Abstract
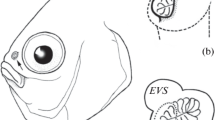
The structure of the olfactory organ in scissortail sergeant Abudefduf sexfasciatus was studied. Smaller specimens with a total length of <30–35 mm have two nostrils, while larger fish retain only the posterior one. The olfactory rosette is arrow-shaped, oval; the total number of lamellae devoid of secondary folding increases with the growth of the fish, but does not exceed 15 (with a total length of 145 mm). Two ventilation sacs adjoin the olfactory cavity: a large lacrimal sac, consisting of two compartments of unequal size, and an ethmoid sac that is much smaller in volume. The scheme of ventilation of the olfactory cavity is proposed. Comparison of the macromorphology and ventilation of the olfactory organ of A. sexfasciatus and the previously studied A. vaigiensis, along with obvious similarities, also reveals differences, the causes of which may be related to the structure of the head skeleton and the feeding modes of these fish.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Aguilar-Medrano, R. and Barber, P.H., Ecomorphological diversification in reef fish of the genus Abudefduf (Perciformes, Pomacentridae), Zoomorphology, 2016, vol. 135, no. 1, pp. 103–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00435-015-0291-6
Allen, G.R., Damselfishes of the World, Melle: Mergus, 1991.
Arvedlund, M., McCormick, M.I., Fautin, D.G., and Bildsøe, M., Host recognition and possible imprinting in the anemonefish Amphiprion melanopus (Pisces: Pomacentridae), Mar. Ecol.: Prog. Ser., 1999, vol. 188, pp. 207–218. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps188207
Arvedlund, M., Larsen, K., and Winsor, H., The embryonic development of the olfactory system in Amphiprion melanopus (Perciformes: Pomacentridae) related to the host imprinting hypothesis, J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K., 2000, vol. 80, no. 6, pp. 1103–1109. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315400003179
Arvedlund, M., Brolund, T.M., and Nielsen, L.E., Morphology and cytology of the olfactory organs in small juvenile Dascyllus aruanus and Amphiprion ocellaris (Pisces: Pomacentridae), J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K., 2003, vol. 83, no. 6, pp. 1321–1326. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315403008762
Atema, J., Kingsford, M.J., and Gerlach, G., Larval reef fish could use odour for detection, retention and orientation to reefs, Mar. Ecol.: Prog. Ser., 2002, vol. 241, pp. 151–160. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps241151
Berenshtein, I., Kiflawi, M., Shashar, N., et al., Polarized light sensitivity and orientation in coral reef fish post-larvae, PLoS One, 2014, vol. 9, no. 2, art. ID e88468. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088468
Booth, D.J., Ability to home in small site-attached coral reef fishes, J. Fish Biol., 2016, vol. 89, no. 2, pp. 1501–1506. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.13043
Bertrand, J.A.M., Borsa, P., and Chen, W.-J., Phylogeography of the sergeants Abudefduf sexfasciatus and A. vaigiensis reveals complex introgression patterns between two widespread and sympatric Indo-West Pacific reef fishes, Mol. Ecol., 2017, vol. 26, no. 9, pp. 2527–2542. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.14044
Bianchi, S., Delfino, G., and Ercolini, A., Morphology and fine structure of the olfactory organ in Uegitglanis zammaranoi Gianferrari (Claridae, Siluriformes), anophthalmic phreatic fish from Somalia, Monit. Zool. Ital., 1978, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 157–171. https://doi.org/10.1080/03749444.1978.10736866
Cappock, A.G., Gardiner, N.M., and Jones, G.P., Olfactory responses of coral-reef fishes to coral degradation and crown-of-thorns (Acanthaster planci), Mar. Freshwater Res., 2016, vol. 67, no. 5, pp. 605–611. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF14424
Colleye, O. and Parmentier, E., Overview on the diversity of sounds produced by clownfishes (Pomacentridae): importance of acoustic signals in their peculiar way of life, PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7, no. 11, art. ID e49179. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0049179
Cooper, W.J. and Westneat, M.W., Form and function of damselfish skulls: rapid and repeated evolution into a limited number of trophic niches, BMC Evol. Biol., 2009, no. 9, art. ID 24. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0049179
Devitsina, G.V. and El-Attar El-Saied, A.B., Morphometric study of the olfactory and visual analyzers in three species of cyprinids, Vestn. Mosk. Univ., Ser. 16: Biol., 1987, no. 1, pp. 9–16.
