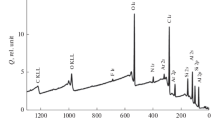
Abstract
Auger electron spectroscopy was used to determine the phase composition of Cr2GeC MAX phase thin films. A distinctive feature of the formation of carbon-containing MAX phases is the shape of carbon Auger peaks, which is characteristic of metal carbides spectra. Features of the Auger spectra in the presence of secondary phases of chromium germanides are found. Their presence can manifest itself in an increase in the energy of the germanium peaks, which is caused by a chemical shift during the formation of the Cr–Ge bond. Moreover, we have detected the accumulation of electronic charge, which can be explained by the features of the surface morphology.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. J. Tallman, B. Anasori, and M. W. Barsoum, “A critical review of the oxidation of Ti2AlC, Ti2AlC2 and Cr2AlC in air,” Mater. Res. Lett. 1, 115–125 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2013.806364
D. Yu and Yo. Tan, “Oxidation behaviors of compositionally complex MAX phases in air,” Ceram. Int. 47, 30188–30193 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.07.198
T. S. Mathis, K. Maleski, A. Goad, A. Sarycheva, M. Anayee, A. C. Foucher, K. Hantanasirisakul, C. E. Shuck, E. A. Stach, and Yu. Gogotsi, “Modified MAX phase synthesis for environmentally stable and highly conductive Ti2C2 MXene,” ACS Nano 15, 6420–6429 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c08357
A. D. Bortolozo, O. H. Sant’Anna, C. A. M. dos Santos, and A. J. S. Machado, “Superconductivity at 9.5 K in the Ti2GeC compound,” Mater. Sci.-Poland 30, 92–97 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s13536-012-0013-4
Z. Babar, J. Fatheema, N. Arif, M. S. Anwar, S. Gul, M. Iqbal, and S. Rizwan, “Magnetic phase transition from paramagnetic in Nb2AlC-MAX to superconductivity-like diamagnetic in Nb2C-MXene: An experimental and computational analysis,” (2020).
A. S. Ingason, M. Dahlqvist, and J. Rosen, “Magnetic MAX phases from theory and experiments; a review,” J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 28, 433003 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/28/43/433003
J. Yang, G. Yao, S. Sun, Z. Chen, S. Yuan, K. Wu, X. Fu, Q. Wang, and W. Cui, “Structural, magnetic properties of in-plane chemically ordered (Mo2/3R1/3)2AlC (R = Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er and Y) MAX phase and enhanced capacitance of Mo1.33C MXene derivatives,” Carbon 179, 104–110 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2021.03.062
J. Dey, E. Jedryka, R. Kalvig, U. Wiedwald, M. Farle, J. Rosen, and M. Wójcik, “Helical magnetic structure of epitaxial films of nanolaminated Mn2GaC MAX phase,” Phys. Rev. B 108, 54413 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.108.054413
A. S. Ingason, A. Mockute, M. Dahlqvist, F. Magnus, S. Olafsson, U. B. Arnalds, B. Alling, I. A. Abrikosov, B. Hjörvarsson, P. O. Å. Persson, and J. Rosen, “Magnetic self-organized atomic laminate from first principles and thin film synthesis,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 195502 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.110.195502
Z. Liu, T. Waki, Y. Tabata, and H. Nakamura, “Mn-doping-induced itinerant-electron ferromagnetism in Cr2GeC,” Phys. Rev. B 89, 54435 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.89.054435
S. Lin, Ya. Huang, L. Zu, X. Kan, J. Lin, W. Song, P. Tong, X. Zhu, and Yu. Sun, “Alloying effects on structural, magnetic, and electrical/thermal transport properties in MAX-phase Cr2 − xMxGeC (M = Ti, V, Mn, Fe, and Mo),” J. Alloys Compd. 680, 452–461 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.197
D. Briggs and M. P. Seah, Practical Surface Analysis by Auger and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, 1983).
