Abstract
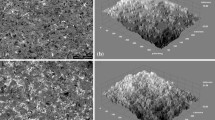
Magnesium alloys are known for their lightweight and high specific strength properties and being used as bio-degradable implant material. Materials’ surface roughness and surface hardness play a major role when coating has to be applied and may subject to wear and abrasion. Grit blasting is one of the common techniques to remove surface impurities, corrosion products and modify the surface characteristics for better adhesion of protective coatings, as well as, surface hardness. In the present study, the effect of grit blasting media and blasting pressure on the surface characteristics and surface hardness of magnesium alloy is investigated. The surface characteristics such as mean surface roughness (Ra), highest peak values (Rp), deepest valley values (Rv) are measured using atomic force microscopy (AFM) and show a linear relation with blasting pressure. The surface topography is observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The surface hardness results indicate 41% increase in hardness with blasting pressure. The statistical findings using analysis of variance (ANOVA) shows that both blasting pressure and blasting media contribute to final surface roughness and surface hardness. The blasting pressure imparts major contribution to it.





















Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
G. E. J. Poinern, S. Brundavanam, and D. Fawcett, “Biomedical magnesium alloys: a review of material properties, surface modifications and potential as a biodegradable orthopaedic implant,” Am. J. Biomed. Eng. 2, 218–240 (2012). https://doi.org/10.5923/j.ajbe.20120206.02
S. Agarwal, J. Curtin, B. Duffy, and S. Jaiswal, “Biodegradable magnesium alloys for orthopaedic applications: A review on corrosion, biocompatibility and surface modifications,” Mater. Sci. Eng., C 68, 948–963 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.06.020
A. Francis, Y. Yang, S. Virtanen, and A. Boccaccini, “Iron and iron-based alloys for temporary cardiovascular applications,” J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 26, 138 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-015-5473-8
P. Wen, M. Voshage, L. Jauer, Ya. Chen, Yu. Qin, R. Poprawe, and J. Schleifenbaum, “Laser additive manufacturing of Zn metal parts for biodegradable applications: Processing, formation quality and mechanical properties,” Mater. Des. 155, 36–45 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2018.05.057
D. Xue, Ye. Yun, Z. Tan, Z. Dong, and M. Schulz, “In vivo and in vitro degradation behavior of magnesium alloys as biomaterials,” J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 28, 261–267 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/s1005-0302(12)60051-6
R. Walter and M. B. Kannan, “Influence of surface roughness on the corrosion behaviour of magnesium alloy,” Mater. Des. 32, 2350–2354 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2010.12.016
S. Agarwal, J. Curtin, B. Duffy, and S. Jaiswal, “Biodegradable magnesium alloys for orthopaedic applications: A review on corrosion, biocompatibility and surface modifications,” Mater. Sci. Eng., C 68, 948–963 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.06.020
A. E. Coy, F. Viejo, F. J. Garcia-Garcia, Z. Liu, P. Skeldon, and G. E. Thompson, “Effect of excimer laser surface melting on the microstructure and corrosion performance of the die cast AZ91D magnesium alloy,” Corros. Sci. 52, 387–397 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2009.09.025
A. Pandey, A. Awasthi, and K. K. Saxena, “Metallic implants with properties and latest production techniques: A review,” Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 6, 405–440 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068x.2020.1731236
A. Raykowski, M. Hader, B. Maragno, and J. Spelt, “Blast cleaning of gas turbine components: Deposit removal and substrate deformation,” Wear 249, 126–131 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0043-1648(01)00518-x
R. K. Chintapalli, A. Mestra Rodriguez, F. Garcia Marro, and M. Anglada, “Effect of sandblasting and residual stress on strength of zirconia for restorative dentistry applications,” J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 29, 126–137 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2013.09.004
R. K. Chintapalli, F. G. Marro, E. Jimenez-Pique, and M. Anglada, “Phase transformation and subsurface damage in 3Y-TZP after sandblasting,” Dental Mater. 29, 566–572 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2013.03.005
M. S. Islam, L. Tong, and P. J. Falzon, “Influence of metal surface preparation on its surface profile, contact angle, surface energy and adhesion with glass fibre prepreg,” Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 51, 32–41 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijadhadh.2014.02.006
E. Avcu, S. Fidan, Y. Yıldıran, and T. Sınmazçelik, “Solid particle erosion behaviour of Ti6Al4V alloy,” Tribol. Mater., Surf. Interfaces 7, 201–210 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1179/1751584x13y.0000000043
K. Bobzin, M. Öte, T. Linke, J. Sommer, and X. Liao, “Influence of process parameter on grit blasting as a pretreatment process for thermal spraying,” J. Therm. Spray Technol. 25, 3–11 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-015-0297-0
H. F. Li, Y. B. Wang, Y. F. Zheng, and J. P. Lin, “Osteoblast response on Ti- and Zr-based bulk metallic glass surfaces after sand blasting modification,” J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B: Appl. Biomater. 100B, 1721–1728 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.32738
D. Randman, “Deformation mechanisms in magnesium alloy ElektronTM 675,” PhD Thesis (Department of Engineering Materials, The University of Sheffield, Sheffield, 2010).
M. Zhao and K. T. Ramesh, “Deformation and failure mechanisms in a magnesium alloy under uniaxial compressive loading,” J. Dynamic Behav. Mater. 6, 303–316 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40870-020-00246-8
D. Hull and D. J. Bacon, Introduction to Dislocations, 4th ed. (Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-7506-4681-9.X5000-7
M. R. Barnett, “Twinning and the ductility of magnesium alloys,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 464, 8–16 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.02.109
Q. Yu, J. Wang, Ya. Jiang, R. J. McCabe, N. Li, and C. N. Tomé, “Twin–twin interactions in magnesium,” Acta Mater. 77, 28–42 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.05.030
Y. Chun and C. Davies, “Texture effects on development of shear bands in rolled AZ31 alloy,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 556, 253–259 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.06.083
J. Marteau, M. Bigerelle, P.-E. Mazeran, and S. Bouvier, “Relation between roughness and processing conditions of AISI 316L stainless steel treated by ultrasonic shot peening,” Tribol. Int. 82, 319–329 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2014.07.013
K. Tosha, “Influence of residual stresses on the hardness number in the affected layer produced by shot peening,” in 2nd Asia-Pacific Forum on Precision Surface Finishing and Deburring Technology, Seoul, Korea, 2002 (2002), pp. 48–54.
K. Iida and K. Tosha, “Behavior of surface residual stress induced by shot peening (II),” in Advances in Surface Treatments, Ed. by A. Niku-Lari (Pergamon, 1987), pp. 139–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-034923-7.50021-8
C. E. Peñuela-Cruz, A. Márquez-Herrera, E. Aguilera-Gómez, A. Saldaña-Robles, R. Mis-Fernández, J. L. Peña, F. Caballero-Briones, M. Loeza-Poot, and E. Hernández-Rodríguez, “The effects of sandblasting on the surface properties of magnesium sheets: A statistical study,” J. Mater. Res. Technol. 23, 1321–1331 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.01.117
G. A. Gamal, F. A. Al-Mufadi, M. Salah, M. Salman, and H. Zein, “The relationship of surface roughness and hardness of BiSn solder alloys due to the variation of sn content,” Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 6 (7), 103–109 (2018).
Funding
This work was supported by ongoing institutional funding. No additional grants to carry out or direct this particular research were obtained.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, F., Manzoor, M.U., Kamran, M. et al. The Effect of Grit Blasting on Surface Roughness and Hardness of Magnesium Alloy AZ31B: A Statistical Study. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 124, 1620–1631 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X23601506
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X23601506