Dixson, D.L., Jones, G.P., Munday, P.L., et al., Coral reef fish smell leaves to find island homes, Proc. R. Soc. B, 2008, vol. 275, no. 1653, pp. 2831–2839. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2008.0876
Dixson, D.L., Munday, P.L., Pratchett, M.S., and Jones, G.P., Ontogenetic changes in responses to settlement cues by Anemonefish, Coral Reefs, 2011, vol. 30, no. 4, pp. 903–910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-011-0776-9
Dixson, D.L., Jones, G.P., Munday, P.L., et al., Experimental evaluation of imprinting and the role innate preference plays in habitat selection in a coral reef fish, Oecologia, 2014, vol. 174, no. 1, pp. 99–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-013-2755-z
Døving, K.B. and Kasumyan, A.O., Chemoreception, in Fish Larval Physiology, Finn, R.N. and Kapoor, B.G., Eds., Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 2008, pp. 331–394. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780429061608-15
Elliot, J., Elliot, J.M., and Mariscal, R.N., Host selection, location, and association behaviors of anemonefishes in field settlement experiments, Mar. Biol., 1995, vol. 122, no. 3, pp. 377–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350870
Eschmeyer’s catalog of fishes: genera, species, references, Version 08/2021, Fricke, R., Eschmeyer, W.N., and van der Laan, R., Eds., 2021. http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/ research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatmain.asp.
Eurich, J.G., Matley, J.K., Baker, R., et al., Stable isotope analysis reveals trophic diversity and partitioning in territorial damselfishes on a low‑latitude coral reef, Mar. Biol., 2019, vol. 166, no. 17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-018-3463-3
FishBase, Version 08/2021, Froese, R. and Pauly, D., Eds., 2021. https://www.fishbase.org.
Fishelson, L., Comparative morphology and cytology of the olfactory organs in moray eels with remarks on their foraging behavior, Anat. Rec., 1995, vol. 243, no. 4, pp. 403–412. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.1092430402
Fishelson, L., Golani, D., Galil, B., and Goren, M., Comparison of the nasal olfactory organs of various species of lizardfishes (Teleostei, Aulopiformes, Synodontidae), with additional remarks on the brain, Int. J. Zool., 2010, vol. 2010, art. ID 807913. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/807913
Frédérich, B., Fabri, G., Lepoint, G., et al., Trophic niches of thirteen damselfishes (Pomacentridae) at the Grand Récif of Toliara, Madagascar, Ichthyol. Res., 2009, vol. 56, no. 1, pp. 10–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-008-0053-2
Frédérich, B., Sorenson, L., Santini, F., et al., Iterative ecological radiation and convergence during the evolutionary history of damselfishes (Pomacentridae), Am. Nat., 2013, vol. 181, no. 1, pp. 94–113. https://doi.org/10.1086/668599
Frédérich, B., Olivier, D., Gajdzik, L., and Parmentier, E., Trophic ecology of damselfishes, in Biology of Damselfishes, Frédérich, B. and Parmentier, E., Eds., Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 2016, pp. 152–167. http://hdl.handle.net/2268/190309
Gajdzik, L., Aguilar-Medrano, R., and Frédérich, B., Diversification and functional evolution of reef fish feeding guilds, Ecol. Lett., 2019, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 572–582. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.13219
Gerlach, G. and Atema, J., The use of chemical cues in habitat recognition and settlement, in Chemical Ecology in Aquatic Systems, Brönmark, C. and Hansson, L.-A., Eds., Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press, 2012, pp. 72–81. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:osobl/9780199583096.003.0006
Gerlach, G., Atema, J., Kingsford, M.J., et al., Smelling home can prevent dispersal of reef fish larvae, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2007, vol. 104, no. 3, pp. 858–863. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0606777104
Ghosh, S.K., Cellular organization of the olfactory epithelium during growth, maturation, spawning and post-spawning phases of freshwater catfish, Eutropiichthys vacha (Hamilton, 1822) (Teleostei: Siluriformes), Iran. J. Ichthyol., 2018, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 126–138. https://doi.org/10.22034/iji.v5i2.278
Ghosh, S.K. and Chakrabarti, P., Histological and scanning electron microscopic organization and functional aspects of the surface olfactory epithelium of the freshwater minor carp, Puntius sophore (Hamilton), Proc. Zool. Soc., 2010, vol. 63, no. 2, pp. 115–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12595-010-0016-2
Ghosh, S.K. and Chakrabarti, P., Studies on the morphology of the olfactory organ in the freshwater teleost, Labeo bata (Hamilton), Mesopotamian J. Mar. Sci., 2013, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 163–174.
