [Electronic resource], URL: http//www.khai.edu/csp/nauchportal/Arhiv/AKTT/2008/AKKT-108/15.pdf.
A. M. Kozlitin, A. I. Popov, and P. A. Kozlitin, Theoretical Principles and Practices of Analyzing Man-Made Risks. Probabilistic Methods for Quantitatively Estimating the Technospheric Hazards (SGTU, Saratov, 2002) [Electronic resource], URL: http://risk-2005.narod.ru/download/Chapter_5_the_Book_about_risk_2002-.pdf.
S. P. Malyshenko, V. I. Prigozhin, and A. R. Savich, “Steam generation efficiency in megawatt-class hydrogen-oxygen steam generators,” Teplofiz. Vys. Temp. 50(5), 1–10 (2012).
A Virtual Tour over the Balakovo NPP [Electronic resource], URL: http://balatom.ru/official/vt/Bala-kovka.html.
M. Braun, “Oil fire in a power plant,” Munich Re, Schadenspiegel, No. 2 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © R.Z. Aminov, V.A. Khrustalev, A.V. Portyankin, 2015, published in Teploenergetika.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aminov, R.Z., Khrustalev, V.A. & Portyankin, A.V. The effectiveness of power-generating complexes constructed on the basis of nuclear power plants combined with additional sources of energy determined taking risk factors into account. Therm. Eng. 62, 130–137 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040601515020019
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040601515020019