Abstract—
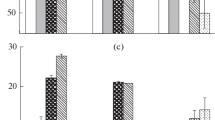
Thyroid and sex steroid hormones have been studied in spawners of the pink salmon Oncorhynchus gorbuscha at the stage of changing the marine section of the spawning migration path to freshwater one. Males of smaller size enter the Keret River earlier than larger specimens; such differences were not found in females. Compared to specimens in the sea, females in the river are characterized by a high level of triiodothyronine and an increased rate of deiodination, and males have a high testosterone level. Females both in the sea and in the river differ from males by a high level of 17ß-estradiol and a low value of the ratio of testosterone concentrations to 17ß-estradiol.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Alekseev, M.Yu., Tkachenko, A.V., Zubchenko, A.V., et al., Distribution, spawning and the possibility of fishery of introduced pink salmon (Oncorhynchus gorbusha Walbaum) in rivers of Murmansk oblast, Russ. J. Biol. Invasions, 2019, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 109–117.
Altukhov, Yu.P., Salmenkova, E.A., and Omel’chenko, V.T., Populyatsionnaya genetika lososovykh ryb (Population Genetics of Salmonids), Moscow: Nauka, 1997.
Barannikova, I.A., Funktsional’nye osnovy migratsii ryb (Functional Basis of Fish Migrations), Leningrad: Nauka, 1975.
Arjona, F.J., Vargas-Chacoff, L., del Río, M.P., et al., Effects of cortisol and thyroid hormone on peripheral outer ring deiodination and osmoregulatory parameters in the Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis), J. Endocrinol., 2011, vol. 208, no. 3, pp. 323–330. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-10-0416
Berg, O.K. and Jonsson, B., Growth and survival rates of anadromous trout (Salmo trutta L.) from the Vardnes River, northern Norway, Environ. Biol. Fish., 1990, vol. 29, pp. 145–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00005031
Biddiscombe, S. and Idler, D.R., Plasma levels of thyroid hormones in sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) decrease before spawning, Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 1983, vol. 52, no. 3, pp. 467–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(83)90187-9
Campinho, M.A., Teleost metamorphosis: the role of thyroid hormone, Front. Endocrinol., 2019, vol. 10, pp. 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00383
Collins, J.J., Occurrence of pink salmon (Oncorhynchus gorbuscha) in Lake Huron, J. Fish. Res. Board Can., 1975, vol. 32, no. 3, pp. 402–404. https://doi.org/10.1139/f75-047
Comeau, L.A. and Campana, S.E., Correlations between thyroidal and reproductive endocrine status in wild Atlantic cod, Can. Tech. Rep. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 2006, no. 2682.
Dahl, J., Dannewitz, J., Karlsson, L., et al., The timing of spawning migration: implications of environmental variation, life history, and sex, Can. J. Zool., 2015, vol. 82, no. 12, pp. 1864–1870. https://doi.org/10.1139/z04-184
de Leeuw, J.J., ter Hofstede, R., and Winer, H.V., Sea growth of anadromous brown trout (Salmo trutta), J. Sea Res., 2007, vol. 58, no. 2, pp. 163–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2006.12.001
Dickhoff, W.W., Yan, L., Plisetskaya, E.M., et al., Relationship between metabolic and reproductive hormones in salmonid fish, Fish Physiol. Biochem., 1989, vol. 7, nos. 1–6, pp. 147–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00004701
Dorofeeva, E.A., Morphobiological adaptations of pink salmon in the White Sea, Materialy XXVIII Mezhdunarodnoi konferentsii “Biologicheskie resursy Belogo morya i vnutrennikh vodoemov Evropeiskogo Severa” (Proc. XXVIII Int. Conf. “Biological Resources of the White Sea and Inland Reservoirs of European North”), St. Petersburg, 2009, pp. 195–202.
