Abstract
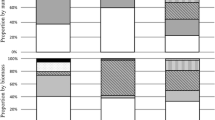
Influence of biotic and abiotic environmental factors on feeding of the predatory fish in the Rybinsk Reservoir in 1953−2012 has been analyzed. It is revealed that the feeding spectrum of the majority of piscivores (sander Sander lucioperca, burbot Lota lota, pike Esox lucius and adult perch Perca fluviatilis) includes 16−18 fish species, while only seven in Volga sander Sander volgensis. Three aboriginal fish species (perch, ruff Gymnocephalus cernuus and roach Rutilus rutilus) and two invasive species (European smelt Osmerus eperlanus and Black-Azov tyulka Clupeonella cultriventris) are the main food items for piscivores. In some years, these species accounted for 97% of the total number of prey. Introduction and naturalization into the reservoir of smelt (during the period of climatic norm) and Black-Azov tyulka (during regional climate warming) considerably changed proportions of species serving as potential prey for predatory fish. During these periods, the share of invasive species in the ration of pelagic zone piscivores was increasing, but this increase was not proportional to the abundance of these prey species. After decline in abundance of smelt and tyulka (while, at the same time, these species were still dominant) their shares in the feeding of predators decreased, while the role of more available mass aboriginal species increased again. It is revealed that predatory fish are selective to certain prey items: sander, Volga sander, and large perch prefer to feed on perch yearlings; burbot, on yearlings of perch and on ruff; and pike, on roach.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Atlas presnovodnykh ryb Rossii (Atlas of Freshwater Fishes of Russia), Reshetnikov, Yu.S., Ed., Moscow: Nauka, 2003, vol. 2.
Bakastov, S.S., The data on the bottom temperature in Rybinsk reservoir under ice, Byull. Inst. Biol. Vodokhran., 1960, nos. 8–9, pp. 62–66.
Barsukov, V.V., Age composition of a herd and growth rate of zander in Rybinsk reservoir, Tr. Inst. Biol. Vodokhran., Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1959, no. 1 (4), pp. 188–210.
Berg, L.S., Ryby presnykh vod SSSR i sopredel’nykh stran (Freshwater Fishes of Soviet Union and Adjacent Countries), Moscow: Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1949, part 3, pp. 929–1381.
Chirkova, Z.N., Distribution and growth of perch juveniles from Rybinsk reservoir, Tr. Biol. Stn. Borok, 1955, no. 2, pp. 191–199.
Ekologicheskie faktory prostranstvennogo raspredeleniya i peremeshcheniya gidrobiontov (Ecological Factors of Spatial Distribution and Migration of Hydrobionts), St. Petersburg: Gidrometeoizdat, 1993.
Ekologicheskie problemy Verkhnei Volgi (Ecological Problems of Upper Volga), Kopylov, A.I., Ed., Yaroslavl: Yarosl. Gos. Tekh. Univ., 2001.
Fortunatova, K.R. and Popova, O.A., Pitanie i pishchevye vzaimootnosheniya khishchykh ryb v del’te Volgi (Feeding and Food Relations of Predator Fishes in Volga River Delta), Moscow: Nauka, 1973.
Gerasimov, Yu.V. and Novikov, D.A., Ichthyomass and distribution of fishes in Rybinsk reservoir, in Ekologicheskie problemy Verkhnei Volgi (Ecological Problems of Upper Volga), Yaroslavl: Yarosl. Gos. Tekh. Univ., 2001, pp. 194–202.
Gerasimov, Yu.V. and Poddubnyi, S.A., Rol’ gidrologicheskogo rezhima v formirovanii skoplenii ryb na melkovod’yakh ravninnykh vodokhranilishch (Role of Hydrological Regime in Formation of Fish Agglomerations in the Shallows of Lowland Reservoirs), Yaroslavl: Yarosl. Gos. Tekh. Univ., 1999.
Gerasimov, Yu.V., Strel’nikov, A.S., and Ivanova, M.N., Dynamics of structural indices of populations of zander Stizostedion lucioperca (Percidae) of the Rybinsk Reservoir for 1954–2010, J. Ichthyol., 2013, vol. 53, no. 1, pp. 41–51.
Gordeev, N.A., The stages of development of ichthyofauna in Rybinsk reservoir, Materialy konferentsii “Volga-1,” Tezisy dokladov (Proc. Conf. “Volga-1,” Abstracts of Papers), Kuibyshev: Kuibyshevsk. Knizhn. Izd., 1971, pp. 244–253.
Il’ina, L.K., Different quality of juveniles and heterogenic growth of scale in underyearlings of the European perch Perca fluviatilis L., Vopr. Ikhtiol., 1970, vol. 10, no. 1 (60), pp. 170–174.
Il’ina, L.K. and Poddubnyi, A.G., Dynamics of herds of commercial fish species in Rybinsk reservoir, Tr. Soveshch. Ikhtiol. Kom., Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1961, no. 13, pp. 374–380.
