Abstract
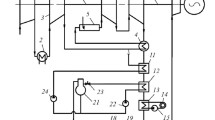
Various schematic solutions for implementing a hydrogen cycle on the basis of thermal and nuclear power stations are discussed. Different approaches to construction of cooling systems for the combustion chambers used in hydrogen-oxygen steam generators are described. An example of solution is given in which the combustion chamber is cooled by steam, which is the most efficient one in the thermodynamic respect. Results from an assessment of the thermodynamic efficiency of hydrogen cycles organized on the basis of the power unit of a wet-steam nuclear power station equipped with a K-1000-60/1500 turbine are presented. The thermodynamic efficiency of different schematic and parametric versions of implementing a hydrogen cycle, including those with a satellite turbine operating on displaced steam, is carried out. It is shown that the use of satellite turbines allows the power output and efficiency of the power unit of a wet-steam nuclear power station to be upgraded in a reliable and effective manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Verfondern, “Nuclear Energy for Hydrogen Production,” Schriften des Forschungszentrums Jülich, Reihe Energietechnik, No. 58 (2007).
C. W. Forsberg and M. S. Kazimi, Nuclear Hydrogen Using High-Temperature Electrolysis and Light-Water Reactors for Peak Electricity Production (Massachusetts Inst. of Technol., 2009).
S. L. Malyshenko, O. V. Nazarova, and Yu. A. Sarumov, “The Thermodynamic Aspects of Using Hydrogen for Solving Some Problems of Power Engineering,” Therm. Eng., No. 10 (1986).
S. L. Malyshenko, O. V. Nazarova, and Yu. A. Sarumov, “Some Thermodynamic and Technical-Economic Aspects of Using Hydrogen as an Energy Carrier in Electric Power Engineering,” in Nuclear-Hydrogen Power Engineering and Technology (Energoatomizdat, Moscow, 1986), No. 7, pp. 105–126.
F. W. Hochmuth, “Burning Hydrogen and Oxygen to Superheat Steam,” US Patent No. 693252, Int. Cl. F 24 H 1/20, CA1074636(A1), 1980-04-01.
R. Z. Aminov, A. N. Bairamov, and A. N. Egorov, “A Nuclear Power Station’s Turbine Unit (Versions),” RF Patent No. 2459293, Otkr., Izobr., No. 23 (2012).
R. Z. Aminov and A. N. Bairamov, “A Hydrogen Combustion System for Steam-Hydrogen Superheating of Live Steam in the Cycle of a Nuclear Power Station,” RF Patent No. 2427048, Int. Cl.7 F 22B 1/26, G 21D5/16, F 01K3/18, Otkr., Izobr., No. 23 (2011).
B. M. Troyanovskii, Turbines for Nuclear Power Stations (Energiya, Moscow, 1978) [in Russian].
R. Z. Aminov, V. A. Khrustalev, A. S. Dukhovenskii, and A. I. Osadchii, Nuclear Power Stations Equipped with VVER Reactors: Operating Modes, Characteristics, and Efficiency (Energoatomizdat, Moscow, 1990) [in Russian].
R. Z. Aminov and A. N. Bairamov, “System Efficiency of Hydrogen Cycles Implemented on the Basis of Off-Peak Electric Energy Produced by a Nuclear Power Station,” Izv. Ross. Akad. Nauk, Energetika, No. 4, 52–61 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © R.Z. Aminov, A.N. Egorov, 2013, published in Teploenergetika.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aminov, R.Z., Egorov, A.N. Evaluating the thermodynamic efficiency of hydrogen cycles at wet-steam nuclear power stations. Therm. Eng. 60, 255–261 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040601513040010
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040601513040010