Ghosh, S.K. and Chakrabarti, P., Structural characterization of the olfactory epithelium of freshwater olive barb, Puntius sarana (Hamilton, 1822), Int. J. Aquat. Biol., 2014, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 147–154. https://doi.org/10.22034/ijab.v2i3.78
Goel, H.R., Functional anatomy of the olfactory organ in the fresh water teleost, Heteropneustes fossilis (BL.), Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 1978, vol. 55, no. 5, pp. 289–300.
Hansen, A. and Zeiske, E., The peripheral olfactory organ of the zebrafish, Danio rerio: an ultrastructural study, Chem. Sens., 1998, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 39–48. https://doi.org/10.1093/chemse/23.1.39
Hobbs, J.-P.A. and Allen, G.R., Hybridisation among coral reef fishes at Christmas island and the Cocos (Keeling) islands, Raffles Bull. Zool., 2014, vol. 30, pp. 220–226. http:// hdl.handle.net/20.500.11937/26586.
Kapoor, A.S. and Ojha, P.P., Functional anatomy of the olfactory organs in the moray, Muraena undulata, Jpn. J. Ichthyol., 1972, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 82–88. https://doi.org/10.11369/jji1950.19.82
Kasumyan, A.O., The olfactory system in fish: structure, function, and role in behavior, J. Ichthyol., 2004, vol. 44, suppl. 2, pp. S180–S223.
Kasumyan, A., Olfaction and gustation in Acipenseridae, with special references to the Siberian sturgeon, Acipenser baerii, in The Siberian Sturgeon (Acipenser baerii, Brandt, 1869), Vol. 1: Biology, Williot, P., et al., Eds., Cham: Springer-Verlag, 2018, pp. 173–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61664-3_10
Kavanagh, K.D. and Alford, R.A., Sensory and skeletal development and growth in relation to the duration of the embryonic and larval stages in damselfishes (Pomacentridae), Biol. J. Linn. Soc., 2003, vol. 80, no. 2, pp. 187–206. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1095-8312.2003.00229.x
Kavanagh, K.D. and Frédérich, B., Ontogeny and early life stages of damselfishes, in Biology of Damselfishes, Frédérich, B. and Parmentier, E., Eds., Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 2016, pp. 168–182. http://hdl.handle.net/ 2268/190305.
