Abstract—
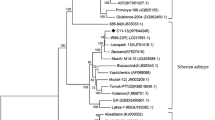
This paper reports the analysis of the nucleotide sequences of the 5'-untranslated region (5'-UTR) of tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) genomic RNA isolated from 39 individual taiga ticks collected in several regions of Northern Eurasia. The sequences of 5'-UTRs of the Siberian and Far East TBEV genotypes were 89% and 95% identical to the prototype strains (Zausaev and 205), respectively. The detected nucleotide substitutions were typical for these two TBEV genotypes, which made possible unambiguous identification. Both conservative and variable motifs were detected in the 5'-UTR RNA. The B2, C1, and C2 elements of the Y-shaped 5'-UTR structure and the presumable viral RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase binding site were the most variable. The A2, CS A, CS B elements as well as the start codon were conservative. Interestingly, five substitutions in the 5'-UTR C1 variable element of the TBEVs isolated in different geographical regions were strictly conservative, while 11 different substitutions were detected in this element among the laboratory TBEV variants. A little less that a third of all nucleotide substitutions were mapped outside the main elements of the Y-shaped structure. In general, nucleotide substitutions were localized to stem structures, not being found in the hairpin regions of the TBEV 5'-UTR. The results indicated significant variability of the genomic RNA 5'-UTR in the TBEV laboratory strains and field isolates obtained from different geographical regions. It has been suggested that genetic variability of 5'-UTR is characteristic of the TBEV genome 5'-UTR organization and may serve as a structural basis for virus efficient replication in various avian, mammalian, and ixodic tick cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Simmonds P., Becher B., Bukh J., Gould E.A., Meyers G., Monath T., Muerhoff S., Pletnev A., Rico-Hesse R., Smith D.B., Stapleton J.T., ICTV Report Consortium. 2017. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: flaviviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 98, 2–3. https://doi.org/10.1099/jgv.0.000672
Markoff L. 2003. 5′- and 3′-noncoding regions in flavivirus RNA. Adv. Virus Res. 59, 177–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-3527(03)59006-6
Khromykh A.A., Sedlak P.L., Westaway E.G. 2000. Cis- and trans-acting elements in flavivirus RNA replication. J. Virol. 74, 3253–3263, https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.74.7.3253-3263.2000
Alvarez D.E., Lodeiro M.F., Luduena, J, Pietrasanta L.I., Gamarnik A.V. 2005. Long-range RNA-RNA interactions circularize the dengue virus genome. J. Virol. 79, 6631–6643. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.79.11
Filomatori C.V., Lodeiro M.F., Alvarez D.E., Samsa M.M., Pietrasanta L., Gamarnik A.V. 2006. A 5′ RNA element promotes dengue virus RNA synthesis on a circular genome. Genes Dev. 20, 2238–2249. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1444206
Chausov E.M., Ternovoi V.A., Protopopova E.V., Kononova J.V., Konovalova S.N., Pershikova N.L., Loktev V.B., Romanenko V.N., Ivanova N.V., Bolshakova N.P., Moskvitina N.S. 2010. Variability of the tick-borne encephalitis virus genome in the 5′ noncoding region derived from ticks Ixodes persulcatus and Ixodes pavlovskyi in Western Siberia. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Diseases. 10, 365–375. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2009.0064
Markham N.R., Zuker M. 2008. UNAFold. Bioinformatics. Humana Press, pp. 3–31.
