Abstract
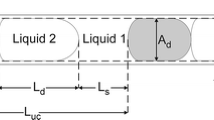
In addition to the previously constructed model of the hydrodynamics of a gas-liquid slug flow, a mathematical model is developed that describes pressure losses taking into account the rearrangement of a velocity profile in liquid slugs and energy losses on the formation and renewal of interfacial area during the motion of bubbles. The contribution of different forms of pressure losses in capillaries is analyzed. It is shown that in microchannels tangential stresses on the surface of a bubble substantially affect the total pressure losses. It is found that the length of bubbles does not affect the rate of surface formation and respective pressure losses if bubbles have the same velocity. The results of modeling are in satisfactory agreement with experimental data of other researchers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hessel, V., Löwe, H., Müller, A., and Kolb, G., Chemical Micro Process Engineering. Processing and Plants. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH Verlag, 2005.
Hessel, V., Mikroverfahrenstechnik Fuer Die Chemische Produktion: Reaktorkonzepte, Anwendungen, Scale-Up, Kostenanalyse, DECHEMA-Regional-Kolloquium “Neue Entwicklungen in der Mikroreaktionstechnik und Mikrotechnik”. Magdeburg: Max-Planck-Institut fuer Dynamik komplexer Technischer Systeme, 2006p. 3.
Roy, S., Bauer, T., Al-Dahhan, M., Lehner, P., and Turek, T., Monoliths as Multiphase Reactors: A Review, AIChE J., 2004, vol. 50, no. 11, p. 2918.
Kreutzer, M.T., Kapteijn, F., Moulijn, J.A., and Heiszwolf, J.J., Multiphase Monolith Reactors: Chemical Reaction Engineering of Segmented Flow in Microchannels, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2005, vol. 60, p. 5895.
Bauer, T., Shubert, M., Lange, R., and Abiev, R.Sh., Intensification of Heterogeneous Catalytic Gas-Liquid Reactions in Reactors with a Multichannel Monolith Catalyst, Zh. Prikl. Khim., 2006, vol. 79, no. 7, p. 1057.
Serizawa, A., Feng, Z., and Kawara, Z., Two-Phase Flow in Microchannels, Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci., 2002, vol. 26, p. 703.
Fukano, T., Kariyasaki, A., and Ide, H., Fundamental Data of the Gas Liquid Two Phase Flow, Proc. 3rd Int. Conf. on Microchannels and Minichannels, Toronto, 2005, p. 1.
Kawahara, A., Chung, P.M.-Y., and Kawaji M., Investigation of Two-Phase Flow Pattern, Void Fraction and Pressure Drop in a Microchannel, Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 2002, vol. 28, p. 1411.
Chung, P.M.-Y. and Kawaji, M. The Effect of Channel Diameter on Adiabatic Two-Phase Flow Characteristics in Microchannels, Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 2004, vol. 30, p. 735.
Liu, H., Vandu, C.O., and Krishna, R., Hydrodynamics of Taylor Flow in Vertical Capillaries: Flow Regimes, Bubble Rise Velocity, Liquid Slug Length, and Pressure Drop, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2005, vol. 44, p. 4884.
Kreutzer, M.T., Kapteijn, F., Moulijn, J.A., et al., Inertial and Interfacial Effects on Pressure Drop of Taylor Flow in Capillaries, AIChE J., 2005, vol. 51, p. 2428.
Dukler, A.E., Moye, Wicks III, and Cleveland, R.G., Pressure Drop and Hold-Up in Two-Phase Flow, AIChE J., 1964, vol. 10, p. 38.
Lockhart, R.W. and Martinelli, R.C., Proposed Correlation of Data for Isothermal Two-Phase, Two-Component Flow in Pipes, Chem. Eng. Prog., 1949, vol. 45, p. 39.
Chisholm, D. and Laird, A.D.K., Two-Phase Flow in Rough Tubes, Trans. ASME, 1958, vol. 80, no. 2, p. 276.
Chisholm, D., A Theoretical Basis for the Lockhart-Martinelli Correlation for Two-Phase Flow, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1967, vol. 10, p. 1767.
Zhao, T.S. and Bi, Q.C., Pressure Drop Characteristics of Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Flow in Vertical Miniature Triangular Channels, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2001, vol. 44, p. 2523.
Mishima, K. and Hibiki, T., Some Characteristics of Air-Water Two-Phase Flow in Small Diameter Vertical Tubes, Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 1996, vol. 22, no. 4, p. 703.
Lee, H.J. and Lee, S.Y., Pressure Drop Correlations for Two-Phase Flow within Horizontal Rectangular Channels with Small Height, Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 2001, vol. 27, p. 783.
Suo, M. and Griffith, P., Two-Phase Flow in Capillary Tubes, J. Basic Eng, 1964, vol. 86, p. 576.
Garimella, S., Killion, J.D., and Coleman, J.W., An Experimentally Validated Model for Two-Phase Pressure Drop in the Intermittent Flow Regime for Circular Microchannels, J. Fluids Eng.-Trans. ASME, 2002, vol. 124, p. 205.
Abiev, R.Sh., Simulation of the Slug Flow of a Gas-Liquid System in Capillaries, Teor. Osn. Khim. Tekhnol., 2008, vol. 42, no. 2, p. 115 [Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 42, no. 2, p. 105].
Frolov, Yu.G., Kurs kolloidnoi khimii (Colloid Chemistry), Moscow: Khimiya, 1988.
Lamb, H., Gidrodinamika (Hydrodynamics), Moscow: Regulyarnaya i Khaoticheskaya Dinamika, 2003, vol. 2.
Bretherton, F.P., The Motion of Long Bubbles in Tubes, J. Fluid Mech., 1961, no. 10, p. 166.
Warnier, M.J.F., de Croon, M.H.J.M., Rebrov, E.V., and Schouten, J.C., Pressure Drop of Gas-Liquid Taylor Flow in Round Micro-Capillaries for Low to Intermediate Reynolds Numbers, Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 2010, vol. 8, no. 1, p. 33.
Aussillous, P. and Quéré, D., Quick Deposition of a Fluid on the Wall of a Tube, Phys. Fluids, 2000, vol. 15, no. 10, p. 2367.
Abiev, R.Sh., Circulation and Bypass Modes of the Slug Flow of a Gas-Liquid Mixture in Capillaries, Teor. Osn. Khim. Tekhnol., 2009, vol. 43, no. 3, p. 313 [Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. (Engl. Transl.), vol. 43, no. 3, p. 298].
Slezkin, N.A., Dinamika vyazkoi neszhimaemoi zhidkosti (Dynamics of Viscous Incompressible Liquid), Moscow: Gostekhteorizdat, 1955.
Abiev, R.Sh., On the Shape of Bubbles in the Taylor Flow Regime for a Gas-Liquid Mixture in Capillaries, Tez. dokl. Mezhdunar. konf. “Matematicheskie metody v tekhnike i tekhnologiyakh” (Proc. Int. Conf. on Mathematical Methods in Engineering and Technologies), Pskov: PPI, 2009, vol. 5, p. 74.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © R.Sh. Abiev, 2011, published in Teoreticheskie Osnovy Khimicheskoi Tekhnologii, 2011, Vol. 45, No. 2, pp. 170–177.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abiev, R.S. Modeling of pressure losses for the slug flow of a gas–liquid mixture in mini- and microchannels. Theor Found Chem Eng 45, 156–163 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040579511020011
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040579511020011