Kuo, S.-R. and Shao, K.-T., Feeding habits of damselfishes (Pomacentridae) from the southern part of Taiwan, J. Fish. Soc. Taiwan, 1991, vol. 18, pp. 165–176. https://doi.org/10.29822/JFST.199109.0001
Lara, M.R., Development of the nasal olfactory organs in the larvae, settlement-stages and some adults of 14 species of Caribbean reef fishes (Labridae, Scaridae, Pomacentridae), Mar. Biol., 2008, vol. 154, no. 1, pp. 51–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-007-0899-2
Lönnstedt, O.M. and McCormick, M.I., Chemical alarm cues inform prey of predation threat: the importance of ontogeny and concentration in a coral reef fish, Anim. Behav., 2011, vol. 82, no. 2, pp. 213–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2011.04.015
Losey, G.S., McFarland, W.N., Loew, E.R., et al., Visual biology of Hawaiian coral reef fishes. I. Ocular transmission and visual pigments, Copeia, 2003, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 433–454. https://doi.org/10.1643/01-053
Manassa, R.P., Dixson, D.L., McCormick, M.I., and Chivers, D.P., Coral reef fish incorporate multiple sources of visual and chemical information to mediate predation risk, Anim. Behav., 2013, vol. 86, no. 4, pp. 717–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2013.07.003
Maruska, K.P. and Peyton, K.A., Interspecific spawning between a recent immigrant and an endemic damselfish (Pisces: Pomacentridae) in the Hawaiian Islands, Pac. Sci., 2007, vol. 61, no. 2, pp. 211–221. https://doi.org/10.2984/1534-6188(2007)61[211:ISBARI]2.0.CO;2
Mitchell, M.D., McCormick, M.I., Ferrari, M.C.O., and Chivers, D.P., Coral reef fish rapidly learn to identify multiple unknown predators upon recruitment to the reef, PLoS One, 2011, vol. 6, no. 1, art. ID e15764. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0015764
Mitchell, M.D., McCormick, M.I., Chivers, D.P., and Ferrari, M.C.O., Generalization of learned predator recognition in coral reef ecosystems: how cautious are damselfish? Funct. Ecol., 2013, vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 299–304. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12043
Murphy, B.F., Leis, J.M., and Kavanagh, K.D., Larval development of the ambon damselfish Pomacentrus amboinensis, with a summary of pomacentrid development, J. Fish Biol., 2007, vol. 71, no. 2, pp. 569–584. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2007.01524.x
Nelson, J.S., Grande, T.C., and Wilson, M.V.H., Fishes of the World, Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119174844
Pashchenko, N.I. and Kasumyan, A.O., Some morphofunctional features of development of olfactory organ in ontogenesis of a minnow, Zool. Zh., 1983, vol. 62, no. 3, pp. 367–377.
Pashchenko, N.I. and Kasumyan, A.O., Morphofunctional features of development of olfactory organ of carps (Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae). I. Morphology and functions of olfactory organs in ontogenesis of the grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella (Val.), Vopr. Ikhtiol., 1986, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 303–317.
Pashchenko, N.I. and Kasumyan, A.O., Scanning electron microscopy of development of the olfactory organ in ontogeny of grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella, J. Ichthyol., 2015, vol. 55, no. 6, pp. 880–899. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945215060132
Pashchenko, N.I. and Kasumyan, A.O., Development of the olfactory organ in the ontogeny of carps (Cyprinidae), J. Ichthyol., 2017, vol. 57, no. 1, pp. 136–151. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945217010088
Pashchenko, N.I. and Kasumyan, A.O., Morphology and ventilation of the olfactory organ in the Indo-Pacific sergeant Abudefduf vaigiensis (Pomacentridae), J. Ichthyol., 2019, vol. 59, no. 2, pp. 167–173. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945219010120
Pashchenko, N.I., Kasumyan, A.O., and Oanh, L.T., Atypical structure of olfactory organ in moon wrasse Thalassoma lunare and sixbar wrasse T. hardwicke (Labridae), J. Ichthyol., 2021, vol. 61, no. 3, pp. 348–360. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945221030073
Pratchett, M.S., Hoey, A.S., Wilson, S.K., et al., Habitat-use and specialization among coral reef damselfishes, in Biology of Damselfishes, Frédérich, B. and Parmentier, E., Eds., Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 2016, pp. 84–121. http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11937/70865.
