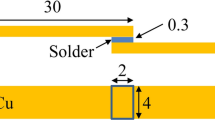
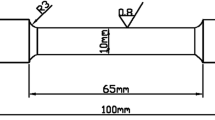
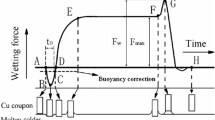
Abstract
This research investigated changes in the properties of Sn–4.0Zn–0.7Cu (SZC407) solder alloy after doping with 0.5 wt % Ni. Specimens of SZC407 and SZC407–0.5Ni solder alloys were characterized in terms of chemical composition, microstructure, mechanical properties, and melting point. The results showed that the addition 0.5 wt % Ni had no significant effect on the ultimate tensile strength and elongation of SZC407 solder alloy but the formation of phases of the intermetallic compound (IMC) CuZnNi in the solder matrix increased the microhardness of the alloy. These IMC phases improved the strength of the solder matrix by the dispersion strengthening mechanism. The fracture surface of both solder alloys was typical of the ductile fracture mode. The microstructure of the solder alloy was improved by the distribution in the solder matrix of new CuZnNi IMC phases. However, the addition of 0.5 wt % Ni slightly increased the solidus and liquidus temperatures, pasty range and peak temperature of the SZC407 solder alloy.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
K. Suganuma, “Advances in lead-free electronics soldering,” Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 5, 55–64 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S13590286(00)00036-X
A. E. Hammad, “Investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of novel Sn0.5Ag0.7Cu solders containing small amount of Ni,” Mater. Des. 50, 108–116 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.03.010
A. A. El-Daly and A. E. Hammad, “Development of high strength Sn0.7Cu solders with the addition of small amount of Ag and In,” J. Alloys Compd. 509, 8554–8560 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.05.119
H. R. Kotadia, O. Mokhtari, M. P. Clode, M. A. Green, and S. H. Mannan, “Intermetallic compound growth suppression at high temperature in SAC solders with Zn addition on Cu and NiP substrates,” J. Alloys Compd. 511, 176–188 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.09.024
S. Y. Chang, C. C. Jain, T. H. Chuang, L. P. Feng, and L. C. Tsao, “Effect of addition of TiO2 nanoparticles on the microstructure, microhardness and interfacial reactions of Sn3.5AgXCu solder,” Mater. Des. 32, 4720–4727 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.06.044
H. Kang, M. Lee, D. Sun, S. Pae, and J. Park, “Formation of octahedral corrosion products in Sn–Ag flip chip solder bump,” Scr. Mater. 108, 126–129 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2015.06.034
S. H. Huh, K. S. Kim, and K. Suganuma, “Effect of Ag addition on the microstructural and mechanical properties of Sn–Cu eutectic solder,” Mater. Trans. 42, 739–744 (2001). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.42.739
M. Date, K. N. Tu, T. Shoji, M. Fujiyoshi, and K. Sato, “Interfacial reactions and impact reliability of Sn–Zn solder joints on Cu or electroless Au/Ni(P) bond-pads,” J. Mater. Res. 19, 2887–2896 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2004.0371
S. H. Chang and S. K. Wu, “Damping characteristics of Sn–3Ag–0.5Cu and Sn–37Pb solders studied by dynamic mechanical analysis,” Scr. Mater. 63, 957–960 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2010.07.004
C. Y. Chou and S. W. Chen, “Phase equilibria of the Sn–Zn–Cu ternary system,” Acta Mater. 54, 2393–2400 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2006.01.014
K. Suganuma and K. S. Kim, “Sn–Zn low temperature solder,” J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 18, 121–127 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-48433-4_7
M. Yamaguchi, T. Ichitsubo, E. Matsubara, H. Kimura, K. Sasamori, H. Irie, S. Kumamoto, and T. Anada, “Atomizing effect on Sn–Zn based solder alloy,” J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 70, 162–165 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2320/jinstmet.70.162
Y. S. Kim, K. S. Kim, C. W. Hwang, and K. Suganuma, “Effect of composition and cooling rate on microstructure and tensile properties of Sn–Zn–Bi alloys,” J. Alloys Compd. 352, 237–245 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8388(02)01168-4
J. M. Song and K. L. Lin, “Behavior of intermetallics in liquid Sn–Zn–Ag solder alloys,” J. Mater. Res. 18, 2060–2067 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2003.0290
K. L. Lin and H. M. Hsu, “Sn–Zn–Al Pb-free solder—An inherent barrier solder for Cu contact,” J. Electron. Mater. 30, 1068–1072 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-001-0131-y
D. Q. Yu, H. P. Xie, and L. Wang, “Investigation of interfacial microstructure and wetting property of newly developed Sn–Zn–Cu solders with Cu substrate,” J. Alloys Compd. 385, 119–125 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2004.04.129
J. E. Lee, K. S. Kim, M. Inoue, J. Jiang, and K. Suganuma, “Effects of Ag and Cu addition on microstructural properties and oxidation resistance of Sn‒Zn eutectic alloy,” J. Alloys Compd. 454, 310–320 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.12.037
A. A. El-Daly, A. E. Hammad, A. Fawzy, and D. A. Nasrallh, “Microstructure, mechanical properties, and deformation behavior of Sn–1.0Ag–0.5Cu solder after Ni and Sb additions,” Mater. Des. 43, 40–49 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.06.058
C. H. Wang and H. T. Shen, “Effects of Ni addition on the interfacial reaction between Sn–Cu solders and Ni substrate,” Intermetallics 18, 616–622 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2009.10.018
A. K. Gain and Y. C. Chan, “The influence of a small amount of Al and Ni nano-particles on the microstructure, kinetic and hardness of Sn–Ag–Cu solder on OSP-Cu pads,” Intermetallics 29, 48–55 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2012.04.019
F. X. Che, W. H. Zhu, S. W. P. Edith, X. W. Zhang, and X. R. Zhang, “The study of mechanical properties of Sn–Ag–Cu lead-free solders with different Ag contents and Ni doping under different strain rates and temperatures,” J. Alloys Compd. 507, 215–224 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.07.160
H. Ma, H. Xie, and L. Wang, “Effect of a trace of Bi and Ni on the microstructure and wetting properties of Sn–Zn–Cu lead-free solder,” J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 23, 81–84 (2007).
Y. Lai, X. Hu, X. Jiang, and Y. Li, “Effect of Ni addition to Sn–0.7Cu solder alloy on thermal behavior, microstructure, and mechanical properties,” J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 27, 6564–6576 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3734-7
A. A. El-Daly and A. M. El-Taher, “Improved strength of Ni and Zn-doped Sn–2.0Ag–0.5Cu lead-free solder alloys under controlled processing parameters,” Mater. Des. 47, 607–641 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.12.081
A. E. Hammad, “Evolution of microstructure, thermal and creep properties of Ni-doped Sn–0.5Ag–0.7Cu low-Ag solder alloys for electronic applications,” Mater. Des. 52, 663–670 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.05.102
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors wish to thank academician Thomas Duncan Coyne for improving the English in this paper.
Funding
This work was supported by the Faculty of Science Research Fund, Prince of Songkla University Contract no. 1-2565-02-002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panisara Sukhontapatipak, Phairote Sungkhaphaitoon The Influence of Nickel Addition on Properties of Sn–4.0Zn–0.7Cu Lead-Free Solder. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 124, 1597–1605 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X23600082
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X23600082