Abstract
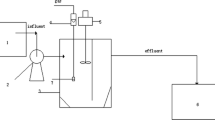
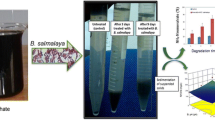
A new method that combines Bacillus subtilis (B. subtilis) with K2FeO4 has been developed to enhance the degradation of phenanthrene (Phe) and benzo(a)pyrene (BaP) in wastewater. The results showed that (i) BaP and Phe after pre-oxidation with K2FeO4 were more easily bio-degraded by the cooperating methods, showed faster kinetics and shorter half-life (t1/2); (ii) removal rate of Phe was always higher than that of BaP in the whole oxidation-biodegradation process; (iii) the optimal parameters for the combination experiments were as follows: the ratio of K2FeO4 and the sum of two contaminants of 10 : 1 (m : m), 10% (v : v) of B. subtilis, an initial pH of 8.0 at 30°C with 250 rpm at the stage of oxidation, and 100 rpm at the stage of both biodegradation and adsorption. Under the above optimal conditions, the removal rate of Chemical Oxygen Demand (CODcr), Phe, and BaP were 59.0, 93.9, and 86.93%, respectively. Based on the experimental results, the mechanism of simultaneous removal of Phe and BaP was elucidated. The three main stages during the whole removal process included oxidation, adsorption, and bio-degradation steps. The degradation rate of BaP contributed more to the removal rate of total BaP than the adsorption did at the end of the experiments, while its oxidation rate was almost constant. The same trends applied for the Phe removal. When the above method and conditions were applied for two kinds of field wastewater, the removal rate of Phe and BaP, in the end, was higher than that of the pure laboratory samples, although the removal rate was a little low in the initial stage.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
J. Vila, M. Tauler, and M. Grifoll, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 33, 95 (2015).
F. X. Zhu, S. Storey, M. M. Ashaari, N. Clipson, and E. Doyle, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 24, 5404 (2017).
G. D. Sayles, C. M. Acheson, M. J. Kupferle, Y. Shan, Q. Zhou, J. R. Meier, L. Chang, and R. C. Brenner, Environ. Sci. Technol. 33, 4310 (1999).
J. W. Talley, U. Ghosh, S. G. Tucker, J. S. Furey, and R. G. Luthy, Environ. Sci. Technol. 36, 477 (2002).
S. N. Chen, H. Yin, and J. Chang, J. Hazard. Mater. 321, 9 (2017).
S. N. Chen, H. Yin, S. Y. Tang, H. Peng, and Z. Dang, Bioresour. Technol. 24, 26 (2016).
N. Nader, R. Bikas, M. Emami, M. Siczek, and T. Lis, Polyhedron 111, 167 (2016).
M. Kastner and B. Mahro, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 44, 668 (1996).
C. E. Cerniglia, Biodegradation 3, 351 (1992).
W. Yan, S. S. Liu, Z. Q. Wang, Z. C. Wang, and S. Z. Wang, Water Air Soil Pollut. 228, 233 (2017).
M. A. Baboshin and L. A. Golovleva, Microbiology 81, 695 (2012).
N. Kyoungphile, R. Wilson, and J. K. Jerome, Chemistry 45, 11 (2001).
S. Y. Zang, P. J. Li, B. Lian, and J. Wang, J. Environ. Sci. 25, 1 (2008).
C. Rafin, E. Veignie, A. Fayeulle, and G. Surpateanu, Bioresour. Technol. 100, 3157 (2009).
Z. Zhou and J. Q. Jiang, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 106, 37 (2015).
K. Manoli, G. Nakhla, A. K. Ray, and V. K. Shama, Chem. Eng. J. 307, 513 (2017).
S. F. Sun, Y. L. Liu, J. Ma, S. Y. Pang, Z. S. Huang, J. Gu, Y. Gao, M. Xue, Y. X. Yuan, and L. Jiang, Chem. Eng. J. 332, 245 (2018).
J. K. Cui, L. Zheng, and Y. Deng, Environ. Sci., Water Res. Technol. 4, 359 (2018).
L. Machala, V. Prochazka, M. Miglierini, V. K. Sharma, Z. Marusak, H.-C. Wille, and R. Zboril, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 21787 (2015).
P. K. Rai, J. Lee, S. K. Kailasa, E. E. Kwon, Y. F. Tsang, Y. S. Ok, and K. H. Kim, Environ. Res. 160, 420 (2018).
C. J. Wang, N. Klamerth, S. A. Messele, A. Singh, M. Belosevic, and M. G. Eldin, Water Res. 100, 476 (2016).
P. Zajíček, M. Kolár, R. Prucek, V. Ranc, P. Bednár, R. S. Varma, V. K. Sharma, and R. Zboril, Purif. Technol. 156, 1041 (2015).
D. Su, P. J. Li, and F. Stagnitti, J. Environ. Sci. 18, 1204 (2006).
S. Y. Zang, P. J. Li, X. C. Yu, K. Shi, H. Zhang, and J. Chen, J. Environ. Sci. 19, 238 (2007).
P. Li, T. Sun, F. Stagnitti, C. Zhang, H. Zhang, X. Xiong, G. Allinson, X. Ma, and M. Allinson, Environ. Sci. Technol. 5, 285 (2002).
N. Ertugay and F. N. Acar, Arab. J. Chem. 10, s1158 (2017).
R. Kanaly, R. Bartha, S. Fogel, and M. Findlay, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63, 4511 (1997).
F. Chen, Z. B. Luo, J. Ma, S. Y. Zeng, Y. J. Yang, and S. L. Zhang, Water Air Soil Pollut. 229, 114 (2018).
F. S. Lang, J. Destain, F. Delvigne, P. Druart, M. Ongena, and P. Thonart, Water Air Soil Pollut. 227, 297 (2016).
W. Wickle, J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 163, 229 (2000).
J. A. Rentz, P. J. J. Alvarez, and J. L. Schnoor, Environ. Pollut. 151, 669 (2008).
A. L. Juhasz and R. Naidu, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 45, 57 (2000).
R. A. Brown, C. Nelson, and M. Leahy, in In Situ and On-site Bioremediation, Ed. by B. C. Alleman and A. Leeson (Battelle, Columbus, OH, 1997).
Y. J. Jiang, J. E. Goodwill, J. E. Tobiason, and D. A. Reckhow, Environ. Sci. Technol. 49, 2841 (2015).
S. Y. Zang, P. J. Li, W. X. Li, D. Zhang, and A. Hamilton, Chemosphere 67, 1368 (2007).
A. S. Tsibart and A. N. Gennadiev, Euras. Soil Sci., 788 (2013).
X. Wang, Y. Liu, Z. Huang, L. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Li, J. Li, J. Qi, and J. Ma, Water Res. 144, 592 (2018).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 41773136 and 41703129), Innovation Talent Support Project of Liaoning (grant no. LR2017073), the National Key R and D Program of China (no. 2017YFD0800301).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zang, S., Zhao, Q., Gomez, M.A. et al. Removal Mechanisms of Phenanthrene and Benzo(a)pyrene from Wastewater by Combining Bacillus subtilis with Ferrate. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 95 (Suppl 2), S242–S251 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024421150267
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024421150267