Abstract
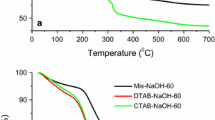
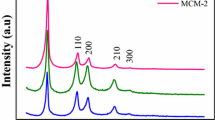
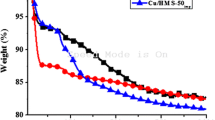
Mesoporous MgO was obtained via the hydrothermal synthesis using both ionogenic and non-ionogenic surfactants as structure-directing templates. The materials prepared were characterized by SEM, BET-N2, XRD, and TG-DTA techniques. MgO particles are spherical 20-μm aggregates of primary oxide particles well shaped as rectangular parallelepipeds. Magnesium oxide samples have the specific surface area of 290–400 m2/g and pore sizes of 3.3–4.1 nm. Their mesoporous structure remained unchanged after calcination up to 350°C. Catalytic activity of mesoporous MgO was studied in acetone condensation reaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Li, W.-L. Dai, and K. Fan, J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 17657 (2008).
C. Pak, A. T. Bell, and T. D. Tilley, J. Catal. 206, 49 (2002).
T. Klicpera and M. Zdražil, J. Catal. 206, 314 (2002).
M. Bhagiyalakshmi, J. Y. Lee, and H. T. Jang, Int. J. Greenhouse Gas Control 4, 51 (2010).
I. V. Mishakov, A. F. Bedilo, R. M. Richards, et al., J. Catal. 206, 40 (2002).
C. Gao, W. Zhang, H. Li, et al., Cryst. Growth Des. 8, 3785 (2008).
X. Li, W. Xiao, G. He, et al., Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 408, 79 (2012).
H. Jeon, D. J. Kim, S. J. Kim, and J. H. Kim, Fuel Process. Technol. 116, 325 (2013).
D. Gu and F. Schüth, Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 313 (2014).
Y. Shi, Y. Wan, and D. Zhao, Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 3854 (2011).
P. T. Huyen, E. Callone, R. Campostrini, et al., Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 64, 10405 (2013).
G. Wang, L. Zhang, H. Dai, et al., Inorg. Chem. 47, 4015 (2008).
Physical and Chemical Aspects of Adsorbents and Catalysts, Ed. by B. G. Linsen (Academic, New York, London, 1970; Mir, Moscow, 1973).
G. I. Kapaev, Cand. Sci. (Chem.) Dissertation (Russ. Chem. Technol. Univ., Moscow, 2009).
G. S. Salvapati, K. V. Ramanamurty, and M. Janardanarao, J. Mol. Catal. 54, 90 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article was translated by the authors.
Published in Russian in Zhurnal Fizicheskoi Khimii, 2016, Vol. 90, No. 6, pp. 902–906.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maerle, A.A., Kasyanov, I.A., Moskovskaya, I.F. et al. Mesoporous MgO: Synthesis, physico-chemical, and catalytic properties. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 90, 1212–1216 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024416060108
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024416060108