A. S. Tarasov, S. A. Lyaschenko, M. V. Rautskii, A. V. Lukyanenko, T. A. Andryushchenko, L. A. Solovyov, I. A. Yakovlev, O. A. Maximova, D. V. Shevtsov, M. A. Bondarev, I. A. Bondarev, S. G. Ovchinnikov, and S. N. Varnakov, “Growth process, structure and electronic properties of Cr2GeC and Cr2 – xMnxGeC thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering,” Processes 11, 2236 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11082236
T. A. Andryushchenko, S. A. Lyaschenko, A. V. Lukyanenko, S. N. Varnakov, and S. G. Ovchinnikov, “Auger electron spectroscopy of the air exposed (Cr0.5Mn0.5)2GaC MAX film surface,” PJTF 49 (14), 22–27 (2023). https://doi.org/10.21883/PJTF.2023.14.55821.19430
M. A. Smith and L. L. Levenson, “Final-state effects in carbon Auger spectra of transition-metal carbides,” Phys. Rev. B 16, 1365–1369 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.16.1365
S. Danyluk, J. Yu. Park, and D. E. Busch, “Auger electron spectroscopy of stoichiometric chromium carbides and carbide precipitates at grain boundaries of type 304 stainless steel,” Scr. Metall. 13, 857–862 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1016/0036-9748(79)90174-1
T. W. Haas, J. T. Grant, and G. J. Dooley, “Chemical effects in Auger electron spectroscopy,” J. Appl. Phys. 43, 1853–1860 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1661409
C. C. Chang, “Auger electron spectroscopy,” Surf. Sci. 25, 53–79 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-6028(71)90210-x
M. W. Ruckman, M. Del Giudice, J. J. Joyce, and J. H. Weaver, “Comparative study of the formation of Cr/Ge and Ge/Cr thin-film interfaces,” Phys. Rev. B 33, 8039–8047 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.33.8039
P. Sander, M. Altebockwinkel, W. Storm, L. Wiedmann, and A. Benninghoven, “Surface and in-depth analysis of hydrogenated carbon layers on silicon and germanium by mass and electron spectroscopy,” J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B: Microelectron. Process. Phenom. 7, 517–528 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1116/1.584778
P. J. Møller and J. He, “Electron beam induced charging of Cu/MgO surfaces,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B: Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 17, 137–140 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-583x(86)90075-3
J. Cazaux, K. H. Kim, O. Jbara, and G. Salace, “Charging effects of MgO under electron bombardment and nonohmic behavior of the induced specimen current,” J. Appl. Phys. 70, 960–965 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.349606
C. C. Chang, Characterization of Solid Surfaces (Plenum Press, New York, 1974).
H. Guo, W. Maus-Friedrichs, and V. Kempter, “Charging phenomena and charge compensation in AES on metal oxides and silica,” Surf. Interface Anal. 25, 390–396 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1096-9918(199706)25:6<390::aid-sia247>3.0.co;2-x
P. Eklund, M. Bugnet, V. Mauchamp, S. Dubois, C. Tromas, J. Jensen, L. Piraux, L. Gence, M. Jaouen, and T. Cabioc’h, “Epitaxial growth and electrical transport properties of Cr2GeC thin films,” Phys. Rev. B 84, 75424 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.84.075424
N. Lundberg, M. Östling, and F. M. D’Heurle, “Chromium germanides: Formation, structure and properties,” Appl. Surf. Sci. 53, 126–131 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-4332(91)90252-f
T. Chihi, M. Fatmi, and M. A. Ghebouli, “Ab initio study of some fundamental properties of the M3X (M = Cr, V; X = Si, Ge) compounds,” Phys. B: Condens. Matter 407, 3591–3595 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2012.05.032
R. M. Hill, “Electrical conduction in ultra thin metal films I. Theoretical,” Proc. R. Soc. London A: Math. Phys. Sci. 309, 377–395 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1969.0048
E. V. Vashchenko, I. A. Gladskikh, S. G. Przhibel’skiĭ, V. V. Khromov, and T. A. Vartanyan, “Conductivity and photoconductivity of granular silver films on a sapphire substrate,” J. Opt. Technol. 80, 263 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1364/jot.80.000263
S. Hofmann, “Charging and charge compensation in AES analysis of insulators,” J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 59, 15–32 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/0368-2048(92)85009-v
C. G. H. Walker, M. M. El-gomati, A. M. D. Assa’d, and M. Zadražil, “The secondary electron emission yield for 24 solid elements excited by primary electrons in the range 250–5000 eV: A theory/experiment comparison,” Scanning 30, 365–380 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/sca.20124
H. H. Madden, “Chemical information from Auger electron spectroscopy,” J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 18, 677–689 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1116/1.570927
J.-W. Park, “Sample charging of insulators with rough surfaces during Auger electron spectroscopy analysis,” J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A: Vac., Surf., Films 15, 292–293 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1116/1.580527
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank the Krasnoyarsk Regional Center of Research Equipment of Federal Research Center “Krasnoyarsk Science Center SB RAS” for obtaining the AFM data, X-ray diffraction patterns, scanning electron micrographs and L. A. Solovyov for the help in processing the XRD data.
Funding
The research was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (grant no. 21-12-00226, http://rscf.ru/project/21-12-00226/).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andryushchenko, T.A., Lyaschenko, S.A., Varnakov, S.N. et al. Auger Electron Spectroscopy of Thin Cr2GeC Films. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 124, 1776–1782 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X2360135X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X2360135X