Abstract
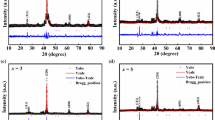
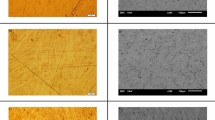
A new alloy intended for single-crystal permanent magnets has been suggested. The new alloy has been designed based on the well-known Fe−Co−Ni−Cu−Al−Ti system and contains to 1 wt % Hf. The alloy demonstrates an enhanced potential ability for single-crystal forming in the course of unidirectional solidification of ingot. Single-crystal permanent magnets manufactured from this alloy are characterized by a high level of magnetic properties. When designing the new alloy, computer simulation of the phase composition and calculations of solidification parameters of complex metallic systems have been performed using the Thermo-Calc software and calculation and experimental procedures based on quantitative metallographic analysis of quenched structures. After the corresponding heat treatment, the content of high-magnetic phase in the alloy is 10% higher than that in available analogous alloys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. V. Sergeev and T. I. Bulygina, Magnetoically Hard Materials (Energiya, Moscow, 1980).
M. V. Pikunov, I. V. Belyaev, and E. V. Sidorov, Crystallization of Alloys and Directional Solidification of Castings (Vladimir. Gos. Univ., Vladimir, 2002) [in Russian].
M. V. Pikunov, “Analysis of the equilibrium crystallization of solid solutions,” Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved. Tsvetn. Metall., No. 5, 151–158 (1959).
M. V. Pikunov, I. V. Belyaev, and E. V. Sidorov, “On the calculation of thr crystallization coefficients of alloys—solid solutions,” Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Chern. Metall., No. 1, 121–124 (1998).
I. V. Belyaev, “Generalized segregation coefficient of multicomponent solid-solution alloys,” Izv. Akad. Nauk., Met., No. 2, 106–108 (1998).
W. A. Tiller, K. A. Jackson, J. W. Rutter, and B. Chalmers, “The redistribution of solute atoms during the solidification of metals,” Acta Metall. 1, 428–437 (1953).
T. T. Cheng, “The mechanism of grain refinement in TiAl alloys by boron addition—An alternative hypothesis,” Intermetallics 8, 29–37 (2000).
Z. W. Huang, “Inhomogeneous microstructure in highly alloyed cast TiAl-based alloys, caused by microsegregation,” Scr. Mater. 52, 1021–1025 (2005).
L. A. Tarshis, J. L. Walker, and J. W. Rutter, “Experiments on the solidification structure of alloy castings,” Metall. Trans. 2, 2589–2597 (1971).
J. A. Spittle and S. Sadli, “Effect of alloy variables on grain refinement of binary aluminum alloys with Al?Ti–B,” Mater. Sci. Techn. 11, 533–537 (1995).
I. Maxwell and A. Hellawell, “Simple model for grain refinement during solidification,” Acta Metall. 23, 229–237 (1975).
A. L. Greer, A. M. Bunn, A. Tronche, P. V. Evans, and D. J. Bristow, “Modeling of inoculation of metallic melts: Application to grain refinement of aluminum by Al–Ti–B,” Acta Mater. 48, 2823–2835 (2000).
P. Desnain, Y. Fautrelle, J.-L. Meyer, J.-P. Riquet, and F. Durand, “Prediction of equiaxed grain density in multicomponent alloys, stirred electromagnetically,” Acta Metall. Mater. 38, 1513–1523 (1990).
M. A. Easton and D. H. St John, “A model of grain refinement incorporating alloy constitution and potency of heterogeneous nucleant particles,” Acta Mater. 49, 1867–1878 (2001).
T. E. Quested, A. T. Dinsdale, and A. L. Greer, “Thermodynamic modeling of growth-restriction effects in aluminum alloys,” Acta Mater. 53, 1323–1334 (2005).
R. Schmid-Fetzer and A. Kozlov, “Thermodynamic aspects of grain growth restriction in multicomponent alloy solidification,” Acta Mater. 59, 6133–6144 (2011).
M. V. Pikunov, I. V. Belyaev, and V. S. Lashuk, “Method of determination of ther intensity of alloy crystallization,” Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved, Chern. Metall., No. 9, 101–104 (1983).
I. B. Kekalo and B. A. Samarin, Physical Metallurgy of Precision Alloys. Alloys with Special Magnetic Properties (Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.V. Belyaev, V.E. Bazhenov, A.V. Moiseev, A.V. Kireev, 2016, published in Fizika Metallov i Metallovedenie, 2016, Vol. 117, No. 3, pp. 224–232.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belyaev, I.V., Bazhenov, V.E., Moiseev, A.V. et al. New Fe−Co−Ni−Cu−Al−Ti Alloy for Single-Crystal Permanent Magnets. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 117, 214–221 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X16010038
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X16010038