Abstract
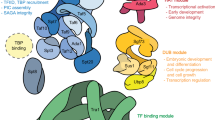
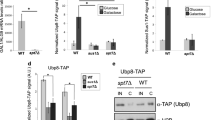
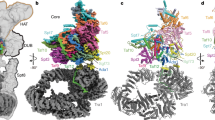
SAGA, the multicomponent complex responsible for acetylation of histone N-terminal lysine residues, is involved in the transcription activation of a wide range of eukaryote genes. SAGA contains a protein module, DUB, which is responsible for histone deubiquitination. In this paper we show that the DUB module may be found within cells independently of SAGA. In the absence of SAGA, the DUB module may be recruited to the promoters of Pol III-transcribed genes, but not to the Pol II-dependent promoters. The DUB module is required to recruit transcription factor Brf1, a subunit of the Pol III-recruiting TFIIIB complex, to the promoters of Pol III-dependent genes. The DUB-module interacts with Pol III in vivo. The DUB-module is essential for recruiting both TFIIIB complexes and PBP complexes to the promoters of Pol III-dependent genes.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Spedale G., Timmers H., Pijnappel W. 2012. ATAC-king the complexity of SAGA during evolution. Genes Dev. 26, 527–541.
Lee K.K., Sardiu M.E., Swanson S.K., Gilmore J.M., Torok M., Grant P.A., Florens L., Workman J.L., Washburn M.P. 2011. Combinatorial depletion analysis to assemble the network architecture of the SAGA and ADA chromatin remodeling complexes. Mol. Systems Biol. 7, 503.
Helmlinger D., Marguerat S., Villén J., Swaney D.L., Gygi S.P., Bähler J., Winston F. 2011. Tra1 has specific regulatory roles, rather than global functions, within the SAGA co-activator complex. EMBO J. 30, 2843–2852.
Nagy Z., Tora L. 2007. Distinct GCN5/PCAF-containing complexes function as co-activators and are involved in transcription factor and global histone acetylation. Oncogene. 26, 5341–5357.
Hong L., Schroth G.P., Matthews H.R., Yau P., Bradbury E.M. 1993. Studies of the DNA binding properties of histone H4 amino terminus. Thermal denaturation studies reveal that acetylation markedly reduces the binding constant of the H4 ‘tail’ to DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 305–314.
Kouzarides T. 2007. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 128, 693–705.
Henry K.W., Wyce A., Lo W.-S., Duggan L.J., Emre N.C.T., Kao C.-F., Pillus L., Shilatifard A., Osley M.A., Berger S.L. 2003. Transcriptional activation via sequential histone H2B ubiquitylation and deubiquitylation, mediated by SAGA-associated Ubp8. Genes Dev. 17, 2648–2663.
Köhler A., Pascual-García P., Llopis A., Zapater M., Posas F., Hurt E., Rodríguez-Navarro S. 2006. The mRNA export factor Sus1 is involved in Spt/Ada/Gcn5 acetyltransferase-mediated H2B deubiquitinylation through its interaction with Ubp8 and Sgf11. Mol. Biol. Cell. 17, 4228–4236.
Zhang X.-Y., Varthi M., Sykes S.M., Phillips C., Warzecha C., Zhu W., Wyce A., Thorne A.W., Berger S.L., McMahon S.B. 2008. The putative cancer stem cell marker USP22 is a subunit of the human SAGA complex required for activated transcription and cell-cycle progression. Mol. Cell. 29, 102–111.
Lang G., Bonnet J., Umlauf D., Karmodiya K., Koffler J., Stierle M., Devys D., Tora L. 2011. The tightly controlled deubiquitination activity of the human SAGA complex differentially modifies distinct gene regulatory elements. Mol. Cell. Biol. 31, 3734–3744.
Zhao Y., Lang G., Ito S., Bonnet J., Metzger E., Sawatsubashi S., Suzuki E., Le Guezennec X., Stunnenberg H.G., Krasnov A., Georgieva S.G., Schule R., Takeyama K.-I., Kato S., Tora L., Devys D. 2008. A TFTC/STAGA module mediates histone H2A and H2B deubiquitination, coactivates nuclear receptors, and counteracts heterochromatin silencing. Mol. Cell. 29, 92–101.
Kohler A., Zimmerman E., Schneider M., Hurt E., Zheng N. 2010. Structural basis for assembly and activation of the heterotetrameric SAGA histone H2B deubiquitinase module. Cell. 141, 606–617.
Samara N.L., Datta A.B., Berndsen C.E., Zhang X., Yao T., Cohen R.E., Wolberger C. 2010. Structural insights into the assembly and function of the SAGA deubiquitinating module. Science (N.Y.). 328, 1025–1029.
Han Y., Luo J., Ranish J., Hahn S. 2014. Architecture of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae SAGA transcription coactivator complex. EMBO J. 33, 2534–2546.
Lee K.K., Swanson S.K., Florens L., Washburn M.P., Workman J.L. 2009. Yeast Sgf73/ataxin-7 serves to anchor the deubiquitination module into both SAGA and Slik(SALSA) HAT complexes. Epigenet. Chromatin. 2, 2.
Morgan M.T., Haj-Yahya M., Ringel A.E., Bandi P., Brik A., Wolberger C. 2016. Structural basis for histone H2B deubiquitination by the SAGA DUB module. Science (N.Y.). 351, 725–728.
Gurskiy D., Orlova A., Vorobyeva N., Nabirochkina E., Krasnov A., Shidlovskii Y., Georgieva S., Kopytova D. 2012. The DUBm subunit Sgf11 is required for mRNA export and interacts with Cbp80 in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 86–96.