Randall, J.E., Ida, H., and Moyer, J.T., A review of the damselfishes of the genus Chromis from Japan and Taiwan, with description of a new species, Jpn. J. Ichthyol., 1981, vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 203–243. https://doi.org/10.11369/jji1950.28.203
Roux, N., Salis, P., Lambert, A., et al., Staging and normal table of postembryonic development of the clownfish (Amphiprion ocellaris), Dev. Dyn., 2019, vol. 248, no. 7, pp. 545–568. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.46
Shanks, A.L., Pelagic larval duration and dispersal distance revisited, Biol. Bull., 2009, vol. 216, no. 3, pp. 373–385. https://doi.org/10.1086/BBLv216n3p373
Siebeck, U.E., Communication in coral reef fish: the role of ultraviolet colour patterns in damselfish territorial behavior, Anim. Behav., 2004, vol. 68, no. 2, pp. 273–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2003.11.010
Siebeck, U.E., Wallis, G.M., and Litherland, L., Colour vision in coral reef fish, J. Exp. Biol., 2008, vol. 211, pp. 354–360. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.012880
Sundin, J., Amcoff, M., Mateos-González, F., et al., Long-term exposure to elevated carbon dioxide does not alter activity levels of a coral reef fish in response to predator chemical cues, Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol., 2017, vol. 71, no. 8, art. ID 108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-017-2337-x
Theisen, B., Functional morphology of the olfactory organ in Spinachia spinachia (L.) (Teleostei, Gasterosteidae), Acta Zool., 1982, vol. 63, no. 4, pp. 247–254. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-6395.1982.tb00784.x
Wright, K.J., Higgs, D.M., Belanger, A.J., and Leis, J.M., Auditory and olfactory abilities of pre-settlement larvae and post-settlement juveniles of a coral reef damselfish (Pisces: Pomacentridae), Mar. Biol., 2005, vol. 147, no. 6, pp. 1425–1434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-005-0028-z
Wyatt, A.S.J., Waite, A.M., and Humphries, S., Stable isotope analysis reveals community-level variation in fish trophodynamics across a fringing coral reef, Coral Reefs, 2012, vol. 31, no. 4, pp. 1029–1044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-012-0923-y
Yamamoto, M., Comparative morphology of fish olfactory organ in teleosts, in Chemoreception in Fishes, Hara, T.J., Ed., New York: Elsevier, 1982, pp. 39–59.
Yamamoto, M. and Ueda, K., Comparative morphology of fish olfactory epithelium. X. Perciformes, Beryciformes, Scorpaeniformes, and Pleuronectiformes, J. Fac. Sci. Univ. Tokyo, 1979, vol. 14, pp. 273–297.
Zeiske, E., Morphologische untersuchungen am Geruchsorgan von Zahnkarpfen (Pisces, Cyprinodontoidea), Z. Morphol. Tiere, 1973, vol. 74, no. 1, pp. 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00291793
Zeiske, E., Morphologische und Morphometrische untersuchungen am Geruchsorgan, oviparer Zahnkarpfen (Pisces), Z. Morphol. Tiere, 1974, vol. 77, no. 1, pp. 19–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00284625
Zeiske, E., Theisen, B., and Breucker, H., Structure, development, and evolutionary aspects of the peripheral olfactory system, in Fish Chemoreception, Hara, T.J., Ed., London: Chapman and Hall., 1992, pp. 13–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-2332-7_2
Zeiske, E., Theisen, H., and Breucker, B. Olfactory organ of the hardhead sea catfish, Arius felis (L.): gross morphology and fine structure, Acta Zool., 1994, vol. 75, no. 2, pp. 115–123. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-6395.1994.tb01116.x
Funding
The materials were sampled with the financial support of the Russian-Vietnam Scientific-Research and Technological Tropical Center. The experimental part of the work, processing of primary data, analysis of the results, and preparation of the paper were financially supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project 19-04-00367. The study was carried out within the framework of the scientific project of the state assignment of Lomonosov Moscow State University no. 121032300100-5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pashchenko, N.I., Oanh, L.T. & Kasumyan, A.O. Morphology and Ventilation of the Olfactory Organ in Scissortail Sergeant Abudefduf sexfasciatus (Pomacentridae). J. Ichthyol. 62, 373–384 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945222030110
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945222030110