Eales, J.G. and Fletcher, G.L., Circannual cycles of thyroid hormones in plasma of winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus Walbaum), Can. J. Zool., 1982, vol. 60, no. 3, pp. 304–309. https://doi.org/10.1139/z82-040
Eales, J.G., Chan, J.P., van der Kraak, G.J., et al., Effects of temperature on plasma thyroxine and iodide kinetics in rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri, Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 1982, vol. 47, no. 3, pp. 295–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(82)90237-4
Ebbesson, L.O.E., Björnsson, B.T., Stefansson, S.O., and Ekström, P., Free plasma thyroxine levels in coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch, during parr-smolt transformation: comparison with total thyroxine, total triiodothyronine, and growth hormone levels, Fish Physiol. Biochem., 2000, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 45–50. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1007841517552
Gordeeva, N.V., Genetic processes in pink salmon naturalized into the White Sea basin, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. (Biol.) Dissertation, Moscow: Vavilov Inst. Gen. Genet., Russ. Acad. Sci., 2003.
Gordeeva, N.V., The results and possible naturalization of pink salmon into the White Sea, Rybn. Khoz. (Vladivostok), 2010, no. 5, pp. 65–67.
Gordeeva, N.V., Salmenkova, E.A., and Altukhov, Yu.P., Genetic differentiation of Pacific pink salmon during colonization of a new area, Dokl. Biol. Sci., 2005, vol. 400, nos. 1–6, pp. 64–67.
Gwinner, E., Circannual systems, in Biological Rhythms, Aschoff, J., Ed., New York: Plenum, 1981, pp. 391–410.
Hesthagen, T. and Sandlund, O.T., Non-native freshwater fishes in Norway: history, consequences and perspectives, J. Fish Biol., 2007, vol. 71, pp. 173–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2007.01676.x
Iwata, M., Downstream migratory behavior of salmonids and its relationship with cortisol and thyroid hormones: a review, Aquaculture, 1995, vol. 135, nos. 1–3, pp. 131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(95)01000-9
Johnston, C.E. and Eales, J.G., Effects of acclimation and assay temperature on outer- and inner-ring thyroxine and 3,5,3-triiodo-L-thyronine deiodination by liver microsomes of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, J. Exp. Zool., 1995, vol. 272, no. 6, pp. 426–434. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.1402720604
Jonsson, B. and Jonsson, N., Ecology of Atlantic salmon and brown trout: habitat as a template for life histories, Fish Fish. Ser., 2011, vol. 33. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-1189-1
Kagawa, H., Young, G., and Nagahama, Y., In vitro estradiol-17 beta and testosterone production by ovarian follicles of the goldfish, Carassius auratus, Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 1984, vol. 54, no. 1, pp. 139–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(84)90209-0
Kennedy, A.J., Greil, R.W., Back, R.C., and Sutton, T.M., Population characteristics and spawning migration dynamics of pink salmon in U.S. Waters of the St. Marys River, J. Great Lakes Res., 2005, vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0380-1330(05)70234-3
Kuderskii, L.A., Naturalization of fishes in Russian reservoirs: states and development, Vopr. Rybolov., 2001, vol. 2, no. 1 (5), pp. 6–85.
Leonard, J.B.K., Iwata, M., and Ueda, H., Seasonal changes of hormones and muscle enzymes in adult lacustrine masu (Oncorhynchus masou) and sockeye salmon (O. nerka), Fish Physiol. Biochem., 2001, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 153–163. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1020512105096
Little, A.G., Kunisue, T., Kannan, K., and Seebacher, F., Thyroid hormone actions are temperature-specific and regulate thermal acclimation in zebrafish (Danio rerio), BMC Biol., 2013, vol. 11, no. 1, art. ID 26. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-11-26
Lorz, H.W. and Northcote, T.G., Factors affecting stream location, and timing and intensity of entry by spawning kokanee (Oncorhynchus nerka) into an inlet of Nicola Lake, British Columbia, J. Fish. Res. Board Can., 1965, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 665–685. https://doi.org/10.1139/f65-060
Ojima, D. and Iwata, M., Central administration of growth hormone-releasing hormone and corticotropin-releasing hormone stimulate downstream movement and thyroxine secretion in fall-smolting coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch), Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 2010, vol. 168, no. 1, pp. 82–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2010.04.007
Pavlov, D.S., Pavlov, E.D., Ganzha, E.V., and Kostin, V.V., Content of thyroid and sex steroid hormones in young-of-the-year of Black Sea trout Salmo trutta labrax from two spatial groups for different duration of starvation, Biol Bull. (Moscow), 2015, vol. 42, no. 4, pp. 347–353. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359015040111
Pavlov, D.S., Pavlov, E.D., Ganzha, E.V., and Kostin, V.V., Content of Na+, K+, Cl–, and Ca2+ in the blood of juveniles of the Black Sea trout Salmo trutta labrax under intrapopulational differentiation, Biol. Bull. (Moscow), 2017, vol. 44, no. 6, pp. 561–567. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359017060085
Pavlov, S.D., The results of naturalization of Far Eastern pink salmon in Europe and stable catches, Rybn. Khoz. (Vladivostok), 2014, no. 2, pp. 85–88.