Popova V.V., Orlova A.V., Kurshakova M.M., Nikolenko J.V., Nabirochkina E.N., Georgieva S.G., Kopytova D.V. 2018. The role of SAGA coactivator complex in snRNA transcription. Cell Cycle. 17, 1859–1870.
Hung K.-H., Stumph W.E. 2011. Regulation of snRNA gene expression by the Drosophila melanogaster small nuclear RNA activating protein complex (DmSNAPc). Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 46, 11–26.
Schramm L., Hernandez N. 2002. Recruitment of RNA polymerase III to its target promoters. Genes Dev. 16, 2593–2620.
Schramm L., Pendergrast P.S., Sun Y., Hernandez N. 2000. Different human TFIIIB activities direct RNA polymerase III transcription from TATA-containing and TATA-less promoters. Genes Dev. 14, 2650–2663.
Leśniewska E., Boguta M. 2017. Novel layers of RNA polymerase III control affecting tRNA gene transcription in eukaryotes. Open Biol. 7, 2.
Jawdekar G.W., Henry R.W. 2008. Transcriptional regulation of human small nuclear RNA genes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1779, 295–305.
Janson L., Weller P., Pettersson U. 1989. Nuclear factor I can functionally replace transcription factor Sp1 in a U2 small nuclear RNA gene enhancer. J. Mol. Biol. 205, 387–396.
Boyd D.C., Greger I.H., Murphy S. 2000. In vivo footprinting studies suggest a role for chromatin in transcription of the human 7SK gene. Gene. 247, 33–44.
Boyd D.C., Pombo A., Murphy S. 2003. Interaction of proteins with promoter elements of the human U2 snRNA genes in vivo. Gene. 315, 103–112.
Stünkel W., Kober I., Seifart K.H. 1997. A nucleosome positioned in the distal promoter region activates transcription of the human U6 gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17, 4397–4405.
Zhao X., Pendergrast P.S., Hernandez N. 2001. A positioned nucleosome on the human U6 promoter allows recruitment of SNAPc by the Oct-1 POU domain. Mol. Cell. 7, 539–549.
Kenneth N.S., Ramsbottom B.A., Gomez-Roman N., Marshall L., Cole P.A., White R.J. 2007. TRRAP and GCN5 are used by c-Myc to activate RNA polymerase III transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104, 14917–14922.
Georgieva S., Nabirochkina E., Dilworth F.J., Eickhoff H., Becker P., Tora L., Georgiev P., Soldatov A. 2001. The novel transcription factor e(y)2 interacts with TAF(II)40 and potentiates transcription activation on chromatin templates. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 5223–5231.
Kurshakova M.M., Krasnov A.N., Kopytova D.V., Shidlovskii Y.V., Nikolenko J.V., Nabirochkina E.N., Spehner D., Schultz P., Tora L., Georgieva S.G. 2007. SAGA and a novel Drosophila export complex anchor efficient transcription and mRNA export to NPC. EMBO J. 26, 4956–4965.
Boehm A.K., Saunders A., Werner J., Lis J.T. 2003. Transcription factor and polymerase recruitment, modification, and movement on dhsp70 in vivo in the minutes following heat shock. Mol. Cell Biol. 23, 7628–7637.
Vorobyeva N.E., Soshnikova N.V., Nikolenko J.V., Kuzmina J.L., Nabirochkina E.N., Georgieva S.G., Shidlovskii Y.V. 2009. Transcription coactivator SAYP combines chromatin remodeler Brahma and transcription initiation factor TFIID into a single supercomplex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106, 11049–11054.
Clemens J.C., Worby C.A., Simonson-Leff N., Muda M., Maehama T., Hemmings B.A., Dixon J.E. 2000. Use of double-stranded RNA interference in Drosophila cell lines to dissect signal transduction pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97, 6499–6503.
Li X., Seidel C.W., Szerszen L.T., Lange J.J., Workman J.L., Abmayr S.M. 2017. Enzymatic modules of the SAGA chromatin-modifying complex play distinct roles in Drosophila gene expression and development. Genes Dev. 31, 1588–1600.
Kopytova D.V., Orlova A.V., Krasnov A.N., Gurskiy D.Y., Nikolenko J.V., Nabirochkina E.N., Shidlovskii Y.V., Georgieva S.G. 2010. Multifunctional factor ENY2 is associated with the THO complex and promotes its recruitment onto nascent mRNA. Genes Dev. 24, 86–96.
Park J.-L., Lee Y.-S., Kunkeaw N., Kim S.-Y., Kim I.-H., Lee Y.S. 2017. Epigenetic regulation of noncoding RNA transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase III. Epigenomics. 9, 171–187.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The work was performed using the equipment of the Center for Collective Use of the IBG RAS. The authors are grateful to R.Kh. Ziganshin. for the MALDI-TOF MS analysis performed on the equipment of the Shemyakin and Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry RAS.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (no. 18-04-00514 A, D.K., E.N., A.G.) and the Russian Science Foundation (no. 20-14-00269, Yu.N., Yu.V.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for animal care and use have been followed.
Additional information
Abbreviations: Pol II, RNA polymerase II; Pol III, RNA polymerase III; DUB-module, deubiquitination module; HAT-module, acetyltransferase module; snRNA, small nuclear RNA; PSE, proximal sequence element; DSE, distal sequence element; PSE-binding protein complex, a complex that binds the proximal element.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikolenko, J.V., Vdovina, Y.A., Fefelova, E.I. et al. The SAGA Deubiquitinilation (DUB) Module Participates in Pol III-Dependent Transcription. Mol Biol 55, 432–440 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893321020278
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893321020278