Abstract
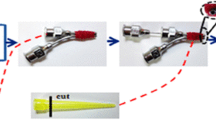
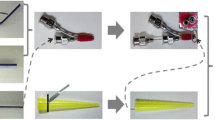
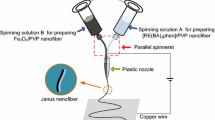
A new nanostructure of luminescent-magnetic-electrical trifunctionality Janus nanofibers with [Fe3O4/polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP)]@[Dy(BA)3phen/Eu(BA)3phen/PVP] coaxial nanocable as one half and polyaniline (PANI)/PVP as the other half has been successfully fabricated by a specially designed co-axis//single-axis spinneret electrospinning device. Moreover, all Janus nanofibers are aligned in the same direction to generate a two-dimensional (2D) array membrane by using an aluminum drum collection device. The electrical conductivity along the length direction is much stronger than the electrical conductivity in the diameter direction (two perpendicular directions). Therefore, the array membrane has excellent anisotropic electrical conduction. The conduction ratio reaches 106 times between length and diameter direction of the Janus nanofibers array membrane, which presents the highest conduction ratio between the two perpendicular directions for nanofibers materials reported internationally. Furthermore, we can modulate degree of electrically conducting anisotropism of the samples by varying the amount of PANI. In addition, the Janus nanofibers array membrane is concurrently endowed by superior and adjustable superparamagnetism and color-tunable fluorescence. What is more important, the construction technique for the novel Janus nanofibers array membrane is of universal significance for the fabrication of other multifunctional nanomaterials-formed membranes.










Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
N. I. Kovtyukhova and T. E. Mallouk, J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 2540 (2005).
C. Feng, K. Liu, J. S. Wu, L. Liu, J. S. Cheng, Y. Y. Zhang, Y. H. Sun, Q. Q. Li, S. S. Fan, and K. L. Jiang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 20, 885 (2010).
J. R. Huang, Y. T. Zhu, W. Jiang, and Q. X. Tang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 1754 (2014).
W. A. D. Heer, A. Chatelain, and D. Ugarte, Science (Washington, DC, U. S.) 270, 1179 (1995).
Q. L. Ma, J. X. Wang, X. T. Dong, W. S. Yu, and G. X. Liu, Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 2436 (2015).
Q. L. Ma, W. S. Yu, X. T. Dong, M. Yang, J. X. Wang, and G. X. Liu, Sci. Rep. 5, 14583 (2015).
L. Han, M. M. Pan, Y. Lv, Y. T. Gu, X. F. Wang, D. Li, Q. L. Kong, and X. T. Dong, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 677 (2015).
X. Xi, Q. L. Ma, M. Yang, X. T. Dong, J. X. Wang, W. S. Yu, and G. X. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 4024 (2014).
J. Tian, Q. L. Ma, W. S. Yu, X. T. Dong, Y. Yang, B. Zhao, J. X. Wang, and G. X. Liu, New J. Chem. 41, 13983 (2017).
X. B. Li, Q. L. Ma, J. Tian, X. Xi, D. Li, X. T. Dong, W. S. Yu, X. L. Wang, J. X. Wang, and G. X. Liu, Nanoscale 9, 18918 (2017).
K. Lun, Q. L. Ma, M. Yang, X. T. Dong, Y. Yang, J. X. Wang, W. S. Yu, and G. X. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 5994 (2015).
Q. L. Ma, J. X. Wang, X. T. Dong, W. S. Yu, and G. X. Liu, Chem. Eng. J. 222, 16 (2013).
H. Shao, Q. L. Ma, X. T. Dong, W. S. Yu, M. Yang, Y. Yang, J. X. Wang, and G. X. Liu, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 21845 (2015).
Q. L. Ma, J. X. Wang, X. T. Dong, W. S. Yu, and G. X. Liu, Nanoscale 6, 2945 (2014).
X. Xi, J. X. Wang, X. T. Dong, Q. L. Ma, W. S. Yu, and G. X. Liu, Chem. Eng. J. 254, 259 (2014).
X. Xi, Q. L. Ma, X. T. Dong, D. Li, W. S. Yu, J. X. Wang, and G. X. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Eletron. 29, 7119 (2018).
Y. Y. Zheng, X. B. Wang, L. Shang, C. R. Li, C. Cui, W. J. Dong, W. H. Tang, and B. Y. Chen, Mater. Charact. 61, 489 (2010).
S. Meshkova, J. Fluoresc. 10, 333 (2000).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51573023, 51803012), Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (20170101101JC, 20180520011JH), Science and Technology Research Planning Project of the Education Department of Jilin Province during the 13th five-year plan period (JJKH20170608KJ, JJKH20181122KJ), and Innovative Foundation (XJJLG-2017-04) and Youth Foundation (XQNJJ-2016-01, XQNJJ-2017-17) of Changchun University of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue Xi, Ma, Q., Dong, X. et al. Anisotropic Conductive Membrane with Superparamagnetism and Color-Tunable Luminescence. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 93, 2444–2451 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024419120331
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024419120331