Ivanova, M.N., Feeding and food chains of raptorial fishes in Rybinsk, Gor’kovskoe, and Kuibyshev reservoirs, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. (Biol.) Dissertation, Leningrad: Leningr. State Pedagog. Inst., 1966.
Ivanova, M.N., Behavior of predator fishes during fattening, Vopr. Ikhtiol., 1969, vol. 9, no. 4 (57), pp. 711–715.
Ivanova, M.N., Ratio of food objects in the diet of pike and zander and intensity of their fattening, Biol. Vnutr. Vod, 1977, no. 34, pp. 47–51.
Ivanova, M.N., Populyatsionnaya izmenchivost’ presnovodnykh koryushek (Population Variability of Freshwater Smelts), Rybinsk: Inst. Biol. Vnutr. Vod, Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1982.
Ivanova, M.N. and Kas’yanov, A.N., On the finding of round goby Neogobius melanostomus (Pallas) (Gobiidae) in the food of burbot Lota lota (L.) of the Rybinskoe water reservoir, Inland Water Biol., 2011, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 393–396.
Ivanova, M.N. and Lapkin, V.V., Effect of temperature on viability and distribution of freshwater smelts in water reservoirs, Biol. Vnutr. Vod, 1982, no. 55, pp. 37–41.
Ivanova, M.N., Svirskaya, A.N., and Litvinov, A.S., Feeding of Volga pikeperch (Sander volgensis) in Rybinsk reservoir, Vopr. Rybolov., 2013, vol. 14, no. 1 (53), pp. 53–59.
Ivlev, V.S., Eksperimental’naya ekologiya pitaniya ryb (Experimental Ecology of Feeding of Fishes), Moscow: Pishchepromizdat, 1955.
Kashin, S.M., Malinkin, L.K., Orlovskii, G.N., and Poddubnyi, A.G., Behavior of some fishes during hunting, Zool. Zh., 1977, vol. 54, no. 9, pp. 1328–1339.
Khal’ko, V.V., Bazarov, M.I., and Dergacheva, N.G., Survival rate of perch juveniles from various ecological groups. 2. Occurrence of weak individuals among perch juveniles from littoral and pelagic agglomerations, Biol. Vnutr. Vod, 1985, no. 68, pp. 37–43.
Kiyashko, V.I., Ecological and trophic relations of Eurasian ruffe Acerina cernua L. in Rybinsk reservoir, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. (Biol.) Dissertation, Moscow: Severtsov Institute of Ecology and Evolution, Acad. Sci. USSR, 1982.
Kiyashko, V.I., Karabanov, D.P., Yakovlev, V.N., and Slyn’ko, Yu.V., Formation and development of the Black Sea-Caspian kilka Clupeonella cultriventris (Clupeidae) in the Rybinsk reservoir, J. Ichthyol., 2012, vol. 52, no. 8, pp. 537–546.
Kodukhova, Y.V., Borovikova, E.A., and Karabanov, D.P., First record of stellate tadpole goby Benthophilus stellatus (Sauvage, 1874) (Actinopterygii: Gobiidae) in the Rybinsk Reservoir, Inland Water Biol., 2016, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 428–430.
Konobeeva, V.K., Groups of fish juveniles in Rybinsk reservoir, in Presnovodnye gidrobionty i ikh biologiya (Freshwater Hydrobionts and Their Biology), Leningrad: Nauka, 1983, pp. 193–206.
Kulemin, A.A., Commercial ichthyofauna of the Volga River basin related to fishery in Rybinsk reservoir, Uch. Zap. Yarosl. Pedagog. Inst., 1944, no. 2, pp. 64–100.
Litvinov, A.S. and Zakonnova, A.V., Thermal regime in the Rybinsk reservoir under global warming, Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol., 2012, vol. 37, no. 9, pp. 640–644.
Ostroumov, A.A., Characteristic of progenies of bream and zander from Rybinsk reservoir, Tr. Inst. Biol. Vodokhran., Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1959, no. 1 (4), pp. 211–234.
Pavlov, D.S., Biologicheskie osnovy upravleniya povedeniem ryb v potoke vody (Biological Principles of the Fish Behavior Control in Water Stream), Moscow: Nauka, 1979.
Pavlov, D.S. and Skorobogatov, M.A., Migratsii ryb v zaregulirovannykh rekakh (Fish Migration in Regulated Rivers), Moscow: KMK, 2014.
Permitin, I.E. and Polovkov, V.V., Specific formation and dynamics of the structure of agglomerations of pelagic fishes, in Teoreticheskie aspekty rybokhozyaistvennykh issledovanii vodokhranilishch (Theory of Fishery Studies of Reservoirs), Leningrad: Nauka, 1978, pp. 78–105.
Poddubnyi, A.G., Ekologicheskaya topografiya populyatsii ryb v vodokhranilishchakh (Ecological Topography of Fish Populations in Reservoirs), Leningrad: Nauka, 1971.
Popova, O.A., Feeding and food relations of pikeperch, perch, and ruffe in reservoirs from various latitudes, in Izmenchivost’ ryb presnovodnykh ekosistem (Variability of Fishes in Freshwater Ecosystems), Moscow: Nauka, 1979, pp. 93–112.