Pemberton, R., Sea trout in North Argyll sea lochs, population, distribution and movements, J. Fish Biol., 1976, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 157–179. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1976.tb04670.x
Pettit, H., Britain’s native salmon are under threat from a pink rival that escaped into the sea from Russian farms, Version 05/2021, 2017. https://www.dailymail.co.uk/ sc-iencetech/article-4829918/Britain-s-native-salmon-threat-pink-rival.html.
Pritchard, A.L., Variation in the time of run, sex proportions, size and egg content of adult pink salmon (Oncorhynchus gorbuscha) at McClinton Creek, Masset Inlet, B.C., J. Biol. Board Can., 1937, vol. 3, no. 5, pp. 403–416. https://doi.org/10.1139/f37-023
Quinn, T.P., McGinnity, P., and Reed, T.E., The paradox of “premature migration” by adult anadromous salmonid fishes: patterns and hypotheses, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 2016, vol. 73, no. 7, pp. 1–68. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfas-2015-0345
Sandlund, O.T., Berntsen, H.H., Fiske, P., et al., Pink salmon in Norway: the reluctant invader, Biol. Invasions, 2019, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 1033–1054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-018-1904-z
Shapovalov, L. and Taft, A.C., The life histories of the steelhead rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri gairdneri) and silver salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch), Fish Bull. Cal. Dep. Fish Game, 1954, vol. 98, pp. 1–375.
Smirnov, A.I., Ecological approaches to work with pink and chum salmons in the basins of the Barents and White seas, Materialy V Vserossiiskogo soveshchaniya “Sistematika, biologiya i biotekhnika razvedeniya lososevykh ryb” (Proc. V All-Russ. Conf. “Taxonomy, Biology, and Biotechnology of Farming of Salmon Fishes”), St. Petersburg, 1994, pp. 181–183.
Sower, S.A. and Schreck, C.B., Steroid and thyroid hormones during sexual maturation of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) in seawater or fresh water, Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 1982, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 42–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(82)90082-x
State Water Register, Version 05/2020, 2020. http://textual. ru/gvr/.
Ueda, H. and Yamauchi, K., Biochemistry of fish migration, in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Fishes, Vol. 5: Environmental and Ecological Biochemistry, Hochachka, P.W. and Mommsen, T.P., Eds., Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1995, ch. 14, pp. 265–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1873-0140(06)80040-8
Ueda, H., Hiroi, O., Hara, A., et al., Changes in serum concentrations of steroid hormones, thyroxine, and vitellogenin during spawning migration of the chum salmon, Oncorhynchus keta, Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 1983, vol. 53, no. 2, pp. 203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(84)90243-0
Youngson, A.F. and Webb, J.H., Thyroid hormone levels in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) during the return migration from the ocean to spawn, J. Fish Biol., 1993, vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 293–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1993.tb00329.x
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to the staff of the North-West Territorial Administration of the Federal Agency for Fisheries for their assistance; M.А. Ruchiev (Severtsov Institute of Ecology and Evolution, Russian Academy of Sciences, Karelian Research Center, Russian Academy of Sciences) for assistance in fish sampling; А.B. Burlakov (Moscow State University) and V.V. Kostin (Severtsov Institute of Ecology and Evolution, Russian Academy of Sciences) for valuable remarks on the manuscript.
Funding
The study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project no. 19-14-00015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Translated by N. Ruban
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavlov, E.D., Ganzha, E.V. & Pavlov, D.S. Thyroid and Sex Steroid Hormone Level in the Pink Salmon Oncorhynchus gorbuscha during Marine and Freshwater Periods of Spawning Migration. J. Ichthyol. 62, 487–494 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945222030122
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945222030122