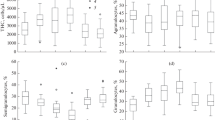
Abstract
The results of hematological, cytochemical, and biochemical surveys for fish blood in the specimen Ocellate river stingray Potamotrygon motoro and two specimens of cat sharks including the Halmahera epaulette shark Hemiscyllium halmahera and the grey bambooshark Chiloscyllium griseumare have been reported. A comparison in the parameters analyzed in the survey between the common carp Cyprinus carpio, the wels catfish Silurus glanis, and the sterlet Acipenser ruthenus has been performed. A high percentage of eosinophils involved in antiparasite immunity in the Cartilaginous fishes is recorded. A high content of cationic protein in lysosomes of neutrophils in these fish species can indicate a considerable potent phagocytic activity of the latter. A low amount of alanine aminotransferase in the analyzed shark and ray specimens compared to the bony fish was recorded, which indicate the strength of membranes in hepatocytes and cardiomyocytes.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Arnold, J.E., Hematology of the sandbar shark, Carcharhinus plumbeus: Standardization of complete blood count techniques for elasmobranchs, Vet. Clin. Pathol., 2005, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 115–123. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1939-165X.2005.tb00023.x
Binder, Th., Diem, H., Fuchs, R., et al., Pappenheim-Färbung: Beschreibung einer hämatologischen Standardfärbung—Geschichte, Chemie, Durchführung, Artefakte und Problemlösungen/Pappenheim Stain: Description of a hematological standard stain – history, chemistry, procedure, artifacts and problem solutions, Laboratoriumsmedizin, 2012, vol. 36, no. 5, pp. 293–309. https://doi.org/10.1515/labmed-2012-0027
Bircan-Yildirim, Y., Çek, Ş., Basusta, N., and Atik, E., Histology and morphology of the epigonal organ with special referance to the lymphomyeloid system in Rhinobatos rhinobatos, Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 2011, vol. 11, pp. 351–358. https://doi.org/10.4194/1303-2712-v11_3_03
Bridle, A., Nosworthy, E., Polinski, M., and Nowak, B., Evidence of an antimicrobial-immunomodulatory role of Atlantic salmon cathelicidins during infection with Yersinia ruckeri, PLoS ONE, 2011, vol. 6, no. 8, Article e23417. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0023417
Browne, M.J., Feng, C.Y., Booth, V., and Rise, M.L., Characterization and expression studies of Gaduscidin-1 and Gaduscidin-2; paralogous antimicrobial peptide-like transcripts from Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua), Dev. Comp. Immunol., 2011, vol. 35, no. 3, pp. 399–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2010.11.010
Burgos-Aceves, M.A., Campos-Ramos, R., and Guerrero-Tortolero, D.A., Description of peripheral blood cells and differential blood analysis of captive female and male leopard grouper Mycteroperca rosacea as an approach for diagnosing diseases, Fish Physiol. Biochem., 2010, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 1263–1269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-010-9406-7
Castiglione, S., Tesone, G., Piccolo, M., et al., A new method for testing evolutionary rate variation and shifts in phenotypic evolution, Methods Ecol. Evol., 2018, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 974–983. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12954
Chang, C.I., Pleguezuelos, O., Zhang, Y.A., et al., Identification of a novel cathelicidin gene in the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, Infect. Immun., 2005, vol. 73, no. 8, pp. 5053–5064. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.73.8.5053-5064.2005
Chang, J., Rabosky, D.L., Smith, S.A., et al., 2019. An R package and online resource for macroevolutionary studies using the ray-finned fish tree of life, Methods Ecol. Evol., vol. 10, no. 7, pp. 1118–1124. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.13182
Claus, M., Antoni, C., and Hofmann, B., Factors associated with elevated alanine aminotransferase in employees of a German chemical company: Results of a large cross-sectional study, BMC Gastroenterol., 2021, vol. 21, no. 1, Article 25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-021-01601-2
Cuesta, A., Meseguer, J., and Esteban, M.A., The antimicrobial peptide hepcidin exerts an important role in the innate immunity against bacteria in the bony fish gilthead seabream, Mol. Immunol., 2008, vol. 45, no. 8, pp. 2333–2342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2007.11.007