Alvarez D.E., Filomatori C.V., Gamarnik A.V. 2008. Functional analysis of dengue virus cyclization sequences located at the 5′ and 3′ UTRs. Virology. 375, 223–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2008.01.014
Sakai M., Yoshii K., Sunden Y., Yokozawa K., Hirano M., Kariwa H. 2014. Variable region of the 3′ UTR is a critical virulence factor in the Far-Eastern subtype of tick-borne encephalitis virus in a mouse model. J. Gen. Virol. 95, 823–835. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.060046-0
Sakai M., Muto M., Hirano M., Kariwa H., Yoshii K. 2015. Virulence of tick-borne encephalitis virus is associated with intact conformational viral RNA structures in the variable region of the 3′-UTR. Virus Res. 203, 36–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2015.03.006
Casati S., Gern L., Pifaretti J.-C. 2006. Diversity of the population of tick-borne encephalitis virus infecting Ixodes ricinus ticks in an endemic area of central Switzerland (Canton Bern). J. Gen. Virol. 87, 2235–2241. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.81783-0
Kartashov M.Y., Glushkova L.I., Mikryukova T.P., Korabelnikov I.V., Egorova Y.I., Tupota N.L., Protopopova E.V., Konovalova, S.N., Ternovoi V.A., Loktev V.B. 2017. Detection of Rickettsia helvetica and candidatus R. tarasevichiae DNA in Ixodes persulcatus ticks collected in Northeastern European Russia (Komi Republic). Ticks Tick-Borne Diseases. 8, 588–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2017.04.001
Tamura K., Peterson D., Peterson N., Stecher G., Nei M., Kumar S. 2011. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 28, 2731–2739. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr121
Ponomareva E.P., Mikryukova T.P., Kartashov M.Y., Protopopova E.V., Chausov E.V., Konovalova S.N., Tupota N.L., Gheorghita S.D., Burlacu V.I., Ternovoi V.A., Loktev V.B. 2015. Detection of Far-Eastern subtype of tick-borne encephalitis viral RNA in ticks collected in the Republic of Moldova. J. Vector Borne Diseases. 52, 334–336.
Achazi K., Ruzek D., Donoso-Mantke D., Schlegel M., Ali H.S., Wenk M., Schmidt-Chanasit J., Ohlmeyer L., Ruhe F., Vor T., Kiffner T., Kallies R., Ulrich R.G., Niedrig M. 2011. Rodents as sentinels for the prevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Diseases. 11, 641–647. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2010.0236
Knap N., Korva M., Dolinsek V., Sekirnik M., Trilar T., Avsic-Zupanc T. 2012. Patterns of tick-borne encephalitis virus infection in rodents in Slovenia. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. Larchmt. 12, 236–242. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2011.0728
Caracciolo I., Bassetti M., Paladini G., Luzzati R., Santon D., Merelli M., Sabbata G.D., Carletti T., Marcell A., D’Agaro P. 2015. Persistent viremia and urine shedding of tick-borne encephalitis virus in an infected immunosuppressed patient from a new epidemic cluster in north-eastern Italy. J. Clin. Virol. 69, 48–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2015.05.019
Mikryukova T.P., Chausov E.V., Konovalova S.N., Kononova Yu.V., Protopopova E.V., Kartashov M.Yu., Ternovoi V.A., Glushkova L.I., Korabel’nikov I.V., Egorova Yu.I., Loktev V.B.2014. Genetic diversity of tick-borne encephalitis virus in Ixodes persulcatus ticks in the northeastern regionof European Russia. Parazitologiya. 48, 131–149.
Gritsun T.S., Nuttall P.A., Gould E.A. 2003. Tick-borne flaviviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 61, 317–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-3527(03)61008-0
Liu Z.-Y., Li X.-F., Jiang T., Deng Y.-Q., Ye Q., Zhao H., Yu J.-Y., Qin C.-F. 2016. Viral RNA switch mediates the dynamic control of flavivirus replicase recruitment by genome cyclization. eLife. 5, e17636. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.17636
Ternovoi V.A., Protopopova E.V., Chausov E.V., Novikov D.V., Leonova G.N., Netesov S.V., Loktev V.B. 2007. Novel variant of tickborne encephalitis virus, Russia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 13, 1574–1578. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1310.070158
Funding
The work was supported by the Russian Federal State Agency for Health and Consumer Rights Surveillance Sectorial Research Program (grant no. 141-00080-20-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The present work doesn’t involve any experimentation using animals or humans performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by E. Martynova
Abbreviation: 5′-UTR, 5′-untranslated region; TBEV, tick-borne encephalitis virus.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponomareva, E.P., Ternovoi, V.A., Mikryukova, T.P. et al. Genetic Variability of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Genome 5'-UTR from Northern Eurasia. Mol Biol 55, 372–380 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S002689332102028X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S002689332102028X