Abstract
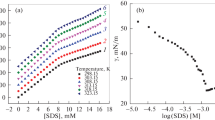
The adsorption of anionic surfactant sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDBS) from aqueous solution on the hydrophilic surfaces of aluminum oxide and iron oxide nanoparticles is studied via UV spectrophotometry, electrophoretic light scattering, and isothermal microcalorimetry. It is shown that the isotherms of the adsorption of SDBS on the surfaces of both oxides in the area of concentrations up to 0.6 mmol/L is linear. It is found that the positive zeta potential of the surfaces of the particles falls to zero and shifts toward the range of negative values due to adsorption. The adsorption of SDBS is characterized by positive enthalpy values over the investigated range of concentrations, while the loss of energy during adsorption indicates it is of an entropic nature. It is concluded that the probable cause of the increase in entropy is the dehydration of SDBS molecules during on surface adsorption. The obtained results are discussed in terms of the formation of hemimicelles of surfactant on the hydrophilic surfaces of metal oxide nanoparticles in an aqueous medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Gao, H. Gu, and B. Xu, Acc. Chem. Res. 42, 1097 (2009).
D. Zhu, X. Li, N. Wang, et al., Curr. Appl. Phys. 9, 131 (2009).
S. Abdeen and P. K. Praseetha, Nanomed. Biother. Disc. 2, 165 (2013).
H. B. Nair, B. Sung, V. R. Yadav, et al., Biochem. Pharmacol. 80, 1833 (2010).
S. Laurent and M. Mahmoudi, Int. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Genet. 2, 367 (2011).
Y. Wang, Y. Zheng, L. Zhang, et al., J. Control. Release 172, 1126 (2013).
A. A. Keller, H. Wang, D. Zhou, et al., Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 1962 (2010).
A. P. Safronov, E. G. Kalinina, T. A. Smirnova, D. V. Leiman, and A. V. Bagazeev, Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 84, 2122 (2010).
X. Li, D. Zhu, and X. Wang, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 310, 456 (2007).
S. Paria and K. C. Khilar, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 110, 75 (2004).
R. Zhang and P. Somasundaran, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 123–126, 213 (2006).
T. D. Pham, M. Kobayashi, and Y. Adachi, Colloid Polym. Sci. 293, 217 (2014).
D. Zhu, X. Li, N. Wang, et al., Curr. Appl. Phys. 9, 131 (2009).
H. Lee, S. Yamaoka, N. Murayama, et al., Mater. Lett. 61, 3974 (2007).
H. M. Vale and T. F. McKenna, Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 268, 68 (2005).
A. M. Gaudin and D. W. Fuerstenau, Trans. AIME 202, 958 (1955).
S. S. Voyutskii, Course of Colloid Chemistry (Khimiya, Moscow, 1976) [in Russian].
Yu. A. Kotov, I. V. Beketov, A. I. Medvedev, and O. R. Timoshenkova, Nanotechnol. Russ. 4, 354 (2009).
Yu. G. Frolov, A Course of Colloid Chemistry. Surface Phenomena and Dispersed Systems (Al’yans, Moscow, 2004) [in Russian].
T. Tadros, Encyclopedia of Colloid and Interface Science (Springer, Berlin, 2013).
Yu. A. Pentin and L. V. Vilkov, Physical Methods in Chemistry (Mir, Moscow, 2003) [in Russian].
E. Calvet and H. Prat, Recent Progress in Microcalorimetry (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1963).
J. Geng, F. G. Johnson, E. H. Wheatley, et al., Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 12, 307 (2013).
K. Holmberg, B. Jonsson, B. Kronberg, and B. Lindman, Surfactans and Polymers in Aqueous Solution (Wiley-VCH, New York, 2002; BINOM, Labor. Znanii, Moscow, 2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © R.R. Mansurov, A.P. Safronov, N.V. Lakiza, 2016, published in Zhurnal Fizicheskoi Khimii, 2016, Vol. 90, No. 6, pp. 890–895.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mansurov, R.R., Safronov, A.P. & Lakiza, N.V. Entropic nature of the adsorption of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate on nanoparticles of aluminum and iron oxides in aqueous medium. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 90, 1200–1205 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024416060121
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024416060121