de Oliveira, A.T., Santos, M.Q.D.C., de Araujo, M.L.G., et al., Hematological parameters of three freshwater stingray species (Chondrichthyes: Potamotrygonidae) in the middle Rio Negro, Amazonas state, Biochem. Syst. Ecol., 2016, vol. 69, pp. 33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2016.07.002
Dong, H.Th., Channarong, R., Hai, D.L., et al., Naturally concurrent infections of bacterial and viral pathogens in disease outbreaks in cultured Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) farms, Aquaculture, 2015, vol. 448, pp. 427–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.06.027
Dove, A.D.M., Arnold, J., and Clauss, T.M., 2010. Blood cells and serum chemistry in the world’s largest fish: The whale shark Rhincodon typus, Aquat. Biol., vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 177–183. https://doi.org/10.3354/ab00252
Esteban, M.A., Cuesta, A., Chaves-Pozo, E., and Meseguer, J., Phagocytosis in teleosts. Implications of the new cells involved, Biology, 2015, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 907–922. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4040907
Flajnik, M.F. and Rumfelt, L.L., The Immune System of Cartilaginous Fish, in Origin and Evolution of the Vertebrate Immune System, Berlin; Heidelberg: Springer, 2000, pp. 249–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-59674-2_11
Galaktionov, V.G., Evolyutsionnaya immunologiya (Evolutionary Immunology), Moscow: Akademkniga, 2005.
Galvin, Z., McDonough, A., Ryan, J., and Stewart, S., Blood alanine aminotransferase levels >1.000 IU/L—causes and outcomes, Clin. Med., 2015, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 244–247. https://doi.org/10.7861/clinmedicine.15-3-244
Gordeev, I.I., Mikryakov, D.V., Balabanova, L.V., and Mikryakov, V.R., The cell composition of the peripheral blood and some hematopoietic organs in the Antarctic starry skate Amblyraja georgiana (Norman, 1938) (Rajiformes: Rajidae) from the Scotia Sea, Russ. J. Mar. Biol., 2019, vol. 45, no. 6, pp. 481–485. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063074019060038
Grushko, M.P., Khvostova, S.M., and Kryuchkov, V.N., Features of hematopoiesis in representatives of cartilaginous fish, Vestn. Astrakhan. Gos. Tekhn. Univ. Ser. Rybn. Khoz-vo, 2012, no. 1, pp. 133–135.
Hammerschlag, N., Osmoregulation in elasmobranchs: A review for fish biologists, behaviourists and ecologists, Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol., 2006, vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 209–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/10236240600815820
Havixbeck, J.J. and Barreda, D.R., Neutrophil development, migration, and function in teleost fish, Biology, 2015, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 715–734. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4040715
Ivanov, A.A., Pronina, G.I., and Koryagina, N.Yu., Gematologiya poikilotermnykh gidrobiontov (Hematology of Poikilothermic Hydrobionts), Irkutsk: Megaprint, 2018.
Kuz’mina, V.V., Protsessy pishchevareniya u ryb. Novye fakty i gipotezy (Digestive Processes in Fish. New Facts and Hypotheses), Yaroslavl: Filigran’, 2018.
Luer, C.A., Walsh, C.J., and Bodine, A.B., The Immune System of Sharks, Skates and Ray, in Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives, Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2004, pp. 369–395.
Manca, R., Delia, M., Abat, M., et al., Evolutionary conservation of a regulative pathway of erythropoiesis in poikilothermic vertebrates, Sci. Rep., 2022, vol. 12, no. 1, Article 3307. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-06617-6
Martin, R.A., A review of shark agonistic displays: comparison of display features and implications for shark-human interactions, Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol., 2007, vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 3–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/10236240601154872
Martins, B.O., Franco-Belussi, L., Siqueira, M.S., et al., The evolution of red blood cell shape in fishes, J. Evol. Biol., 2021, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 537–548. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeb.13757
Meshcheryakova, D.A., Derkho, M.A., and Sereda, T.I., Assessment of leukogram changes in mammary gland tumors in dogs, Vestn. Novosib. Gos. Agrar. Univ., 2014, vol. 2, no. 31, pp. 125–129.