Romanova, G.P., Feeding of zander in Rybinsk reservoir, Tr. Biol. Stn. Borok, 1956, no. 2, pp. 307–326.
Rybopromyslovyi atlas Rybinskogo vodokhranilishcha (Fishery Atlas of Rybinsk Reservoir), Yaroslavl, 1963. https://www.booksite.ru/fulltext/natural/ryboatlas/text.pdf.
Ryby Rybinskogo vodokhranilishcha: populyatsionnaya dinamika i ekologiya (Fishes from Rybinsk Reservoir: Population Dynamic and Ecology), Yaroslavl: Filigran’, 2015.
Sergeev, R.S., Biology of the burbot from Rybinsk reservoir, Tr. Inst. Biol. Vodokhran., Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1959, no. 1 (4), pp. 235–258.
Sovremennoe sostoyanie rybnykh zapasov Rybinskogo vodokhranilishcha (Modern Status of Fish Resources of Rybinsk Reservoir), Yaroslavl: Yarosl. Gos. Tekh. Univ., 1997.
Stepanov, M.V. and Kiyashko, V.I., The role of kilka (Clupeonella cultriventris (Nordmann)) in the diet of predatory fish of the Rybinsk reservoir, Inland Water Biol., 2008, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 393–396.
Stolbunov, I.A. and Gerasimov, Yu.V., Morphological and behavioral variation in juvenile roach Rutilus rutilus (Cyprinidae, Cypriniformes) from different biotopes of the Rybinskoe water reservoir, J. Ichthyol., 2008, vol. 48, no. 2, pp. 177–87.
Stolbunov, I.A. and Pavlov, D.D., Behavioral differences of various ecological groups of roach Rutilus rutilus and perch Perca fluviatilis,J. Ichthyol., 2006, vol. 46, suppl. 2, pp. 213–219.
Stolbunov, I.A., Malin, M.I., and Karabanov, D.P., Finding round goby Neogobius melanostomus (Pallas, 1814) in the Rybinsk reservoir, Inland Water Biol., 2013, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 365–366.
Tsyplakov, E.P., Fishery role of shallow water zone of Kuibyshev reservoir, Izv. Gos. Nauchno-Issled. Inst. Ozern. Rechn. Rybn. Khoz., 1974, no. 89, pp. 137–150.
Vasil’ev, L.I., Development of ichthyofauna of Rybinsk reservoir. Part 1: Change of species composition of ichthyofauna of Upper Volga during first years after establishment, Tr. Biol. Stn. Borok, 1950, no. 1, pp. 236–275.
Vasil’ev, L.I., The vendace from Rybinsk reservoir, Tr. Vses. Gidrobiol.O-va, 1952, vol. 4, pp. 106–114.
Vasnetsov, V.V., Influence of the first year of flooding on ichthyofauna in Rybinsk reservoir, Tr. Biol. Stn. Borok, 1950, no. 1, pp. 203–205.
Yakovlev, V.N., Slyn’ko, Yu.V., and Kiyashko, V.I., Annotated catalog of Cyclostomata fishes and fishes from reservoirs of the Upper Volga basin, in Ekologicheskie problemy Verkhnei Volgi (Ecological Problems of Upper Volga), Kopylov, A.I., Ed., Yaroslavl: Yarosl. Gos. Tekh. Univ., 2001, pp. 53–69.
Zadul’skaya, E.S., Feeding and food relations of predator fishes from the northern part of Rybinsk reservoir, Tr. Darvin. Gos. Zapoved., 1960, part 2, no. 6, pp. 345–405.
Zakonnov, V.V., Hydrological and hydrochemical regime of reservoirs of Upper Volga, in Ekologicheskie problemy Verkhnei Volgi (Ecological Problems in Upper Volga), Yaroslavl: Yarosl. Gos. Tekh. Univ., 2001, pp. 21–25.
Zakonnov, V.V. and German, A.V., Bottom sediments in Rybinsk reservoir and their productivity, Materialy nauchno-prakt. konferentsii “Rybinskoe vodokhranilishche i pribrezhnye territorii: sovremennoe sostoyanie i perspektivy razvitiya” (Proc. Sci.-Pract. Conf. “Rybinsk Reservoir and Coastal Areas: Modern Status and Prospective Development”), Yaroslavl, 2011, pp. 39–41.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The study was supported by the program of the Presidium of the Russian Academy of Sciences I.21P “Biodiversity of Natural Systems. Biological Resources of Russia: Assessment of State and Fundamental Bases of Monitoring”; 2.5 “Influence of Anthropogenic Regulation of the Water Level Regime of Reservoirs and of Temperature on the Dynamic of Number of the Fish with Various Ecologies.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by D. Pavlov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerasimov, Y.V., Ivanova, M.N. & Svirskaya, A.N. Long-Term Changes in the Importance of Aboriginal and Invasive Fish Species for Feeding of Predatory Fish of the Rybinsk Reservoir. J. Ichthyol. 58, 601–616 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945218040045
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945218040045