Old, J.M. and Huveneers, C., Morphology of the blood cells from three species of wobbegong sharks (Orectolobus species) on the east coast of New South Wales, Zoo Biol., 2006, vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 73–82. https://doi.org/10.1002/zoo.20079
Pappenheim, A., Zur Blutzellf ä rbung im klinischen Blut-trockenpr ä parat und zur histologischen Schnittpr ä paratf ä rbung der h ä matopoetischen Gewebe nach meinen Methoden, Folia Haematologica, 1912, vol. 13, pp. 339–345.
Petrovskii, S.V., Kurdeko, A.P., Belko, A.A., and Kovzov, V.V., Metodicheskie ukazaniya po otboru biologicheskogo materiala dlya laboratornykh issledovanii (Guidelines for the Selection of Biological Material for Laboratory Research), Vitebsk: Uchrezhd. Obrazov. Vitebsk. Gos. Akad. Veterinar. Med., 2017.
Pronina, G.I. and Koryagina, N.Yu., Reference values of physiological and immunological parameters of hydrobionts of different species, Vestn. Astrakhan. Gos. Tekhn. Univ. Ser. Rybn. Khoz-vo, 2015, no. 4, pp. 103–108.
Pronina, G.I. and Koryagina, N.Yu., Metodologiya fiziologo-immunologicheskoi otsenki gidrobiontov (Methodology of Physiological and Immunological Assessment of Hydrobionts), Moscow: Lan’, 2017.
Rojas, V., Morales-Lange, B., Avendaño-Herrera, R., et al., Detection of muscle-specific creatine kinase expression as physiological indicator for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) skeletal muscle damage, Aquaculture, 2018, vol. 496, pp. 66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.07.006
Smith, N.C., Rise, M.L., and Christian, S.L., A comparison of the innate and adaptive immune systems in cartilaginous fish, ray-finned fish, and lobe-finned fish, Front. Immunol., 2019, vol. 10, Article 2292. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02292
Smith, S.L., Sim, R.B., and Flajnik, M.F., Immunobiology of the Shark, Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1201/b17773
Stein, R.W., Mull, C.G., Kuhn, T.S., et al., Global priorities for conserving the evolutionary history of sharks, rays and chimaeras, Nat. Ecol. Evol., 2018, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 288–298. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-017-0448-4
Walker, T.I., Day, R.W., Awruch, C.A., et al., Ecological vulnerability of the chondrichthyan fauna of southern Australia to the stressors of climate change, fishing and other anthropogenic hazards, Fish Fish., 2021, vol. 22, no. 5, pp. 1105–1135. https://doi.org/10.1111/faf.12571
Walsh, C.J., Toranto, J.D., Gilliland, C.T., et al., Nitric oxide production by nurse shark (Ginglymostoma cirratum) and clearnose skate (Raja eglanteria) peripheral blood leucocytes, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2006, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2005.03.011
Whitney, N.M., Lear, K.O., Gaskins, L.Ch., and Gleiss, A.C., The effects of temperature and swimming speed on the metabolic rate of the nurse shark (Ginglymostoma cirratum, Bonaterre), J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 2016, vol. 477, pp. 40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2015.12.009
Witeska, M., Kondera, E., Ługowska, K., and Bojarski, B., Hematological methods in fish – not only for beginners, Aquaculture, 2022, vol. 547. Article 737498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737498
Yukhnovets, A.A., Cytochemical parameters of peripheral blood leukocytes in thyroid diseases, Vestn. Vitebsk. Gos. Med. Univ., 2003, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 71–78.
Zhiteneva, L.D., Makarov, E.V., and Rudnitskaya, O.A., Evolyutsiya krovi (Evolution of Blood), Rostov-on-Don: Delovoi Mir, 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Statement on the welfare of humans or animals. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Translated by O. Zhiryakova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pronina, G.I., Orlov, A.M., Meintser, I.V. et al. Components of Blood and Blood Cytochemical and Biochemical Characteristics of Three Cartilaginous Fish Species in Orders Orectolobiformes and Myliobatiformes. J. Ichthyol. 62, 1352–1360 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945222060248
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945222060248